Magnetorheological chemical compound polishing of single crystal SiC substrate
-
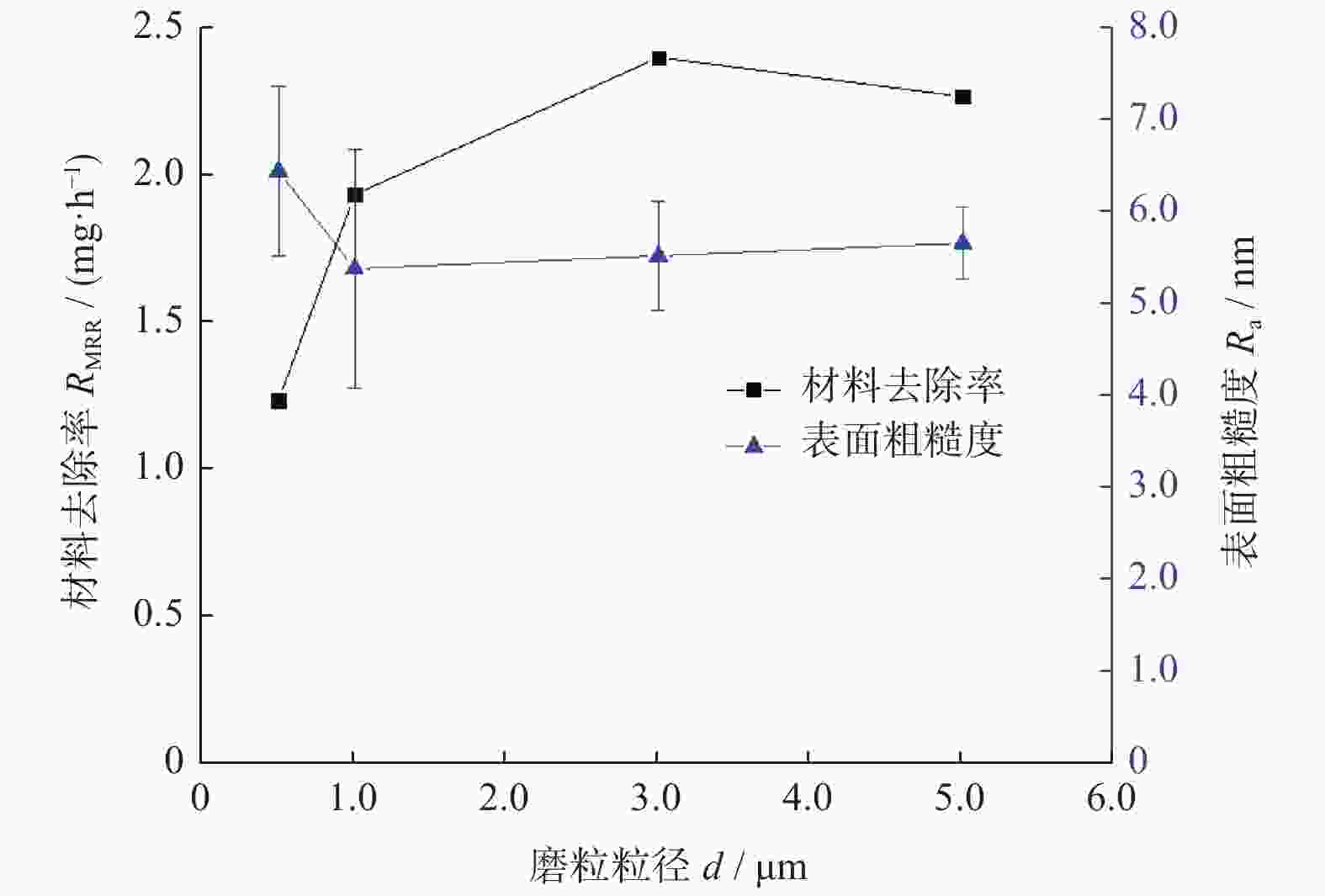
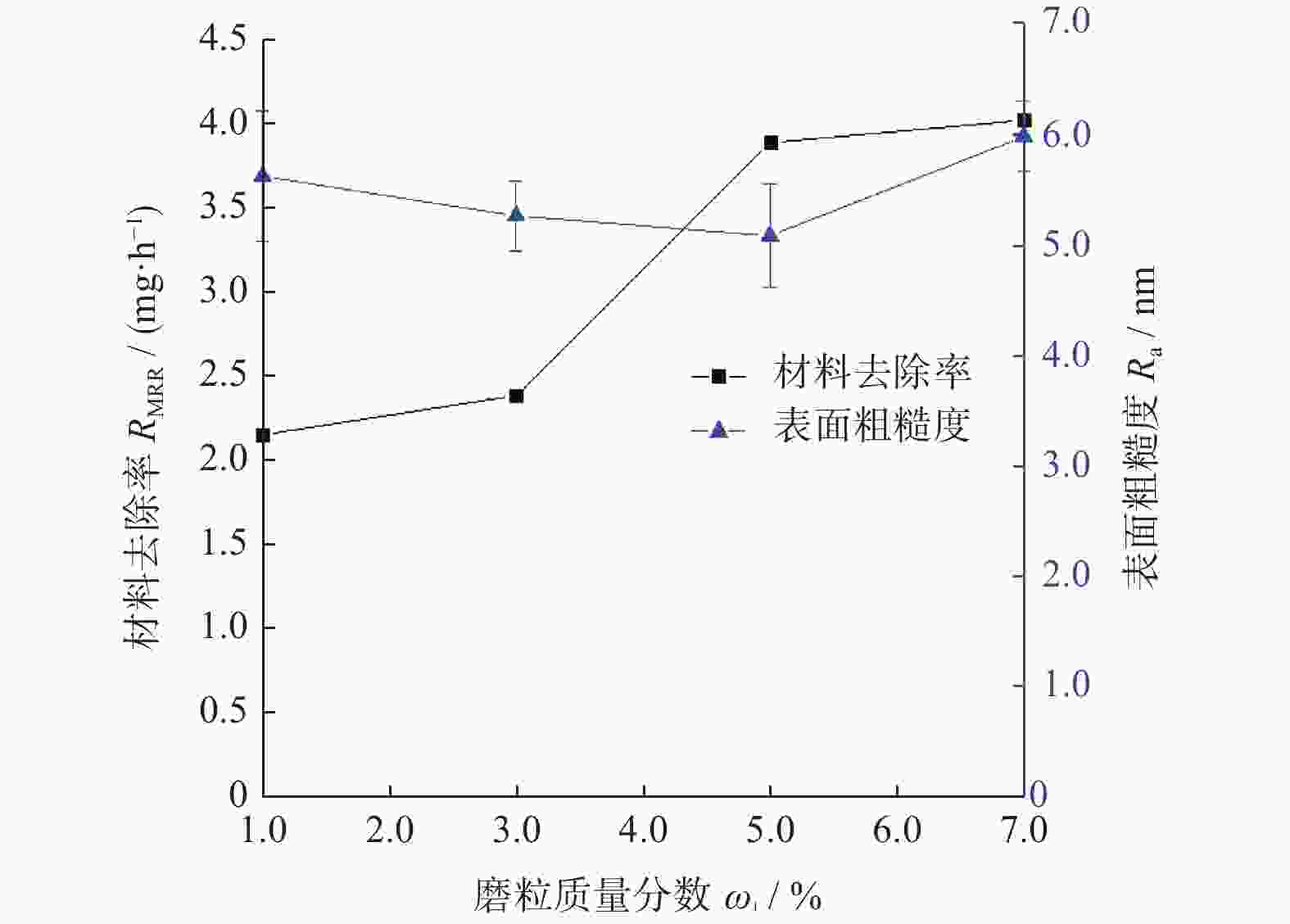
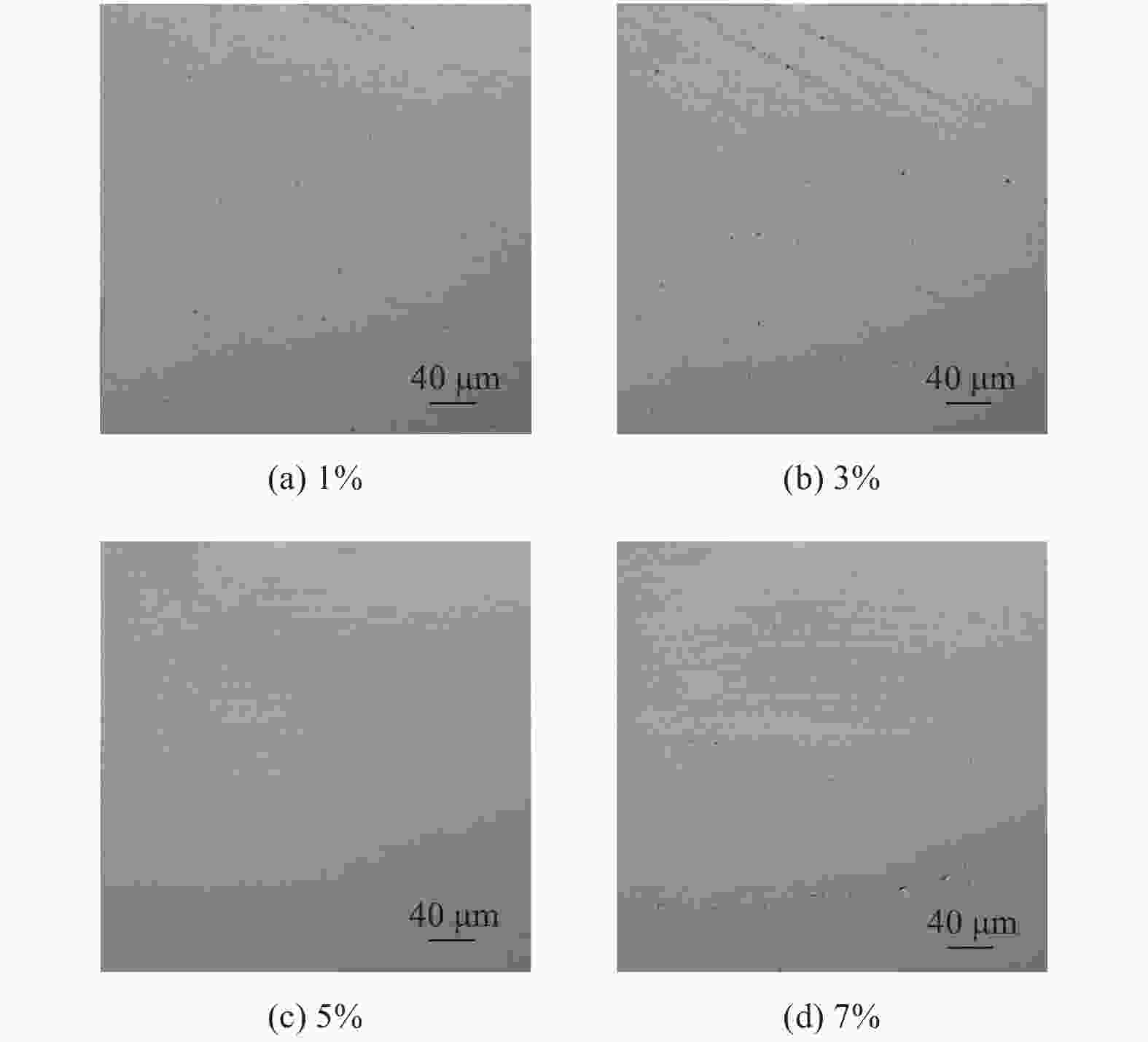
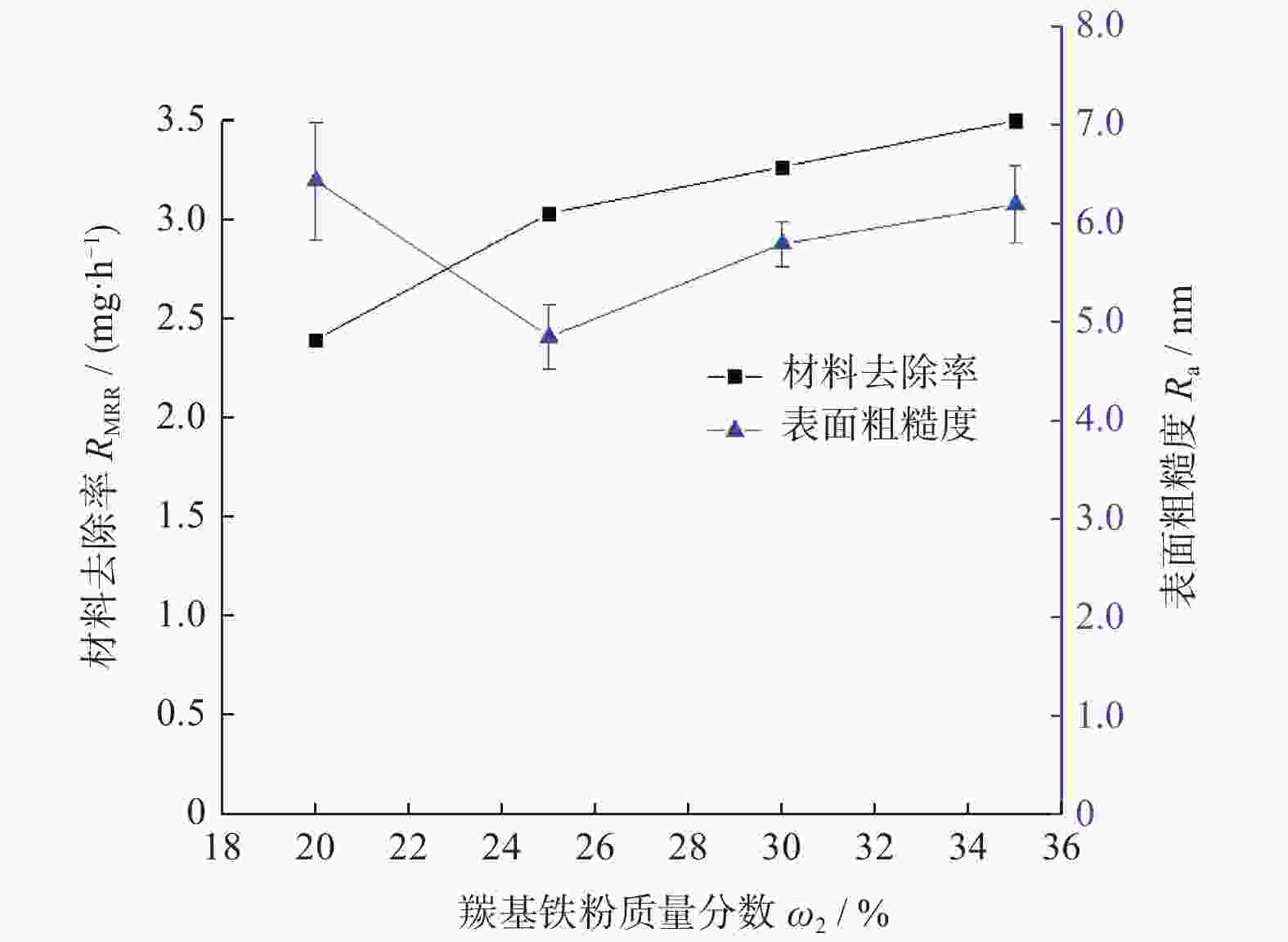
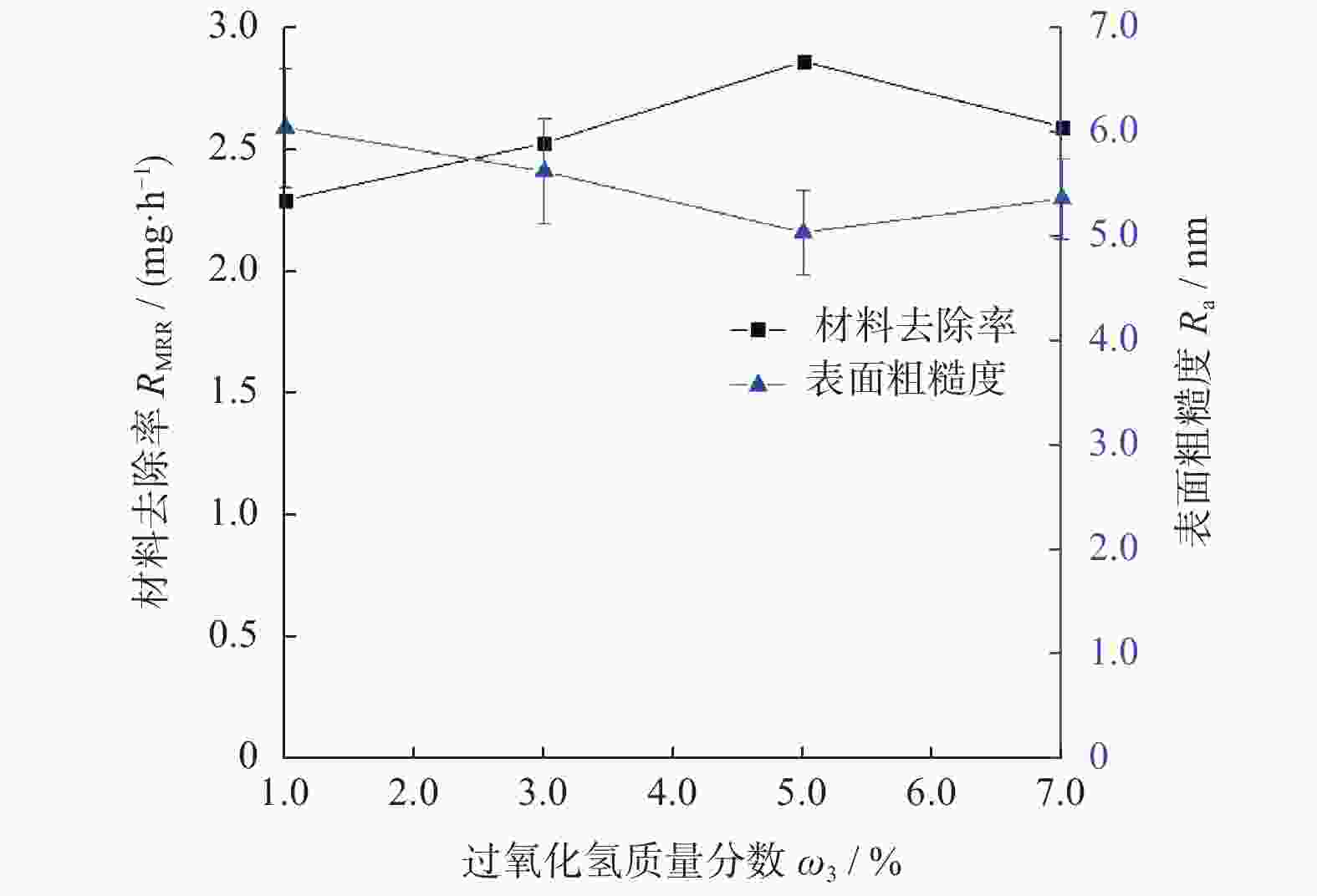
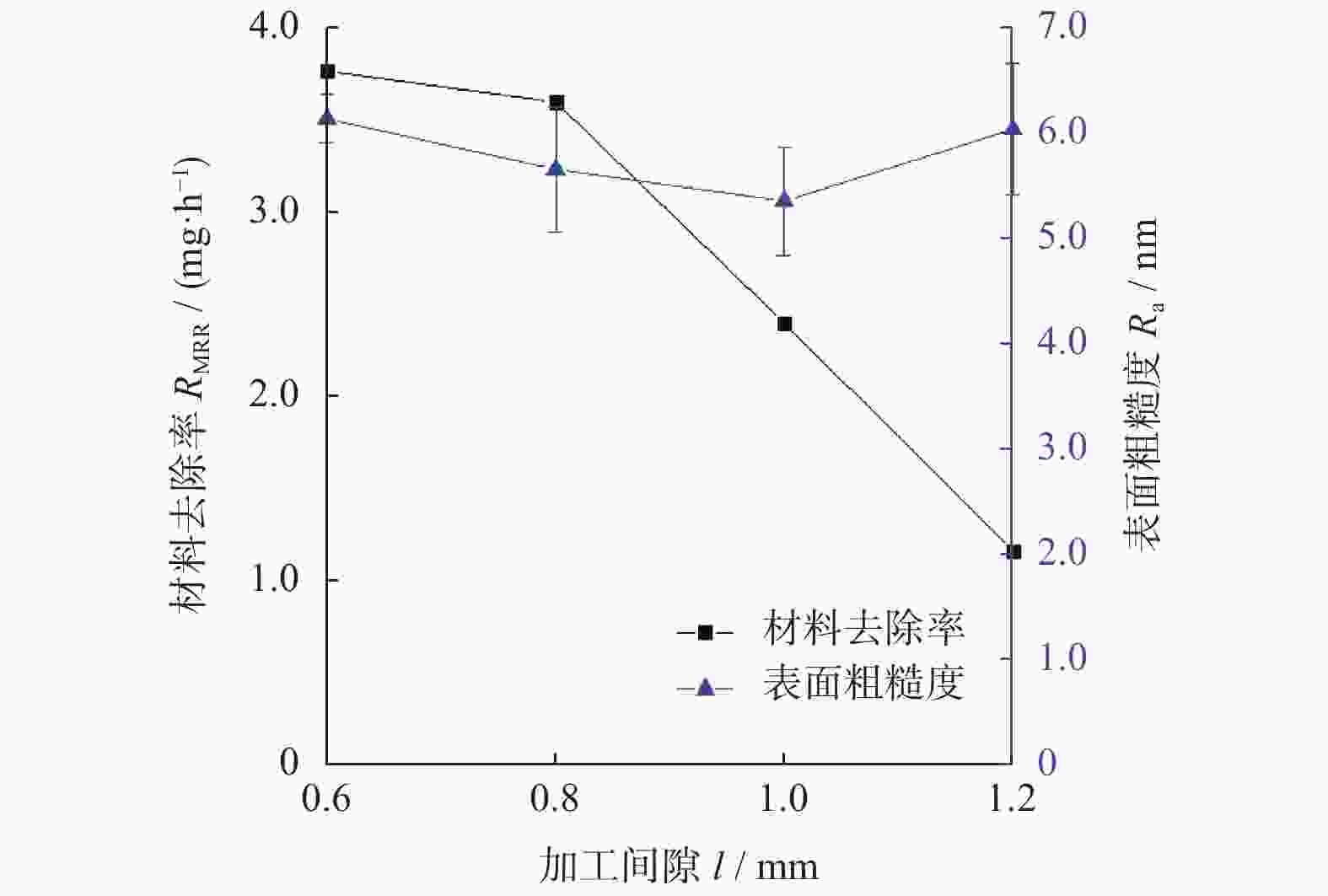
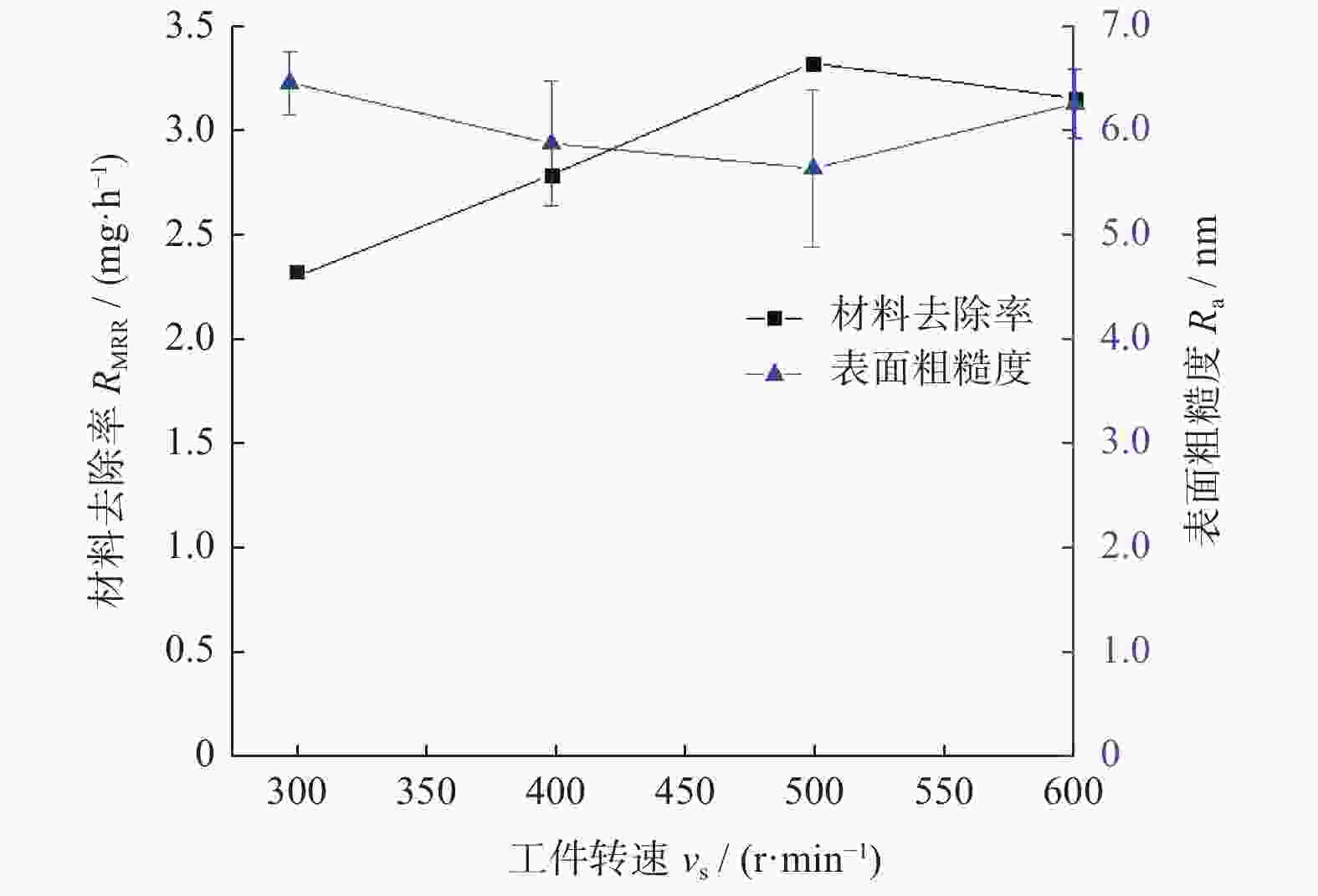
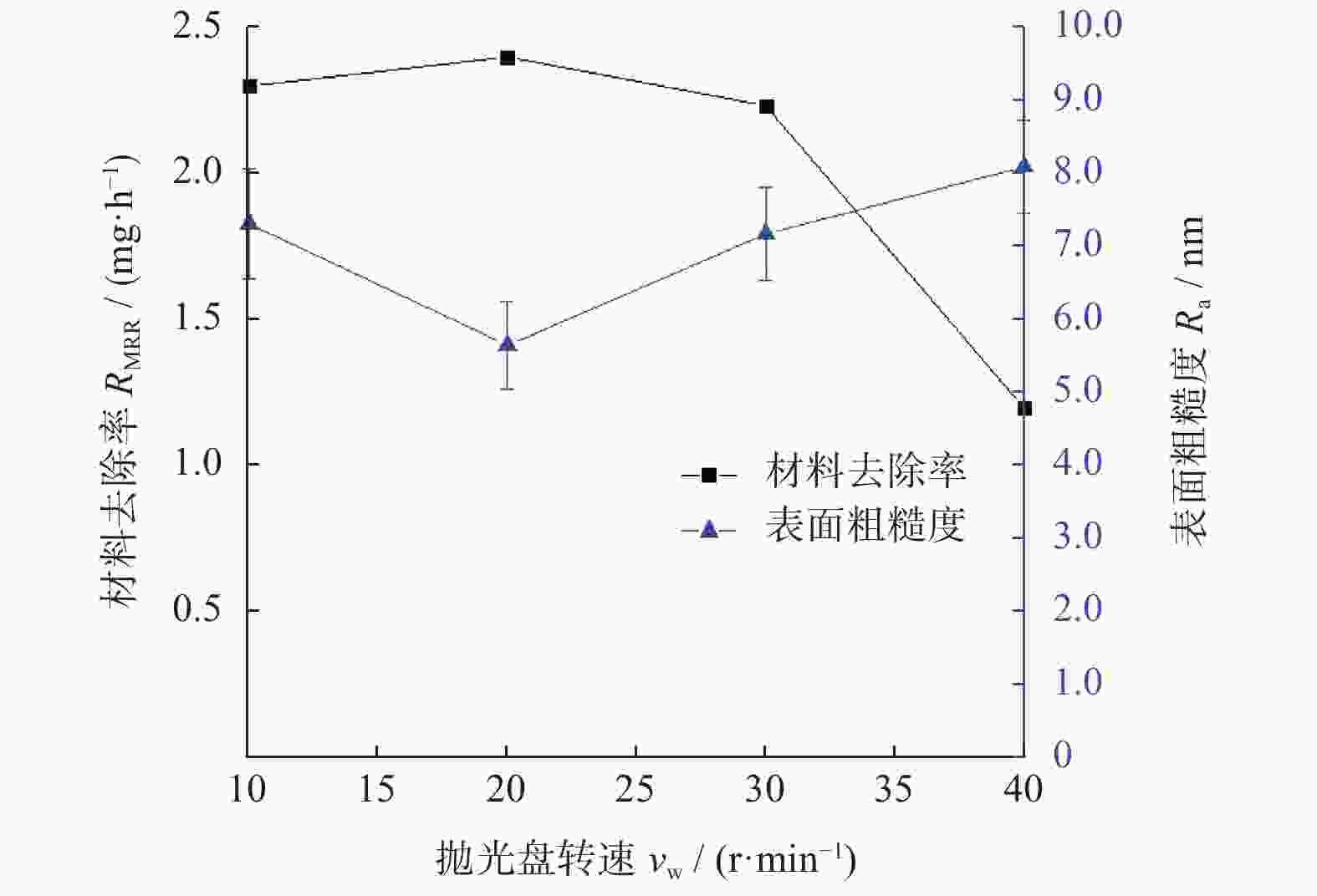
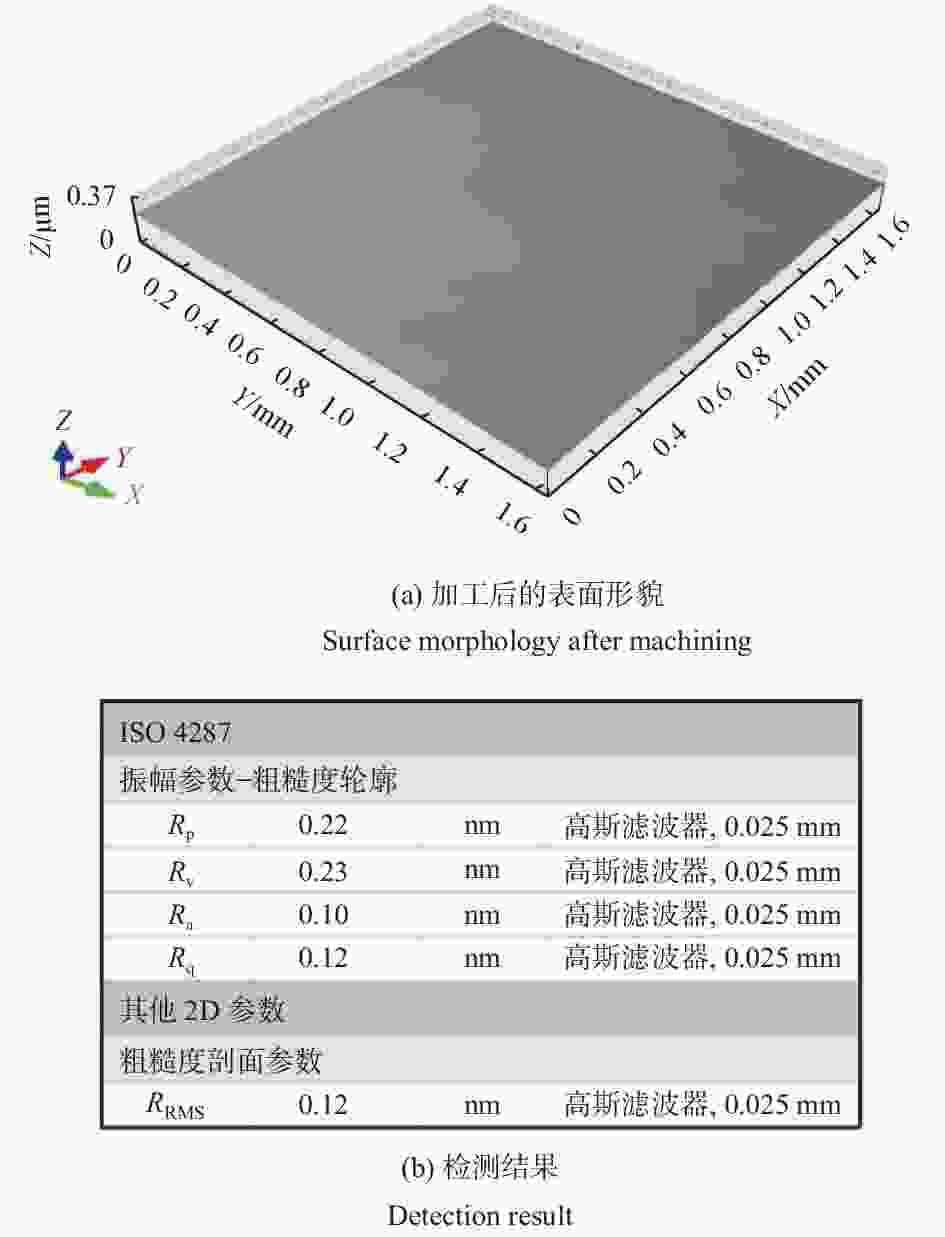
摘要: 基于芬顿反应的磁流变化学复合抛光加工原理,对单晶SiC基片进行磁流变化学复合抛光试验,研究工艺参数对其抛光效果的影响。结果表明:随着金刚石磨粒粒径的增大,材料去除率先增大后减小,而表面粗糙度先减小后增大;随着磨粒质量分数的增大,材料去除率增大,而表面粗糙度先减小后增大;当羰基铁粉质量分数增大时,材料去除率增大,而表面粗糙度呈先减小后增大的趋势;随着氧化剂质量分数增大,材料去除率先增大后减小,而表面粗糙度呈现先减小后增大的趋势;加工间隙对材料去除率的影响较大,加工间隙为1.0 mm时,加工表面质量较好;随着工件转速和抛光盘转速增大,材料去除率均先增大后减小,表面粗糙度均先减小后增大。获得的优化的工艺参数为:磨粒粒径,1.0 μm;磨粒质量分数,5%;羰基铁粉质量分数,25%;过氧化氢质量分数,5%;加工间隙,1.0 mm;工件转速,500 r/min;抛光盘转速,20 r/min。采用优化的工艺参数对表面粗糙度约为40.00 nm的单晶SiC进行加工,获得表面粗糙度为0.10 nm以下的光滑表面。Abstract: Based on the magnetorheological chemical composite polishing principle of Fenton reaction, the magnetorheological chemical composite polishing experiment was carried out on single crystal SiC substrate, and the influence of process parameters on the polishing effect was studied. The results show that with the increase of diamond particle size, material removal increases first and then decreases, while surface roughness decreases first and then increases. With the increase of abrasive mass fraction, material removal rate increases, and surface roughness decreases first and then increases. When the mass fraction of carbonyl iron powder increases, material removal rate increases, while surface roughness decreases first and then increases. With the increase of oxidant mass fraction, material removal increases first and then decreases, while the surface roughness decreases first and then increases. The influence of machining gap on material removal rate varies greatly. When machining gap is 1.0 mm, machined surface quality is better. With the increase of workpiece speed and polishing disc speed, the material removal rate first increases and then decreases, and the surface roughness first decreases and then increases. The optimized process parameters are as follows: the abrasive particle size is 1.0 μm, the mass fraction is 5%, the mass fraction of carbonyl iron powder is 25%, the mass fraction of hydrogen peroxide is 5%, the machining gap is 1.0 mm, the workpiece speed is 500 r/min, and the polishing disc speed is 20 r/min. The single crystal SiC with surface roughness of about 40.00 nm was processed with optimized process parameters to obtain a smooth surface with surface roughness of less than 0.10 nm.
-
Key words:
- magnetorheological chemical compound polishing /
- Fenton reaction /
- SiC
-
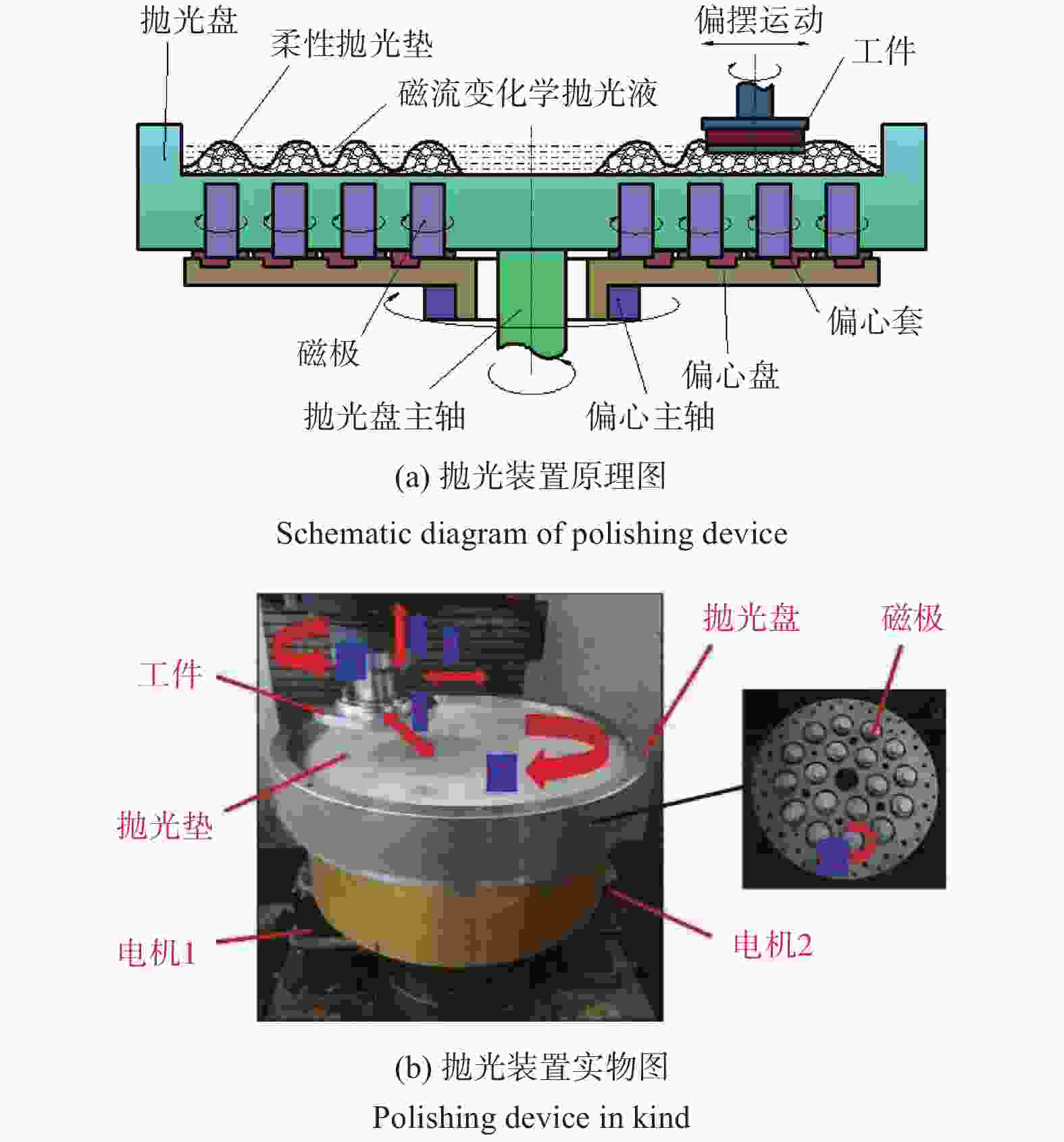
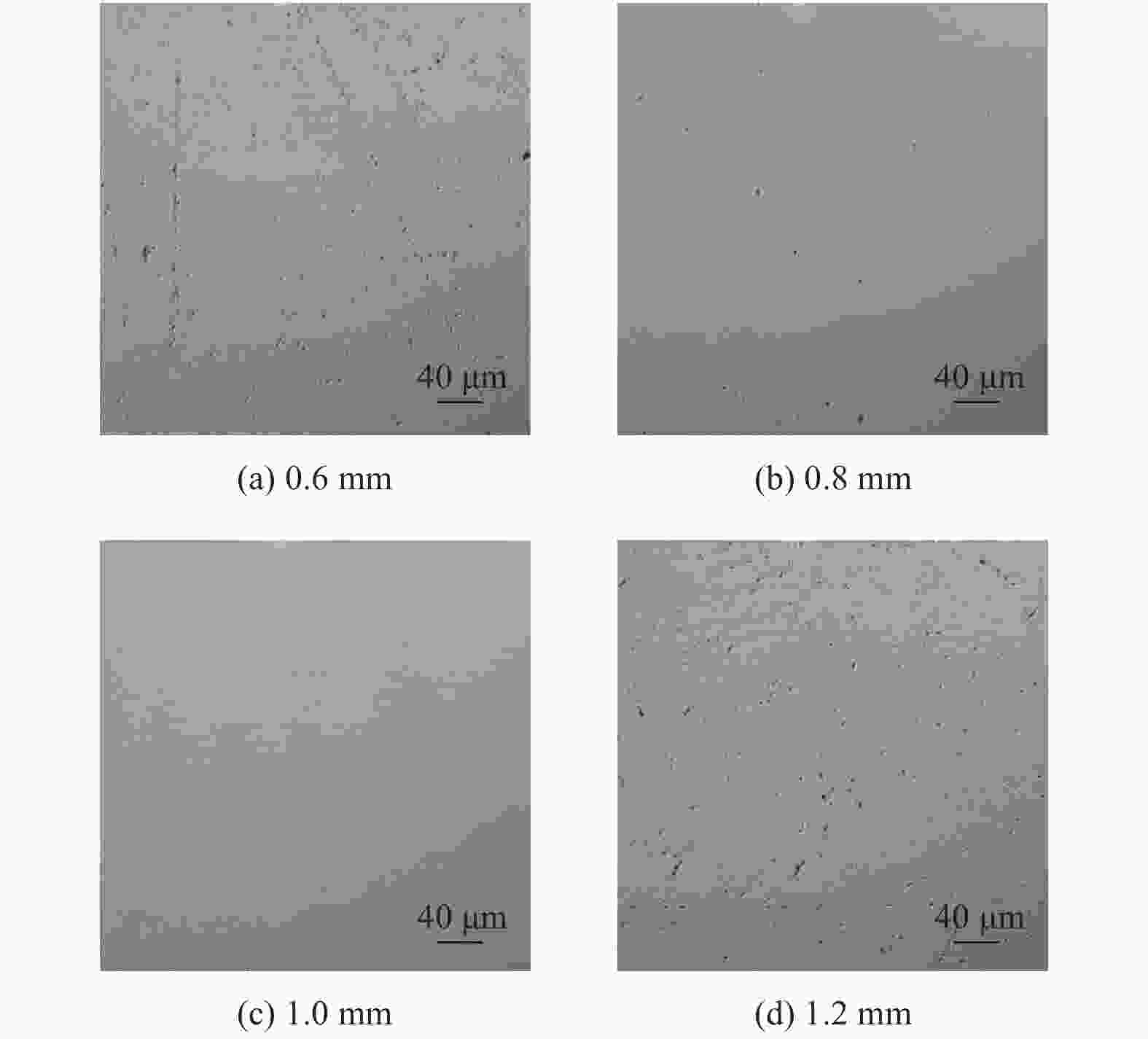
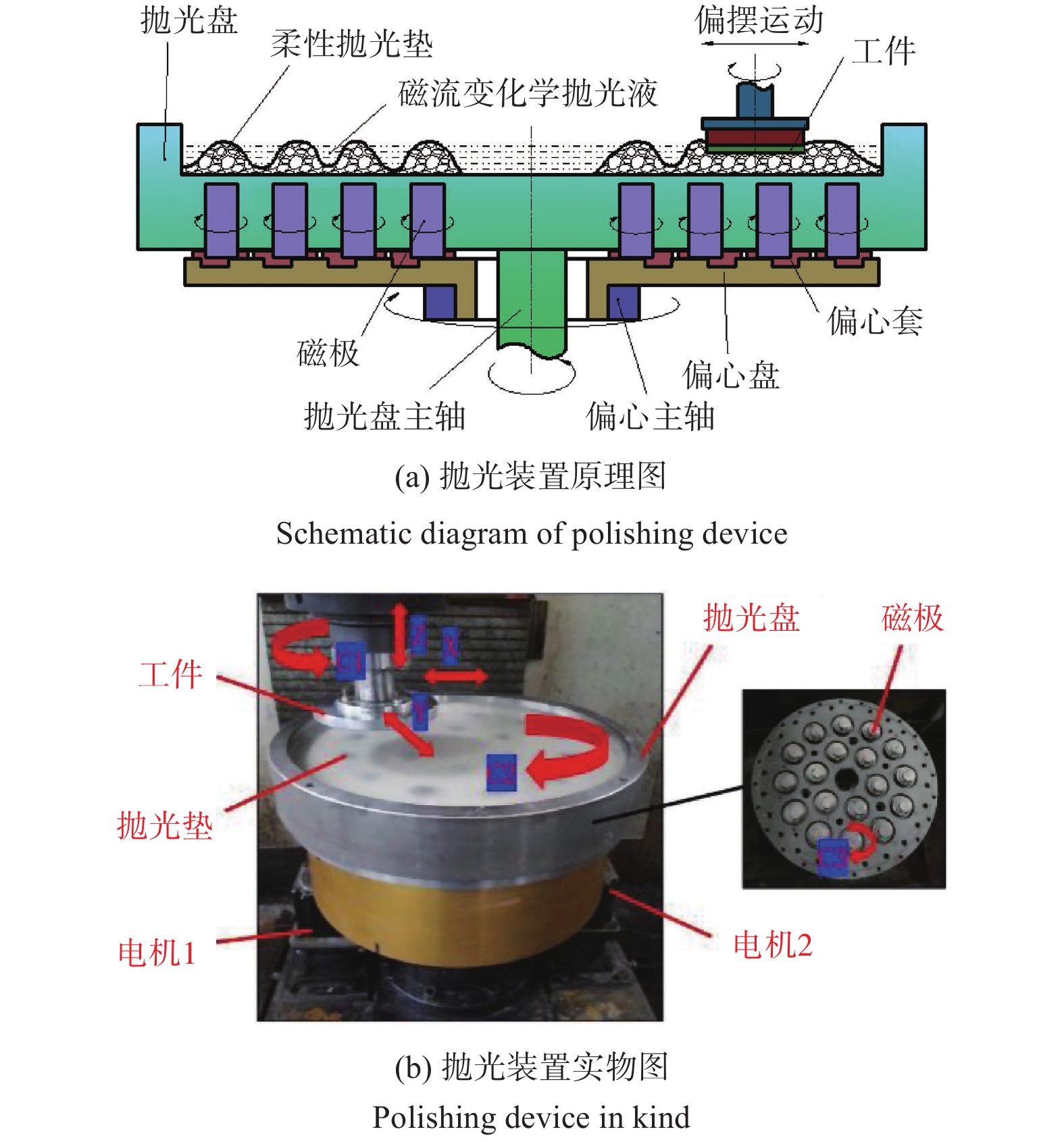
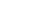
表 1 加工参数
Table 1. Machining parameters
参数名称 数值 磨粒粒径 d / μm 0.5,1.0,3.0,5.0 磨粒质量分数 ω1 / % 1,3,5,7 羰基铁粉质量分数 ω2 / % 20,25,30,35 过氧化氢质量分数 ω3 / % 1,3,5,7 加工间隙 l / mm 0.6,0.8,1.0,1.2 工件转速 vs / (r∙min−1) 300,400,500,600 抛光盘转速 vw / (r∙min−1) 10,20,30,40 -
[1] RAYNAUD C, TOURNIER D, MOREL H, et al. Comparison of high voltage and high temperature performances of wide bandgap semiconductors for vertical power devices [J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2010,19(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2009.09.015 [2] ZHOU L, AUDURIER V, PIROUZ P, et al. Chemomechanical polishing of silicon carbide [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society,1997,144(6):161-163. doi: 10.1149/1.1837711 [3] OKUMURA H. Present status and future prospect of widegap semiconductor high-power devices [J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics,2006,45(10A):7565-7586. doi: 10.1143/JJAP.45.7565 [4] PUSHPAKARAN B N, SUBBURAJ A S, BAYNE S B, et al. Impact of silicon carbide semiconductor technology in photovoltaic energy system [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2016,55:971-989. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.10.161 [5] AIDA H, DOI T, TAKEDA H, et al. Ultraprecision CMP for sapphire, GaN, and SiC for advanced optoelectronics materials [J]. Current Applied Physics,2012,12(9):41-46. [6] SHI X, PAN G, ZHOU Y, et al. Extended study of the atomic step-terrace structure on hexagonal SiC(0001) by chemical-mechanical planarization [J]. Applied Surface Science,2013,284:195-206. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.07.080 [7] 叶子凡, 周艳, 徐莉, 等. 紫外LED辅助的4H-SiC化学机械抛光 [J]. 纳米技术与精密工程,2017,15(5):342-346.YE Zifan, ZHOU Yan, XU Li, et al. Chemical mechanical polishing of 4H-SiC wafer with UV-LED light [J]. Nanotechnology and Precision Engineering,2017,15(5):342-346. [8] 徐少平. 基于芬顿反应的单晶SiC集群磁流变化学复合抛光研究 [D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2016.XU Shaoping. Research on chemical cluster magnetorheological compound polishing of single-crystal SiC based on Fenton reaction [D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong University of Technology, 2016. [9] JAIN V K, RANJAN P, SURI V K, et al. Chemo-mechanical magnetorheological finishing (CMMRF) of silicon for microelectronics applications [J]. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology,2010,59(1):323-328. doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2010.03.106 [10] RANJAN P, BALASUBRAMANIAM R, SURI V K, et al. Development of chemo-mechanical magnetorheological finishing process for super finishing of copper alloy [J]. International Journal of Manufacturing Technology & Management,2013,27(4-6):130-141. [11] 尹韶辉, 王永强, 李叶鹏, 等. 蓝宝石基片的磁流变化学抛光试验研究 [J]. 机械工程学报,2016,52(5):80-87. doi: 10.3901/JME.2016.05.080YIN Shaohui, WANG Yongqiang, LI Yepeng, et al. Experimental study on magnetorheological chemical polishing for sapphire substrate [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2016,52(5):80-87. doi: 10.3901/JME.2016.05.080 [12] NAM S, RENGANATHAN V, TRATNYEK P G. Substituent effects on azo dye oxidation by the FeIII-EDTA-H2O2 system[J]. Chemosphere, 2001, 45(1): 59-65. -




 下载:
下载:

 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
