Optimization of camshaft grinding parameters based on response surface method and NSGA2
-
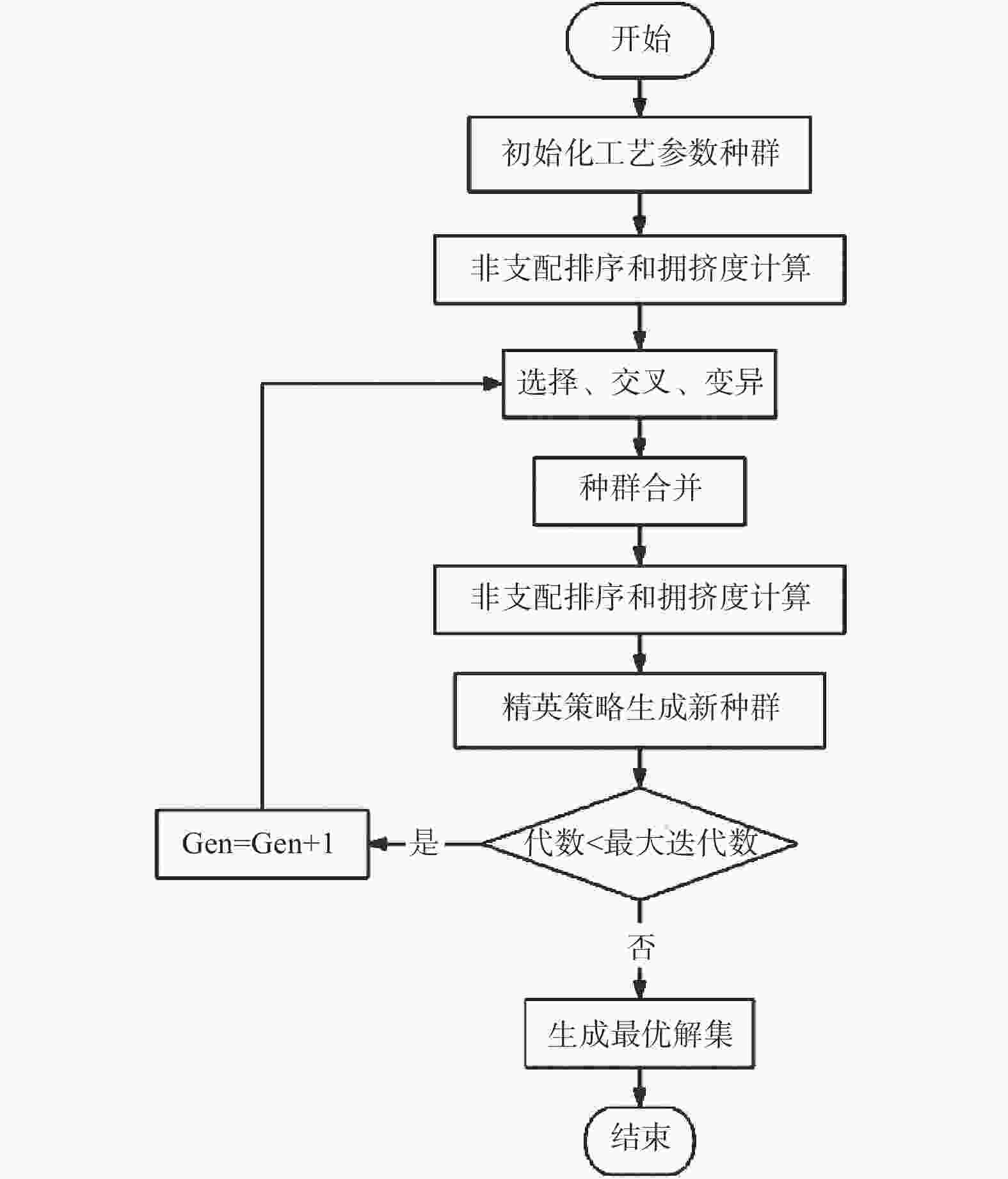
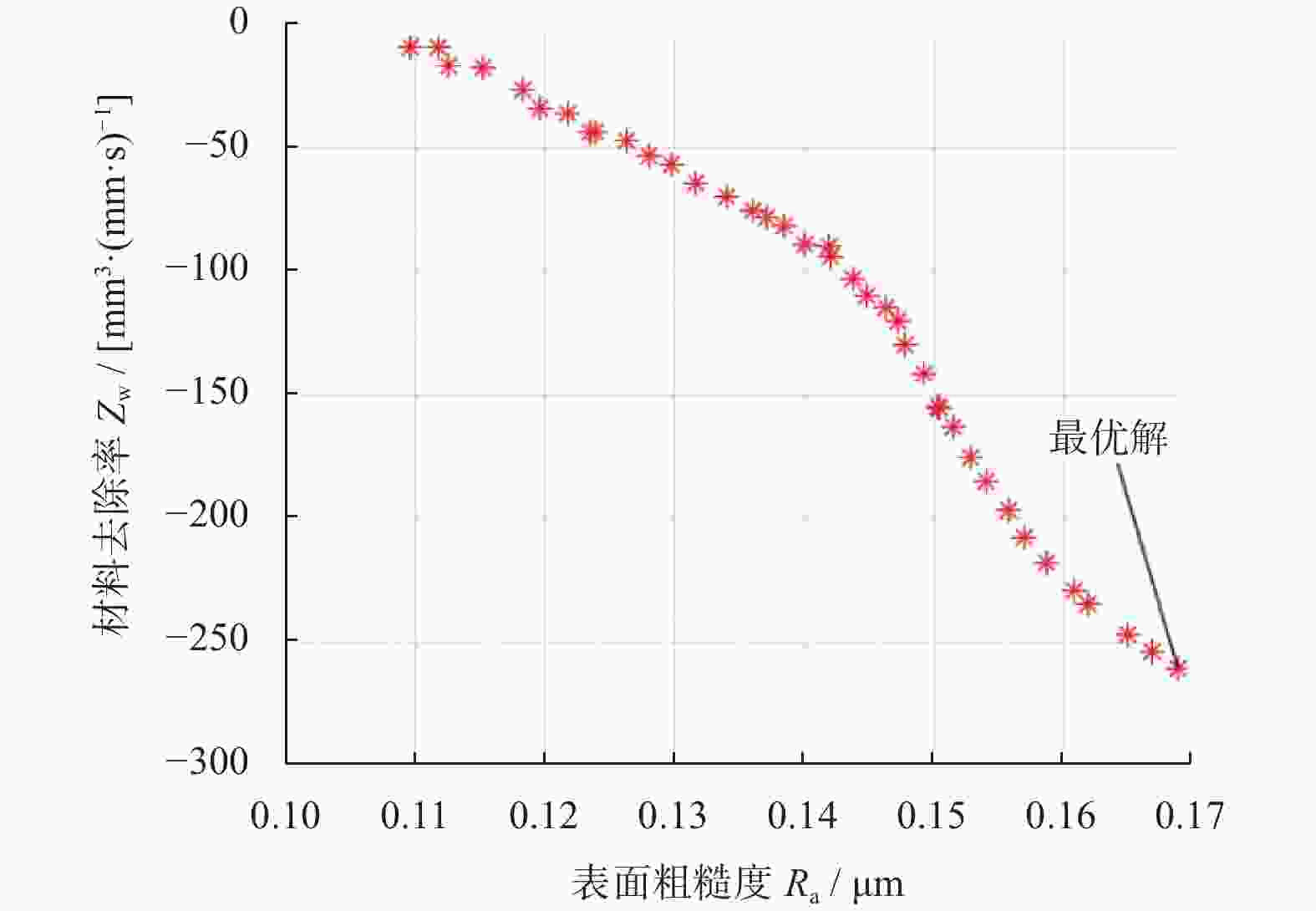
摘要: 为改善20CrMo钢凸轮轴磨削加工的质量和效率,基于响应曲面法进行磨削试验,分析磨削工艺参数对其表面粗糙度的影响,并建立相应的回归模型。根据工件形状特点,建立工件薄弱部位瞬时材料去除率计算模型,将表面粗糙度和材料去除率作为优化目标,利用第二代非支配快速排序遗传算法(non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm-2,NSGA2)进行多目标工艺参数组合寻优并进行试验验证。结果表明:求解得到的最优工艺参数组合是砂轮线速度为60 m/s、工件转速为96 r/min、磨削深度为30 μm,在保证工件薄弱部位表面粗糙度满足加工要求的前提下,可有效提高其磨削加工效率。
-
关键词:
- 凸轮轴磨削 /
- 响应曲面法 /
- 第二代非支配快速排序遗传算法 /
- 参数优化
Abstract: In order to improve the grinding quality and efficiency of 20CrMo steel camshaft, response surface method was used to conduct grinding tests. The influence of grinding process parameters on surface roughness was analyzed, and the corresponding regression model was established. Based on the shape characteristics of the workpiece, the instantaneous material removal rate calculation model of the weak part of the workpiece was established. The model of surface roughness and material removal rate was taken as the optimization objective. The second generation of non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm was used to optimize the combination of multi-objective process parameters and test verification was carried out. The results show that the optimal combination of process parameters, namely the linear speed of the grinding wheel 60 m/s, the workpiece speed 96 r/min and the grinding depth 30 μm, can effectively improve the grinding efficiency under the premise of ensuring that the surface roughness of the weak part meets the machining requirements.-
Key words:
- camshaft grinding /
- response surface methodology /
- NSGA2 /
- parameter optimization
-
表 1 磨削试验参数取值
Table 1. Parameter value of grinding test
水平 因素 砂轮线速度
vs /(m·s−1)工件转速
nw /(r·min−1)磨削深度
ap /μm−1 60 40 10 0 75 70 20 1 90 100 30 表 2 磨削试验方案及结果
Table 2. Grinding test scheme and results
序号 水平取值 $ \mathrm{表}\mathrm{面}\mathrm{粗}\mathrm{糙}\mathrm{度}{R}_{\mathrm{a}} $ /μm $ {v}_{\mathrm{s}} $ $ {n}_{\mathrm{w}} $ $ {a}_{\mathrm{p}} $ 1 −1 −1 0 0.151 2 1 −1 0 0.114 3 −1 1 0 0.143 4 1 1 0 0.196 5 −1 0 −1 0.166 6 1 0 −1 0.121 7 −1 0 1 0.156 8 1 0 1 0.188 9 0 −1 −1 0.127 10 0 1 −1 0.162 11 0 −1 1 0.147 12 0 1 1 0.206 13 0 0 0 0.133 表 3 表面粗糙度回归模型方差
Table 3. Variance of regression model for surface roughness
方差来源 自由度 均方差
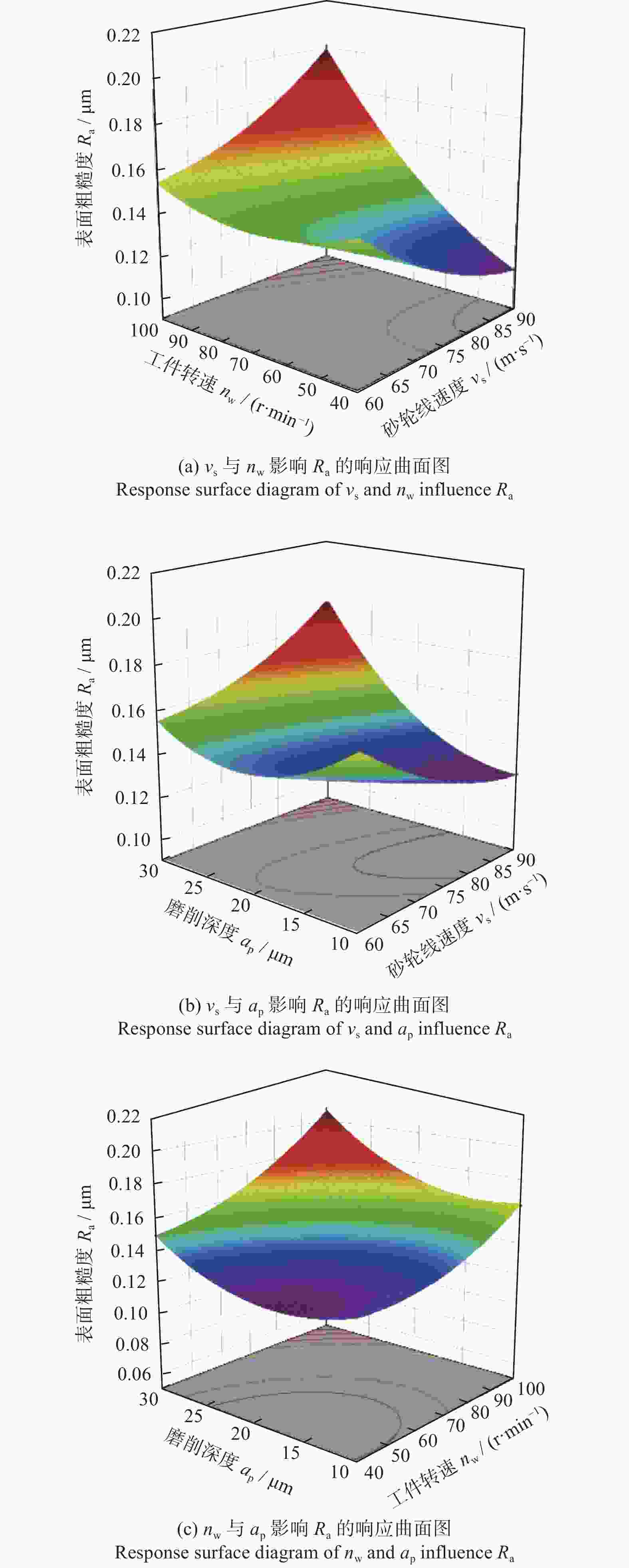
F值 P值 模型 9 0.009 7 20.070 0 0.015 7 $ {v}_{\mathrm{s}} $ 1 $ 1. 125\times {10}^{-6} $ 0.020 9 0.894 1 $ {n}_{\mathrm{w}} $ 1 0.003 5 65.640 0 0.003 9 $ {a}_{\mathrm{p}} $ 1 0.001 8 34.050 0 0.010 0 $ {v}_{\mathrm{s}}{n}_{\mathrm{w}} $ 1 0.002 0 37.670 0 0.008 7 $ {v}_{\mathrm{s}}{a}_{\mathrm{p}} $ 1 0.001 5 27.580 0 0.013 4 $ {n}_{\mathrm{w}}{a}_{\mathrm{p}} $ 1 0.000 1 2.680 0 0.200 2 $ {{v}_{\mathrm{s}}}^{2} $ 1 0.000 1 2.470 0 0.213 9 $ {{n}_{\mathrm{w}}}^{2} $ 1 0.000 2 4.580 0 0.121 9 $ {{a}_{\mathrm{p}}}^{2} $ 1 0.000 7 12.470 0 0.038 6 ${R^2}{\rm{ = }}0.983\;7\;\;\;\;\;R_{{\rm{adj}}}^{\rm{2}} = 0.934\;6$ -
[1] 韩文强, 何辉波, 李华英, 等. TiN涂层刀具对20CrMo钢的干切削性能的影响及磨损机理 [J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2014,45(1):64-70.HAN Wenqiang, HE Huibo, LI Huaying, et al. Effect of TiN coated tools on machinability and wear mechanism in dry turning of 20CrMo steel [J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology),2014,45(1):64-70. [2] 林述温, 刘衍聪, 莫开旺. 轴承沟道磨削工艺参数对磨削变质层的影响规律 [J]. 轴承,1996(12):21-23,28,38.LIN Shuwen, LIU Yancong, MO Kaiwang. Influence of process parameters on grinding deterioration layer in groove grinding of bearing [J]. Bearings,1996(12):21-23,28,38. [3] 刘伟, 商圆圆, 邓朝晖, 等. 基于响应曲面法的轴承钢GCr15高速外圆磨削参数优化 [J]. 中国机械工程,2019,30(23):2829-2834. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2019.23.008LIU Wei, SHANG Yuanyuan, DENG Zhaohui, et al. Parameter optimization of high speed cylindrical grinding for bearing steel GCr15 based on response surface method [J]. China Mechanical Engineering,2019,30(23):2829-2834. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2019.23.008 [4] KABASAKAOGLU U, KARA F, KKLÜ U. Taguchi optimization of surface roughness in grinding of cryogenically treated AISI 5140 steel [J]. Materials Testing,2020,62(10):1041-1047. doi: 10.3139/120.111583 [5] 肖军民, 谢晋. 20CrMnTi高速外圆磨削试验研究及参数优化 [J]. 机床与液压,2015,43(11):56-58,84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2015.11.016XIAO JunMin, XIE Jin. Experimental research and parameters optimization of high-speed cylindrical grinding for 20CrMnTi [J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics,2015,43(11):56-58,84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2015.11.016 [6] CHEN T, ZHU Y J, XI X X, et al. Process parameter optimization and surface integrity evolution in the highspeed grinding of TiAl intermetallics based on grey relational analysis method [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2021,117(9/10):2895-2908. doi: 10.1007/s00170-021-07882-x [7] 李云雁, 胡传荣. 试验设计与数据处理 [M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005.LI Yunyan, HU Chuanrong. Experiment design and data processing [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2005. [8] DENG Z H, ZHANG X H, LIU W, et al. A hybrid model using genetic algorithm and neural network for process parameters optimization in NC camshaft grinding [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2009,45(9/10):859-866. doi: 10.1007/s00170-009-2029-4 [9] ZHANG P H, LI Z H, ZOU L, et al. Optimization of grinding process parameters based on BILSTM network and chaos sparrow search algorithm [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part E: Journal of Process Mechanical Engineering,2022,236(4):1693-1701. doi: 10.1177/09544089221074832 [10] CHEN Z Y, LI X K, ZHU Z U, et al. The optimization of accuracy and efficiency for multistage precision grinding process with an improved particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2020, 17(1): 172988141989350. [11] PHOLDEE N, PATEL V K, SAIT S M, et al. Hybrid spotted hyena-nelder-mead optimization algorithm for selection of optimal machining parameters in grinding operations [J]. Materials Testing,2021,63(3):293-298. doi: 10.1515/mt-2020-0043 [12] 姜惠兰, 安星, 王亚微, 等. 基于改进NSGA2算法的考虑风机接入电能质量的多目标电网规划 [J]. 中国电机工程学报,2015,35(21):5405-5411. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2015.21.003JIANG Huilan, AN Xing, WANG Yawei, et al. Improved NSGA2 algorithm base multi-objective planning of power grid with wind farm considering power quality [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE,2015,35(21):5405-5411. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2015.21.003 [13] 徐童. 凹面凸轮磨削加工磨削力控制方法研究 [D]. 重庆: 重庆理工大学, 2019.XU Tong. Research on grinding force control method for concave cam grinding [D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University of Technology, 2019. [14] 刘涛, 邓朝晖, 罗程耀, 等. 基于动态磨削深度的非圆轮廓高速磨削稳定性建模与分析 [J]. 中国机械工程学报,2021,57(15):264-274. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.15.264LIU Tao, DENG Zhaohui, LUO Chengyao, et al. Stability modeling and analysis of non-circular high-speed grinding with consideration of dynamic grinding depth [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2021,57(15):264-274. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.15.264 [15] DEB K, JAIN H. An evolutionary many-objective optimization algorithm using reference-point-based nondominated sorting approach, part I: Solving problems with box constraints [J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation,2014,18(4):577-601. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2013.2281535 [16] 李蓓智. 高速高质量磨削理论、工艺、装备与应用 [M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2012: 60-63.LI Beizhi. Theory, process, equipment and application of high-speed high quality grinding [M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 2012: 60-63. -





 下载:
下载:



 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
