Comparison of lapping performance between diamond magnetic abrasives and silicon carbide magnetic abrasives
-
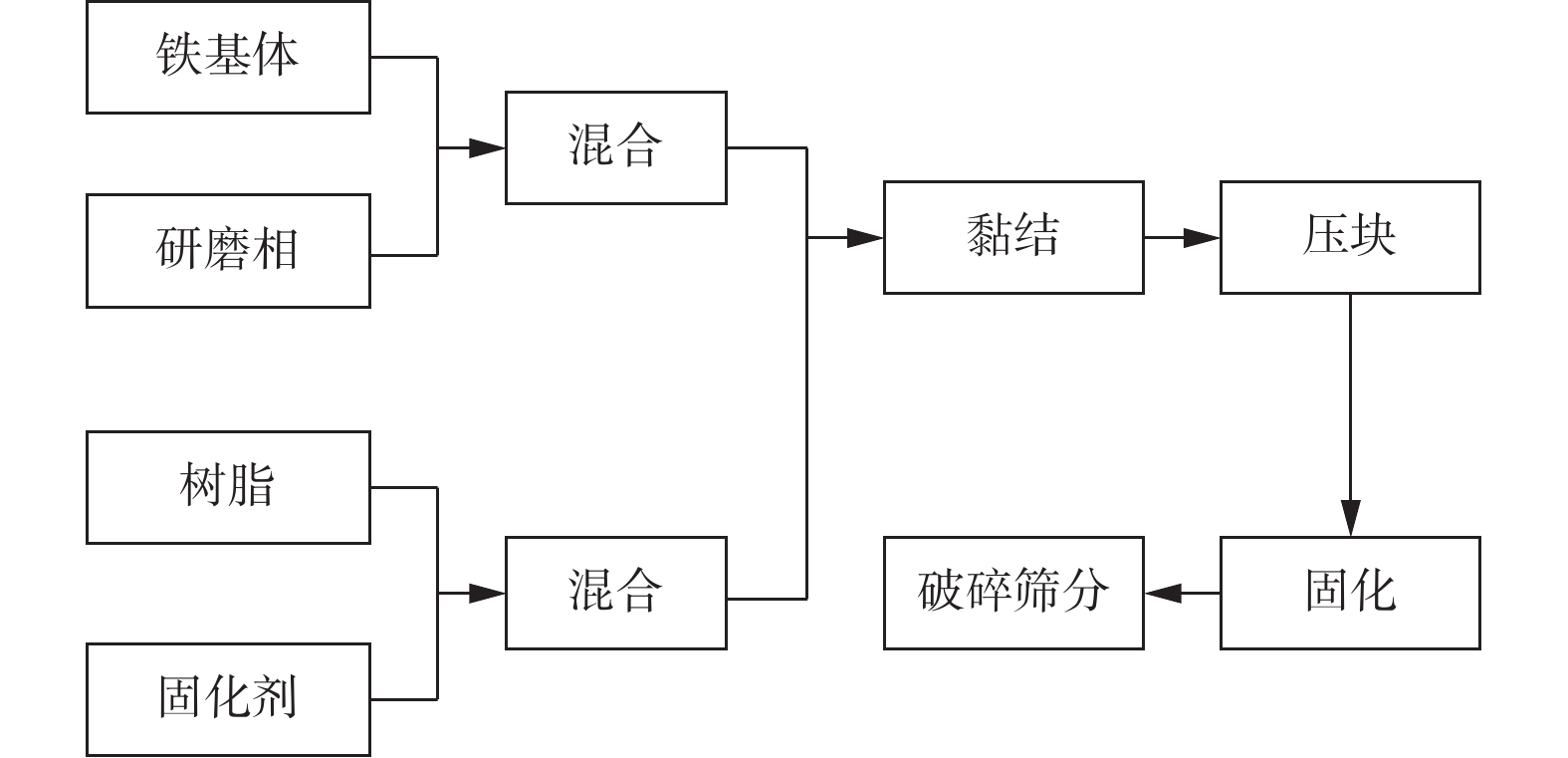
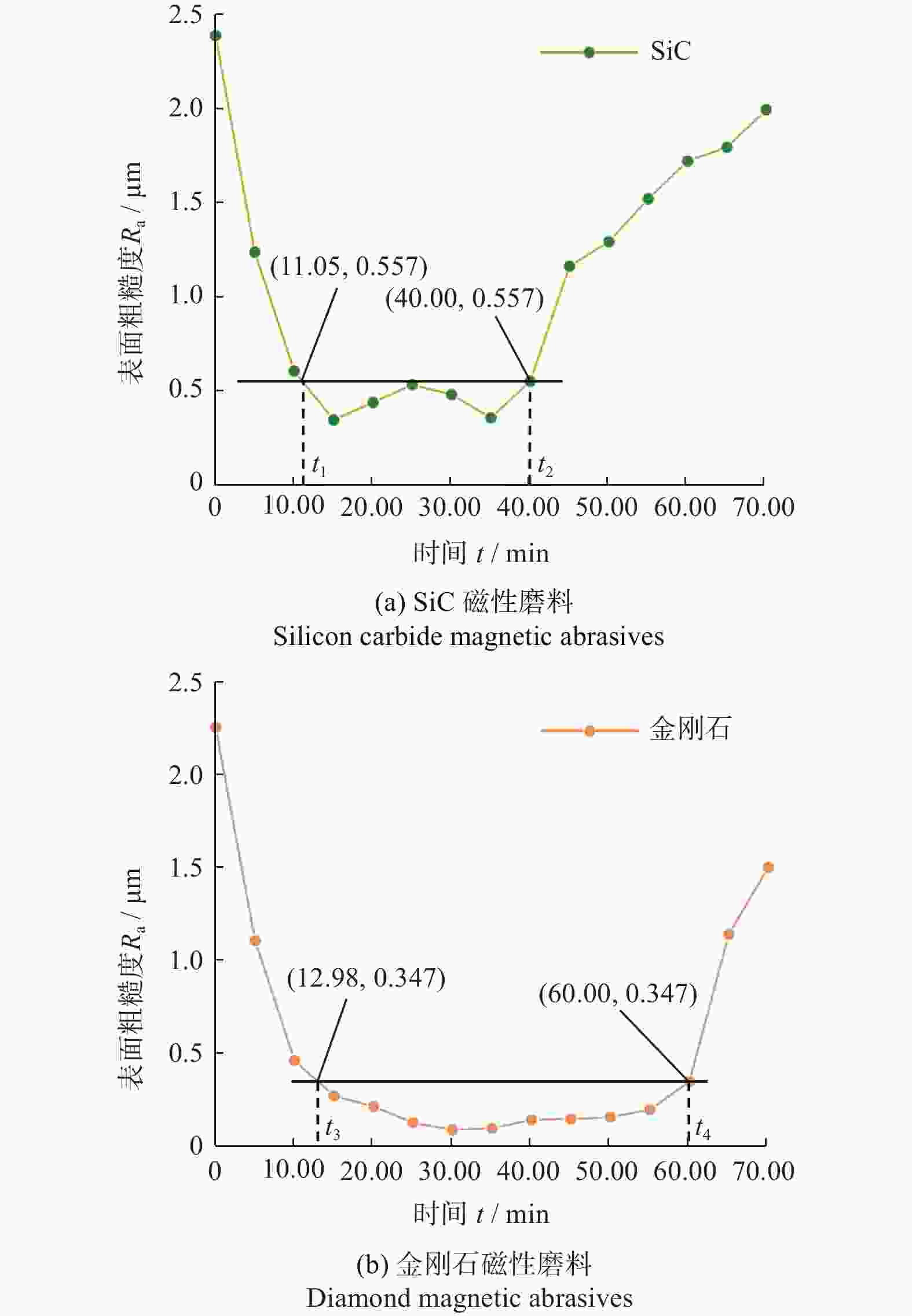
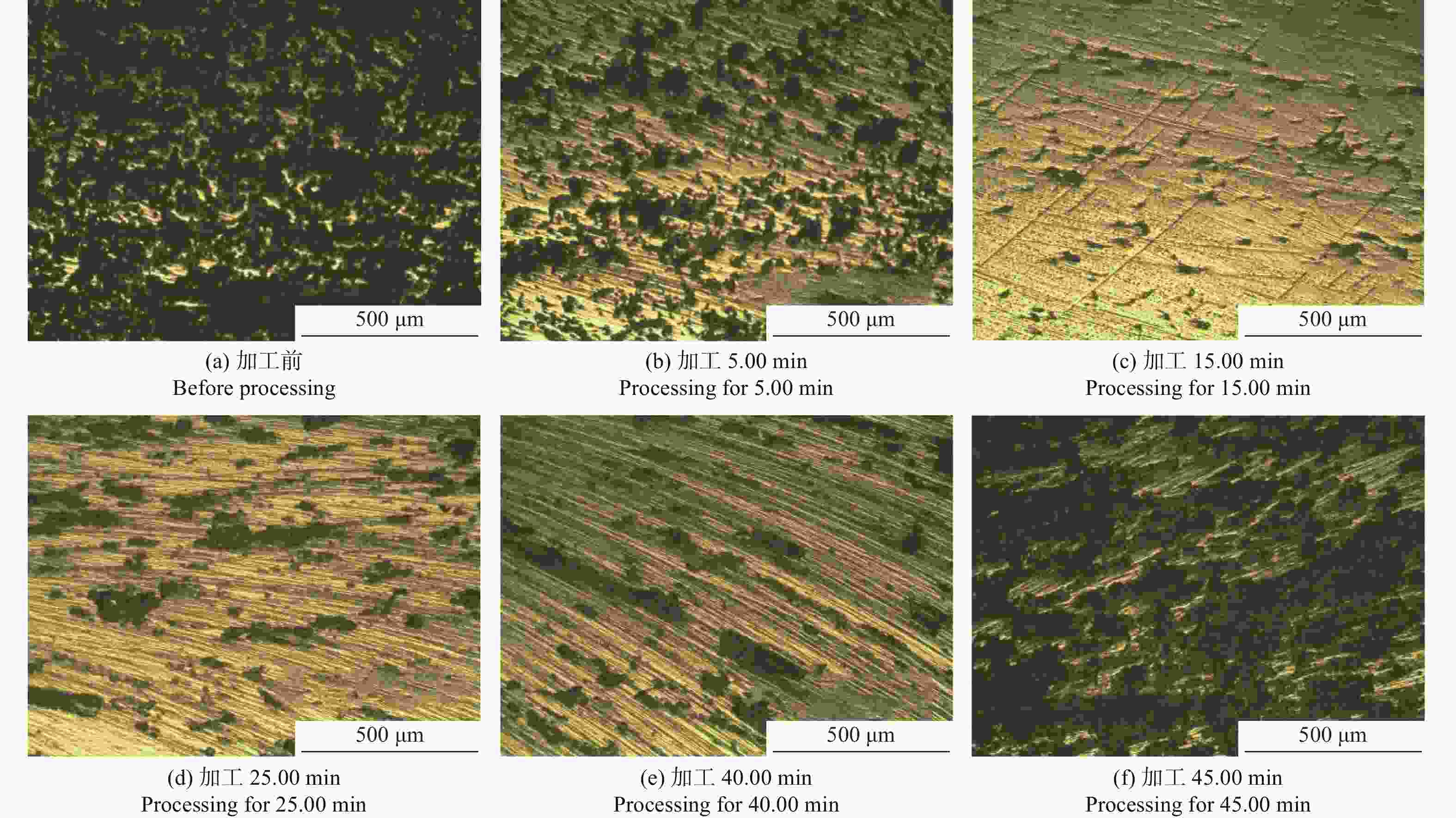
摘要: 针对硬脆材料的硬度高,传统的碳化硅磁性磨料研磨效率低、磨料寿命短等问题,开发以金刚石颗粒作为研磨相的磁性磨料。以高纯铁粉为铁基相,金刚石为研磨相,采用树脂黏结法制备金刚石磁性磨料。以K9玻璃为加工对象,比较金刚石磁性磨料和碳化硅磁性磨料磁力研磨K9玻璃时的使用寿命和加工效率。实验得到金刚石磁性磨料的寿命为60.00 min,能够将K9玻璃的平均表面粗糙度Ra加工至0.036 μm,在使用寿命内能够加工的工件为4.6件;而碳化硅磁性磨料的寿命仅有40.00 min,只能将K9玻璃的平均表面粗糙度Ra加工至0.222 μm,在使用寿命内能够加工的工件为3.6件。金刚石颗粒作为研磨相能够有效地提高磁性磨料的使用寿命、加工能力以及磁力研磨的加工效率。Abstract: The hardness of hard-brittle materials is high, which results in the low lapping efficiency of traditional silicon carbide magnetic abrasive and short abrasive life. In view of this situation, a magnetic abrasive with diamond particle as lapping grit was developed. Using high purity iron powder as iron-based phase and diamond particle as abrasive, diamond magnetic abrasives were prepared by resin bonding method. K9 glass was chosen as the part being machined. The service life and processing efficiency of magnetic lapping K9 glass were compared between with diamond magnetic abrasives and with silicon carbide magnetic abrasives. The lifespan of diamond magnetic abrasive is 60.00 min, and the number of work-piece which can be machined is 4.6 pieces in the service life. The average surface roughness of K9 glass reaches 0.036 μm. However, the service life of the silicon carbide magnetic abrasive particles is only 40 min, and the average surface roughness of the K9 glass workpiece can only be processed to 0.222 μm. Besides, the number of workpieces that can be processed during the service life is 3.6 pieces. Diamond magnetic abrasives can effectively improve the service life, the processing capacity of magnetic abrasives, and the processing efficiency of magnetic grinding.
-
Key words:
- magnetic abrasive /
- diamond /
- silicon carbide /
- service life /
- lapping efficiency
-
表 1 制备参数
Table 1. Prepare parameters
制备参数 参数值 研磨相粒径 d /μm 25 铁基相粒径 D / μm 75 筛网粒径 r / μm 90~180 黏结剂 环氧树脂 表 2 寿命比较试验加工参数
Table 2. Lifespan comparison of experimental processing parameters
加工参数 类型或取值 磁极头转速 v/(r·min−1) 800 加工间隙 d / mm 2 磨料填充量 m /g 2 直线研磨轨迹 l / mm 40 研磨时间 t /(min·次−1) 5 研磨液 油性研磨液 -
[1] ZHAO Z J, YIN T F, ZHU Z W, et al. Material removal energy in ultraprecision machining of micro-lens arrays on single crystal silicon by slow tool servo [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2022,335:130295. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130295 [2] 田可, 郭会茹, 吴勇波, 等. 旋转磁场下非球面工件的磁性混合流体抛光 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2022,42(4):495-503.TIAN Ke, GUO Huiru, WU Yongbo, et al. Magnetic mixed fluid polishing of aspheric workpieces under rotating magnetic fields [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2022,42(4):495-503. [3] 王振忠, 施晨淳, 张鹏飞, 等. 先进光学制造技术最新进展 [J]. 机械工程学报,2021,57(8):23-56. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.08.023WANG Zhenzhong, SHI Chenchun, ZHANG Pengfei, et al. Recent progress of advanced optical manufacturing technology [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2021,57(8):23-56. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.08.023 [4] XIA Z, FANG F, AHEARNE E, et al. Advances in polishing of optical freeform surfaces: A review [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2020,286:116828. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.116828 [5] 伍凡, 戴一帆. 先进光学制造专题导读 [J]. 光电工程,2020,47(8):2-3.WU Fan, DAI Yifan. Introduction to advanced optical manufacturing [J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering,2020,47(8):2-3. [6] 杨震宇, 吕玉山, 邸寒旭, 等. 弹性黏结磁性磨料设计制造及抛光性能的研究 [J]. 组合机床与自动化加工技术,2020(10):44-46,50.YANG Zhenyu, LYU Yushan, DI Hanxu, et al. Research on design, fabrication and polishing properties of elastic bonded magnetic abrasives [J]. Modular Machine Tool& Automatic Manufacturing Technique,2020(10):44-46,50. [7] 姜林志, 张桂香, 秦璞, 等. 磁性磨料和磨粒相粒径对磁力研磨效率的影响 [J]. 电镀与涂饰,2019,38(4):157-160.JIANG LinZhi, ZHANG GuiXiang, QIN Pu, et al. Effects of particle size and core size of magnetic abrasive on efficiency of magnetic abrasive finishing [J]. Electroplating & Finishing,2019,38(4):157-160. [8] 刘文浩, 陈燕, 李文龙, 等. 磁粒研磨加工技术的研究进展 [J]. 表面技术,2021,50(1):47-61.LIU WenHao, CHEN Yan, LI WenLong, et al. Research progress of magnetic abrasive finishing technology [J]. Surface Technology,2021,50(1):47-61. [9] LI W S, LI J J, BO C, et al. Achieving in-situ alloy-hardening core-shell structured carbonyl iron powders for magnetic abrasive finishing [J]. Materials & Design,2021,212:110198. [10] 吕旖旎, 陈燕, 赵杨, 等. 基于研磨氧化锆陶瓷的金刚石/铁磁性磨粒制备研究 [J]. 表面技术,2020,49(9):364-369.LYU Yini, CHEN Yan, ZHAO Yang, et al. Preparation of diamond/iron magnetic abrasive particles based on grinding zirconia ceramics [J]. Surface Technology,2020,49(9):364-369. [11] 丘永亮, 邱腾雄, 阎秋生. K9玻璃磁性研磨抛光表面粗糙度试验研究 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2015,35(3):57-60.QIU Yongliang, QIU Tengxiu, YAN Qiusheng. Research on surface roughness of K9 glass by magnetic abrasive finishing [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2015,35(3):57-60. [12] 耿其东, 李春燕. 磁力研磨加工K9光学玻璃的实验研究 [J]. 表面技术,2018,47(7):112-118.GENG Qidong, LI Chunyan. Experimental study on magnetic abrasive finishing K9 optical glass [J]. Surface Technology,2018,47(7):112-118. [13] WANG L Y, SUN Y L, CHEN F Y, et al. Experimental study on vibration-assisted magnetic abrasive finishing for internal blind cavity by bias external rotating magnetic pole. Precision Engineering[J]. 2022, 74: 69-79. [14] 李建军, 李文生, 成波, 等. 细长锆管表面磁力研磨高精光整参数优化研究 [J]. 稀有金属,2020,46(3):331-339.Li Jianjun, Li Wensheng, Cheng Bo, et al. Optimization parameters of high precision magnetic abrasive finishing to slender zirconium tube [J]. Chinese journal of Rare Metals,2020,46(3):331-339. [15] 康璐. 粘结法制备磁性磨粒的工艺及其性能研究[D]. 鞍山: 辽宁科技大学, 2019.KANG Lu. Study on process and properties of preparation of magnetic abrasive by bonding method[D]. Anshan: University of Science and Technology Liaoning, 2019. [16] 丁叶, 陈燕, 丁文龙, 等. 黏结法制备铁基碳化硼磁性磨粒 [J]. 表面技术,2022,51(3):151-157.DING Ye, CHEN Yan, DING Wenlong, et al. Preparation of iron based boron carbide magnetic abrasive by bonding method [J]. Surface Technology,2022,51(3):151-157. [17] LI K, MA R J, ZHANG M C, et al. Hybrid post-processing effects of magnetic abrasive finishing and heat treatment on surface integrity and mechanical properties of additively manufactured Inconel 718 superalloys [J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2022,128:10-21. [18] JUN X H, HUA Z Y. Application of magnetic abrasive finishing process using alternating magnetic field for finishing polychlorotrifluoroethylene resin[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2022, 1066: 85-90. [19] SOUZA A M, SILVA E J D, YAMAGUCHI H, et al. Magnetic field-assisted finishing processes: From bibliometric analysis to future trends[J]. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 2022, 44(8): 327. [20] 赵文渊, 李文辉, 白小云, 等. 采用粘结法的磁性磨粒制备工艺及实验研究 [J]. 中国机械工程,2019,30(5):535-541. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2019.05.005ZHAO Wenyuan, LI Wenhui, BAI Xiaoyun, et al. Preparation technology and experimental study of magnetic abrasive particles by bonding method [J]. China Mechanical Engineering,2019,30(5):535-541. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2019.05.005 [21] 黄水泉, 高尚, 黄传真, 等. 脆性材料磨粒加工的纳米尺度去除机理 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2022,42(3):257-266.HUANG Shuiquan, GAO Shang, HUANG Chuanzhen, et al. Nanoscale removal mechanism of abrasive processing of brittle materials [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2022,42(3):257-266. [22] 陈修忠. 磁性磨粒的性能指标体系分析与研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2015.CHEN Xiuzhong. Performance indicator system analysis and research of magnetic abrasive[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2015. -





 下载:
下载:







 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
