PCD tool wear in cutting SiCp/6005Al composites
-
摘要:
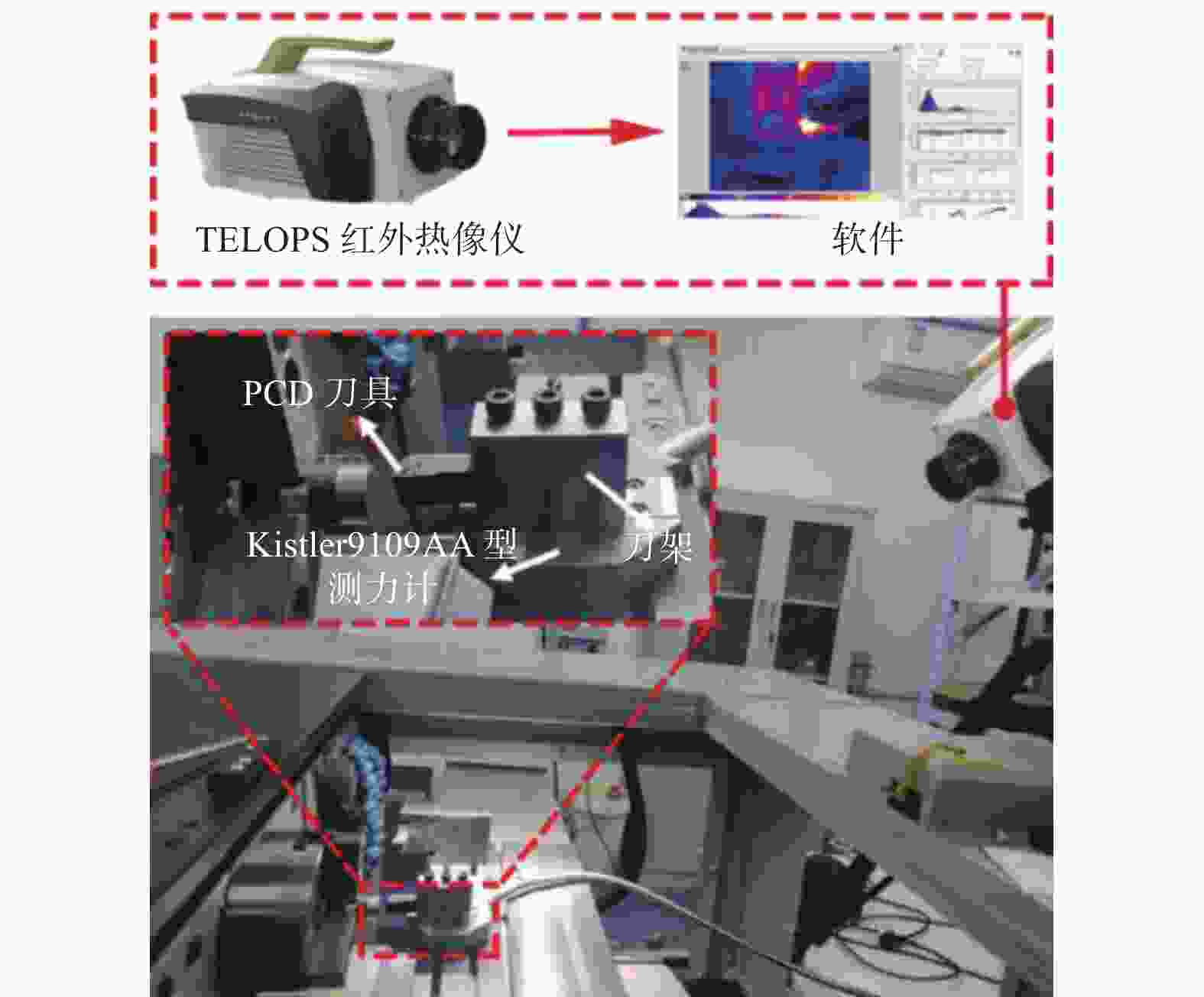
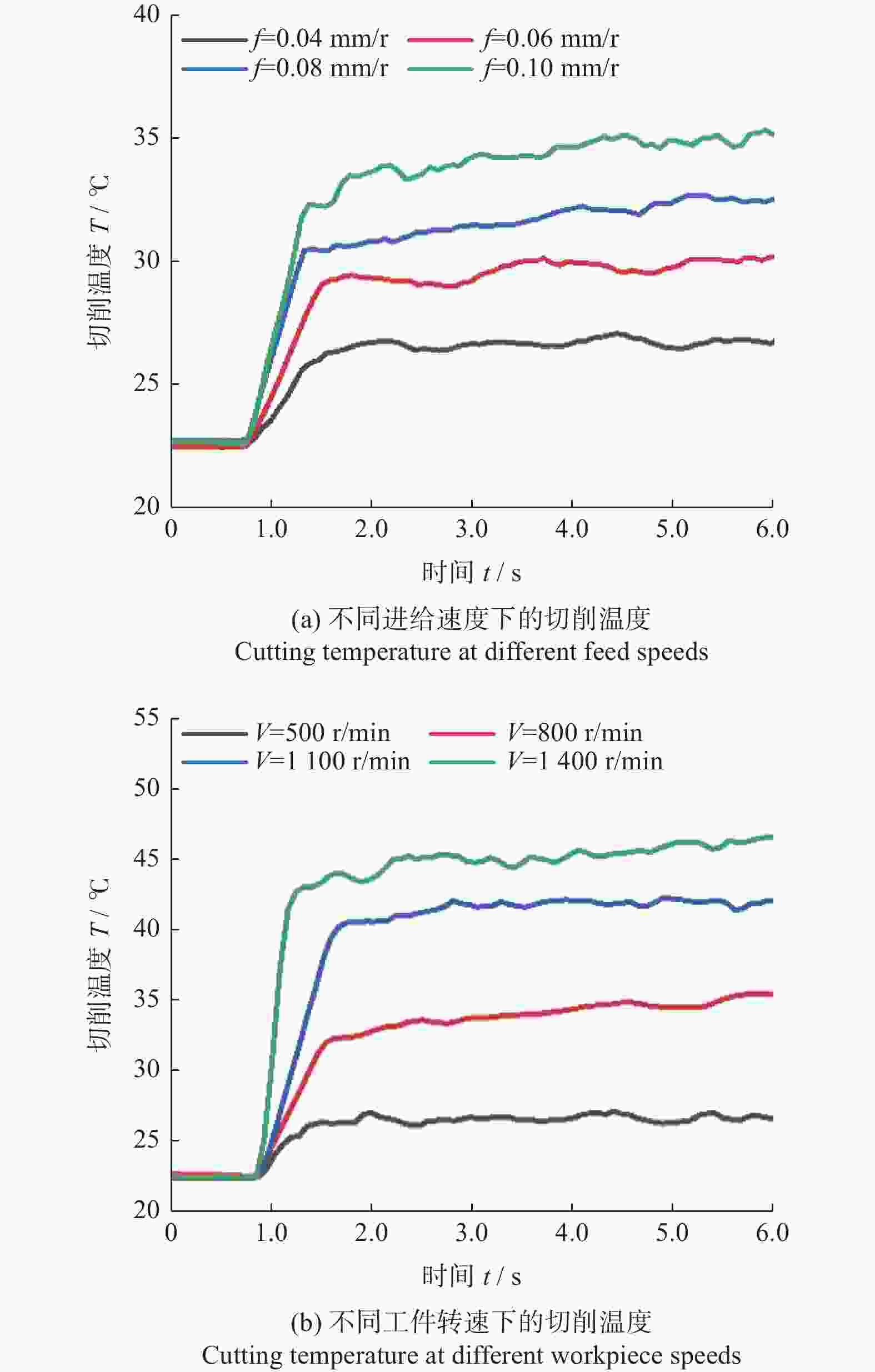
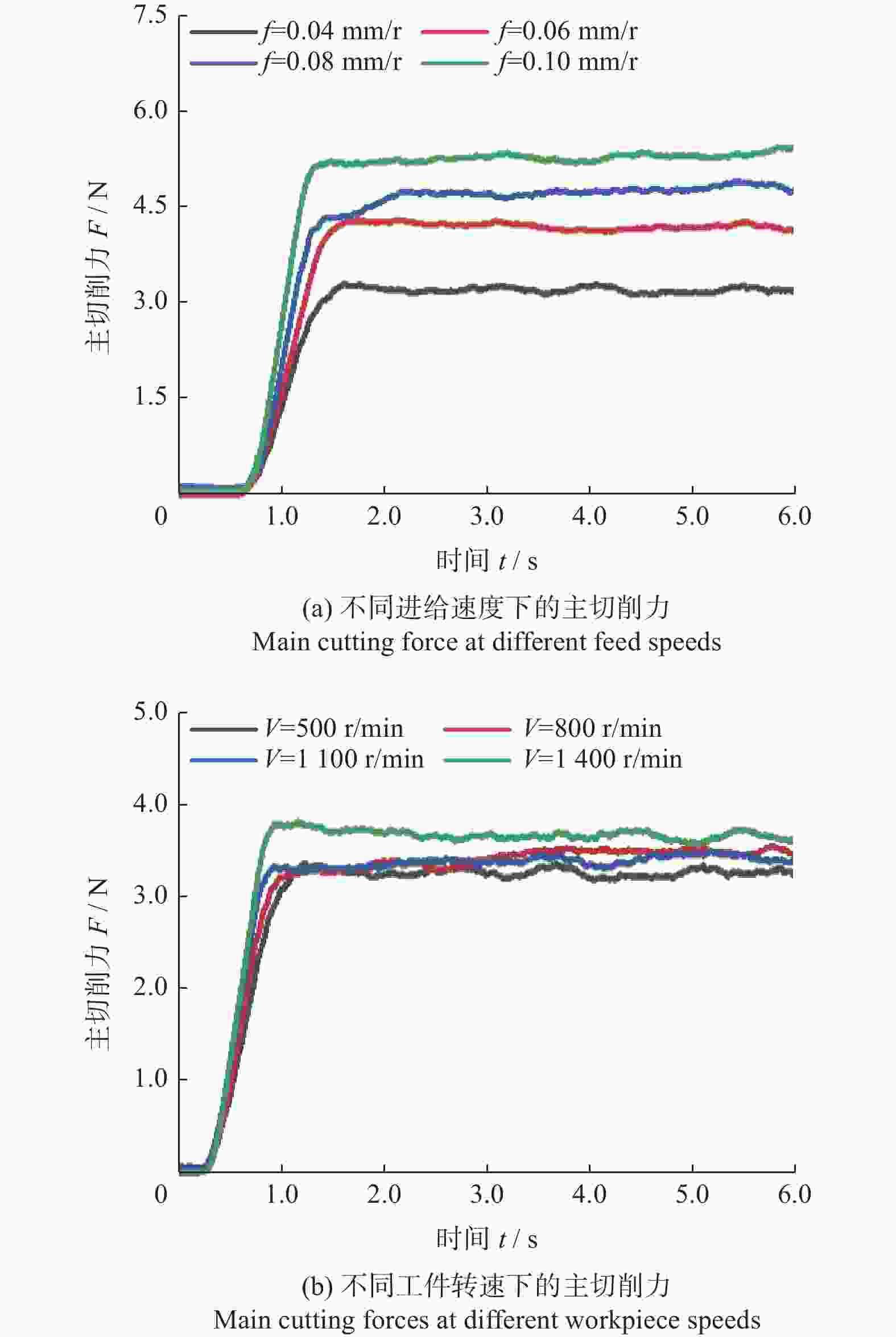
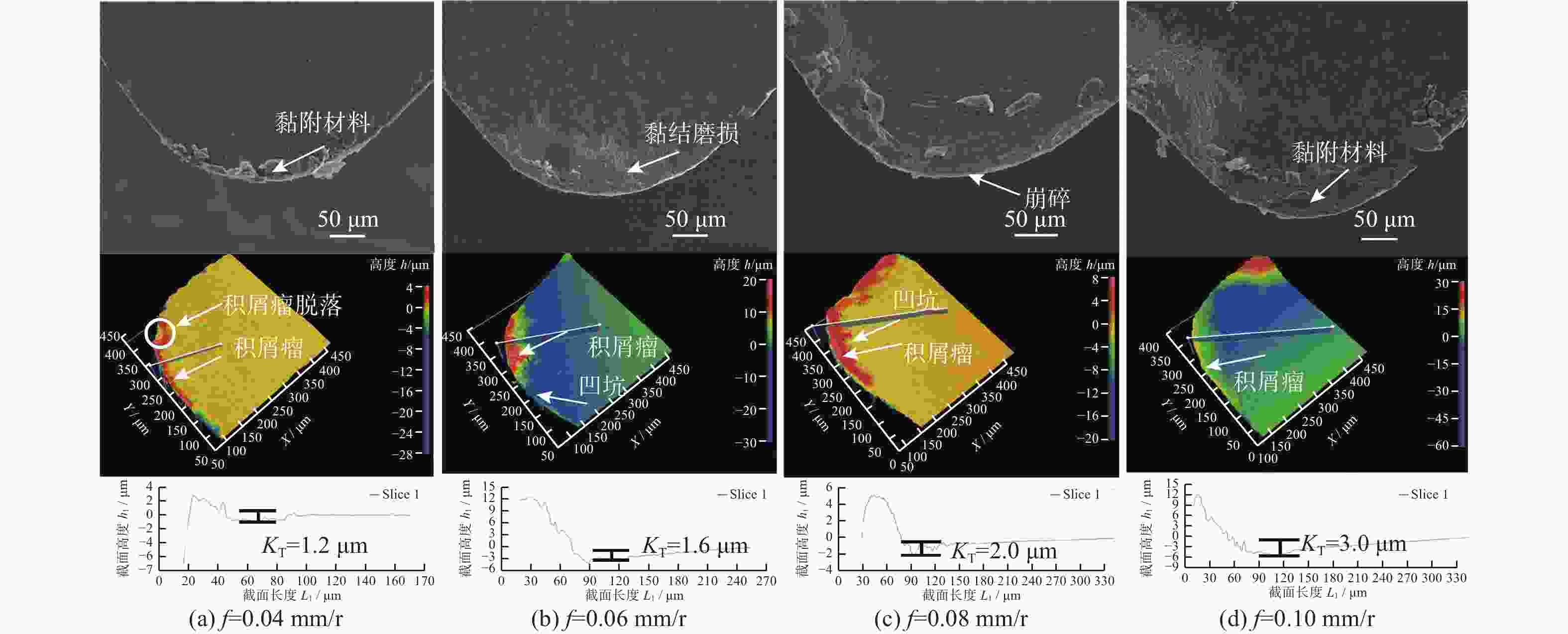
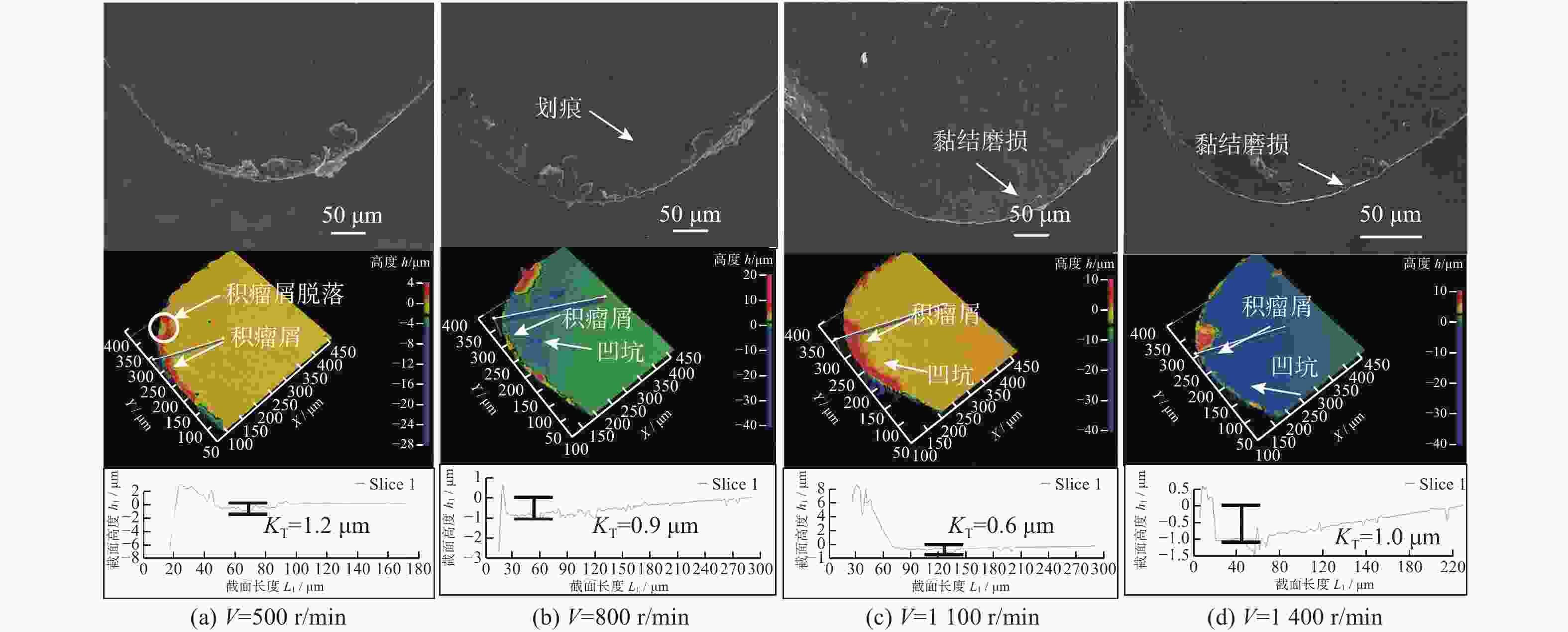
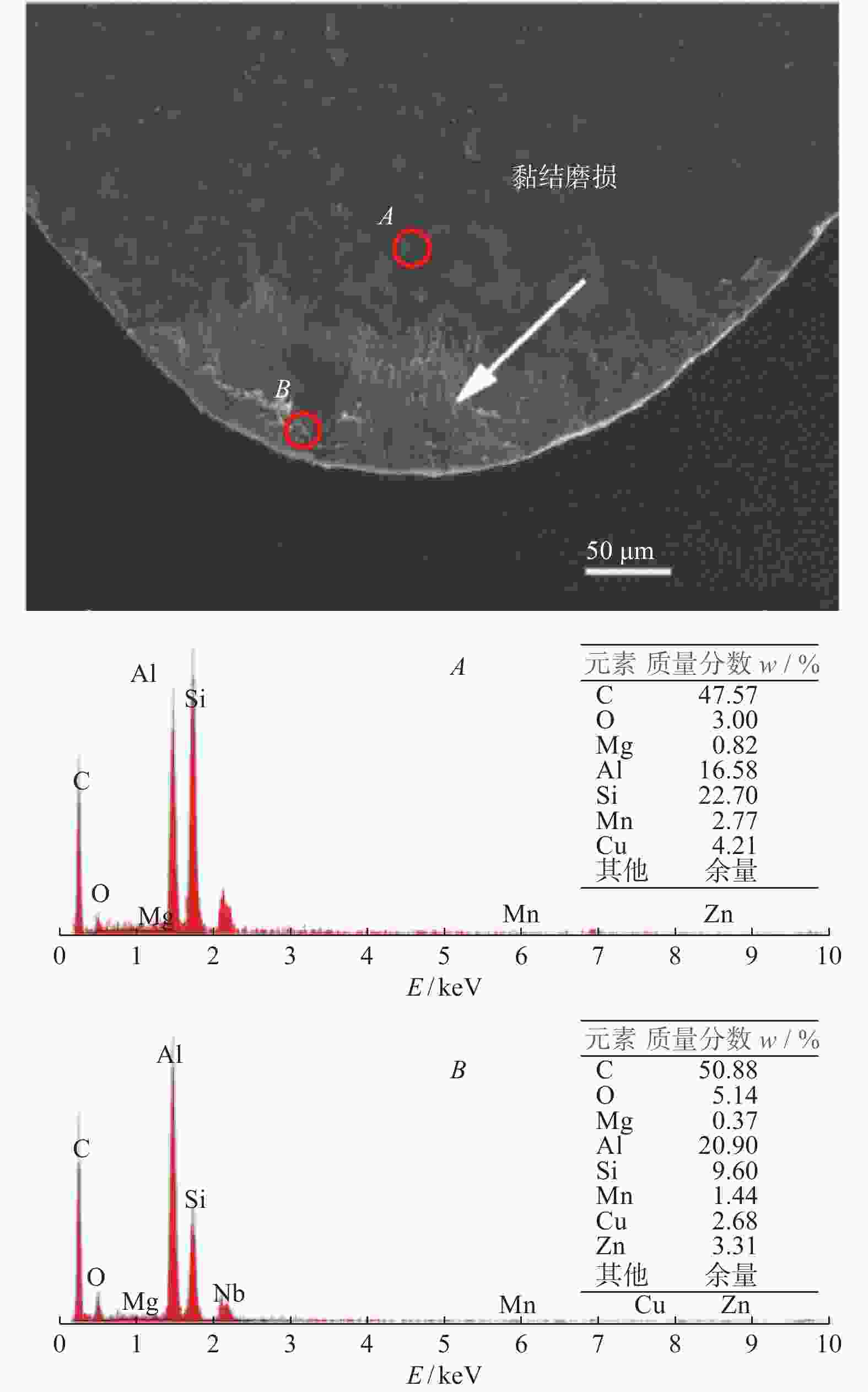
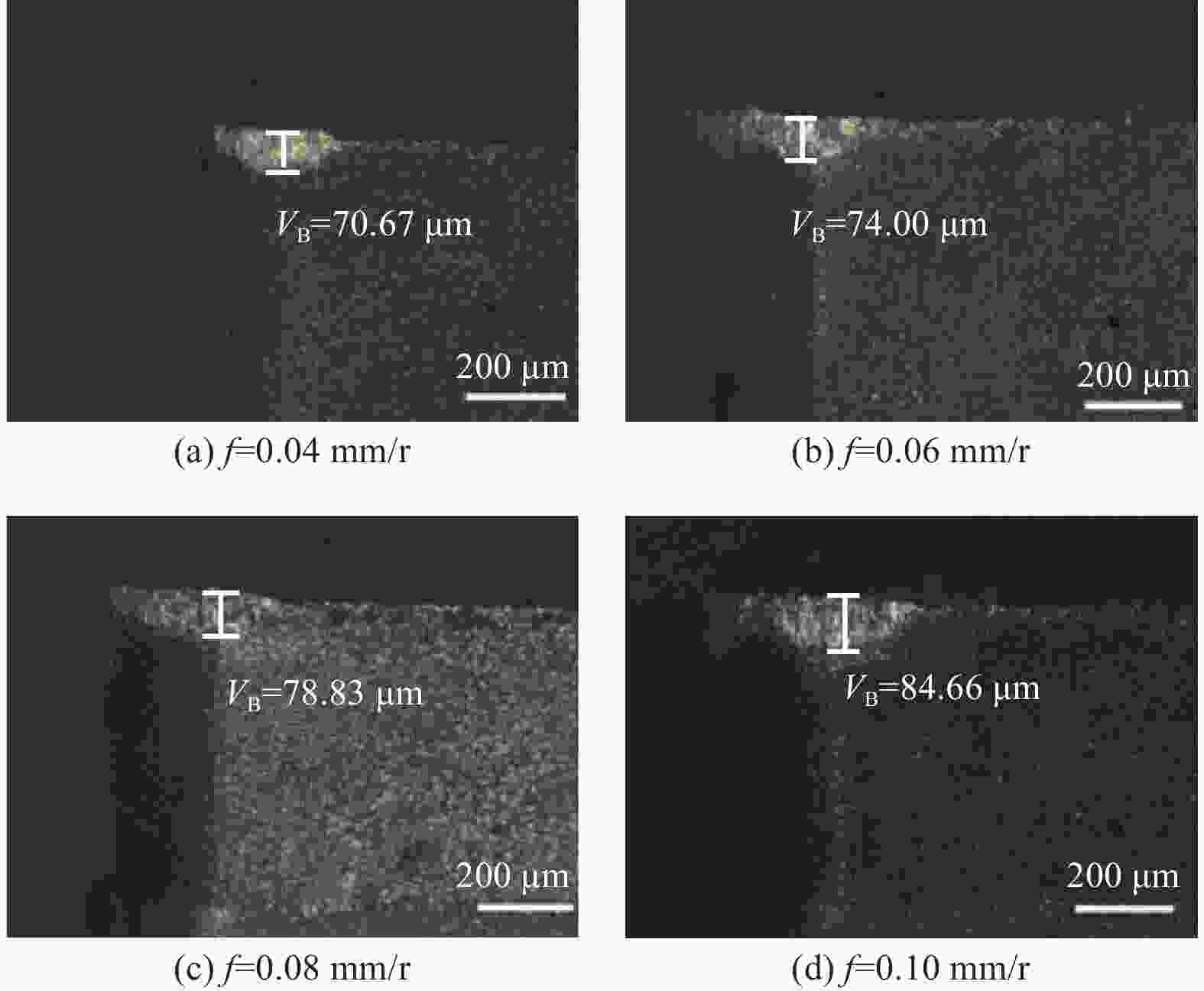
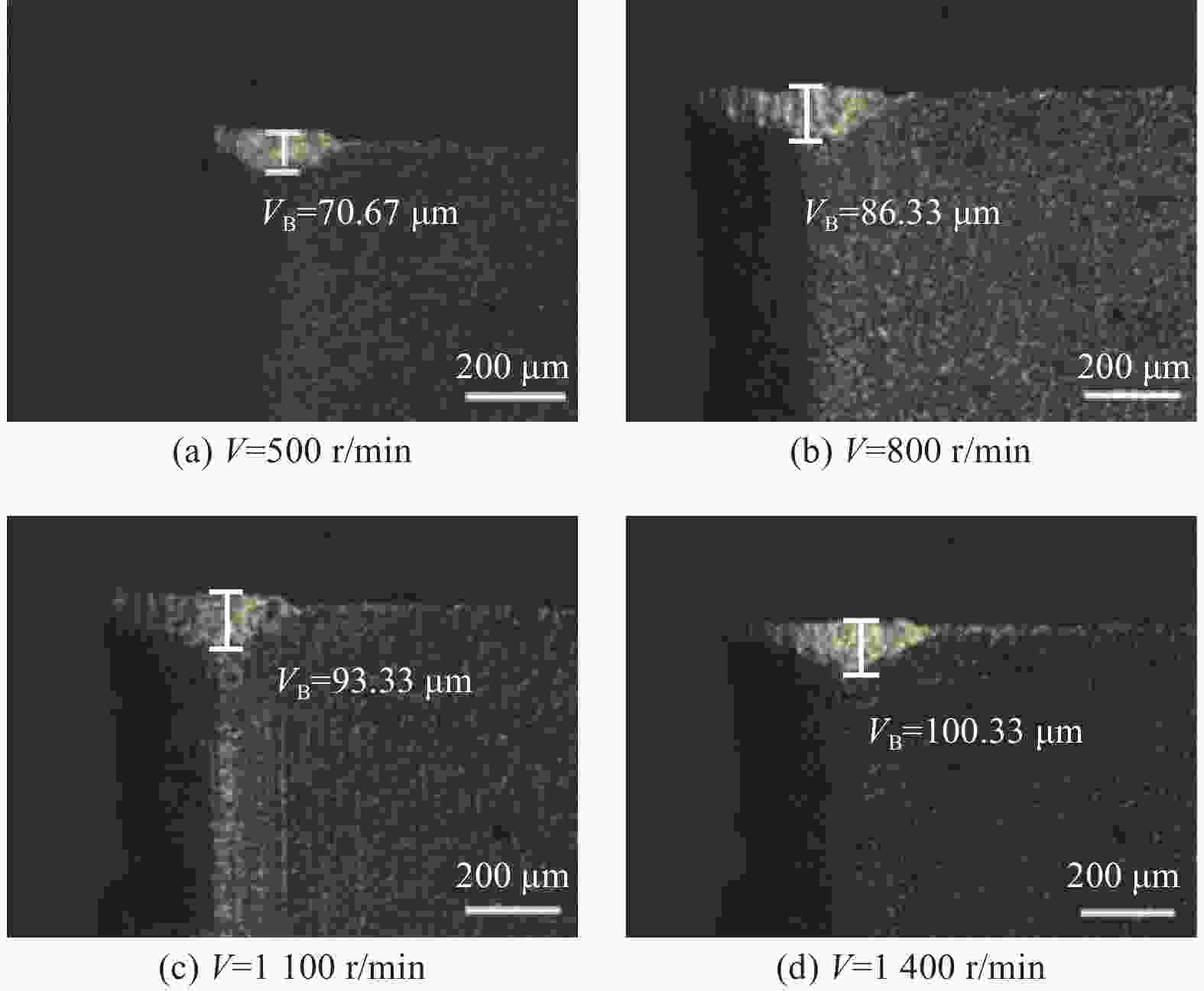
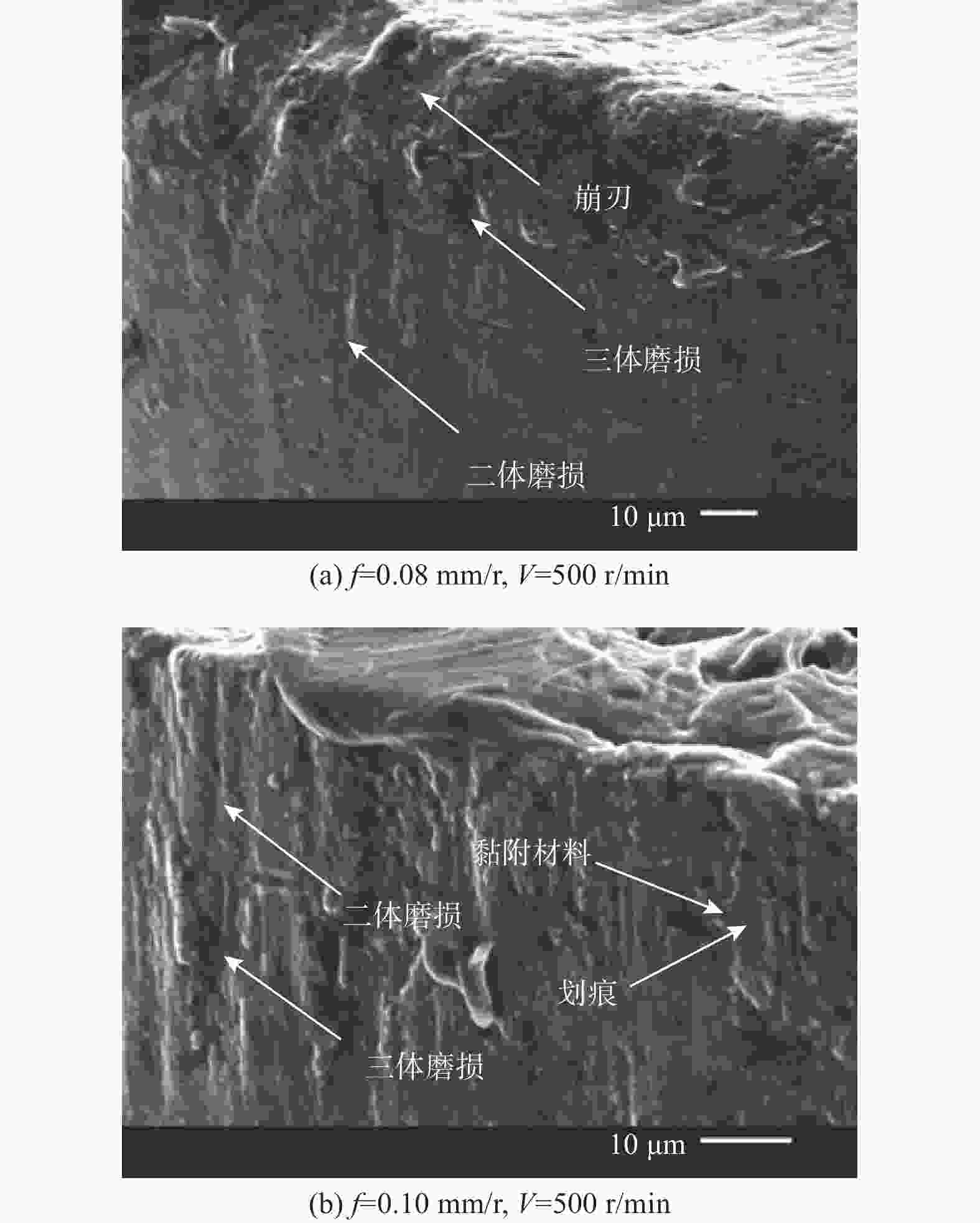
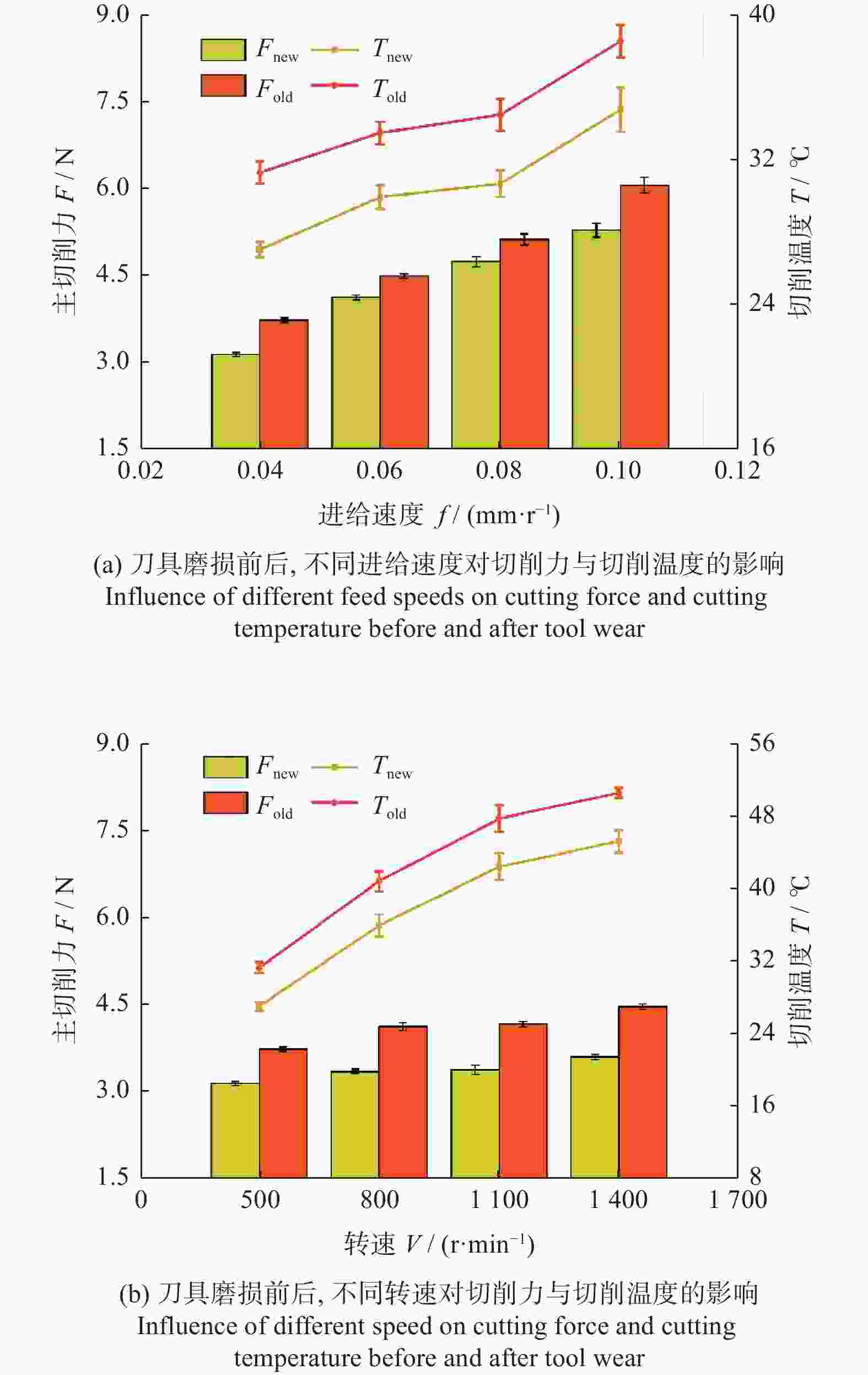
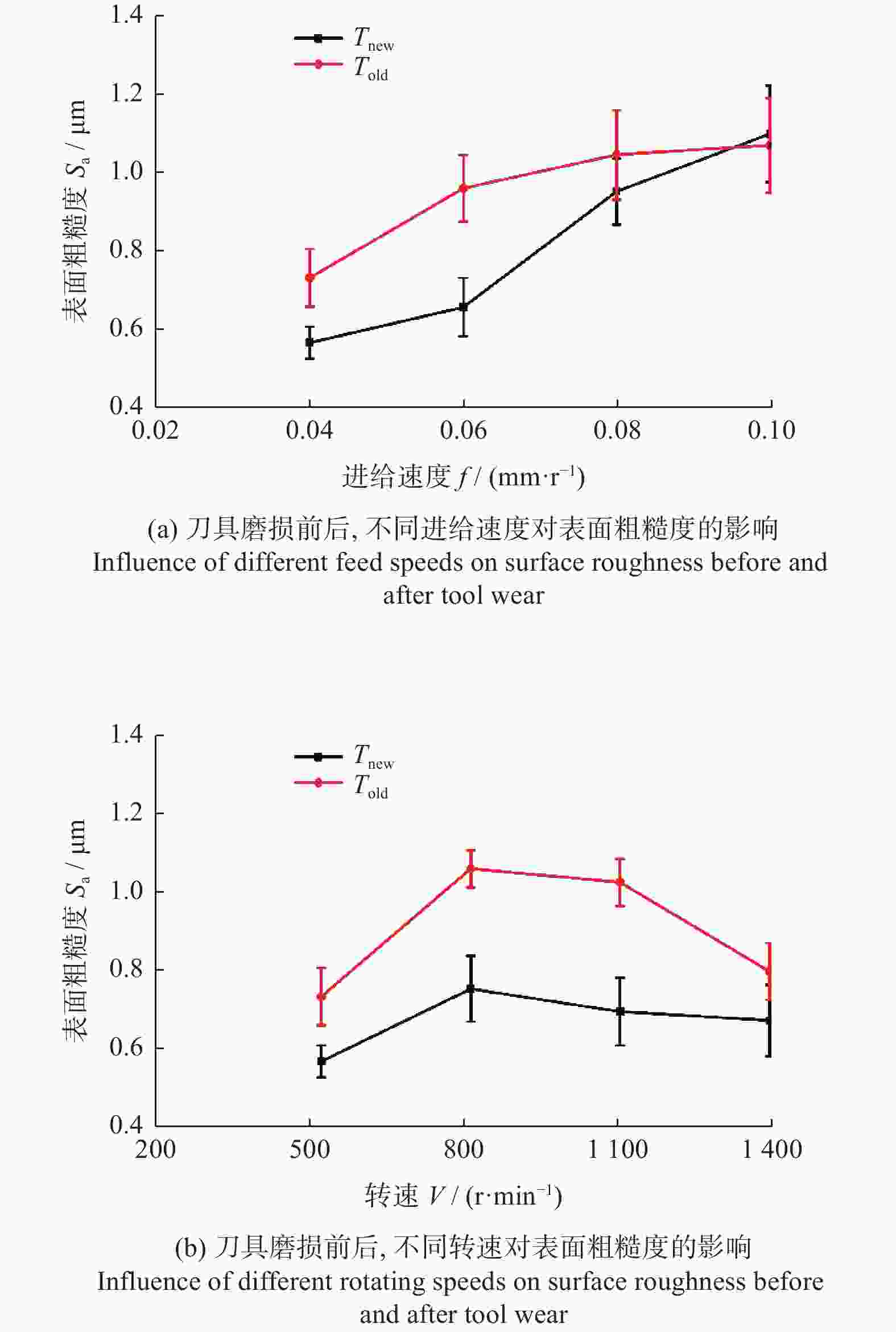
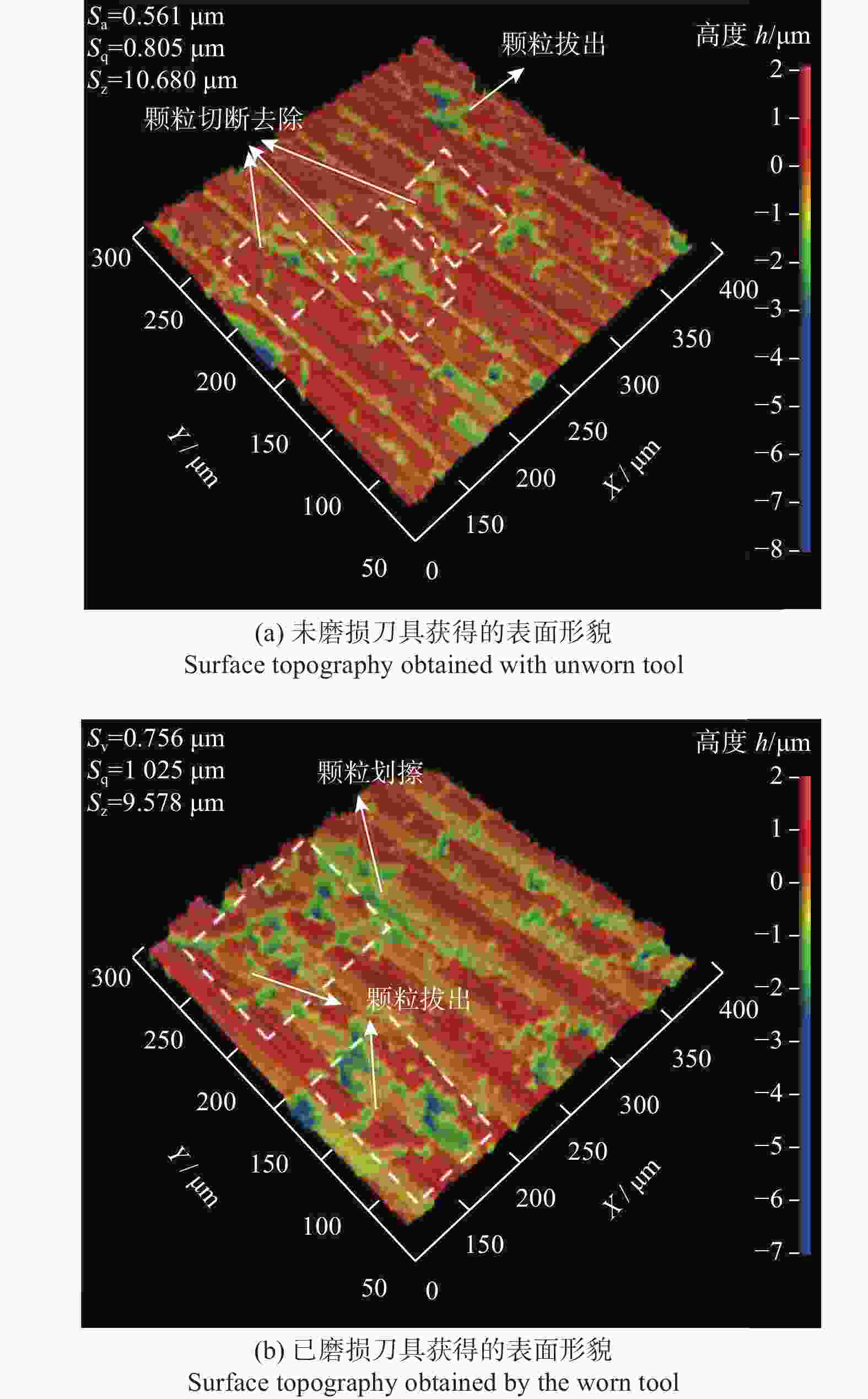
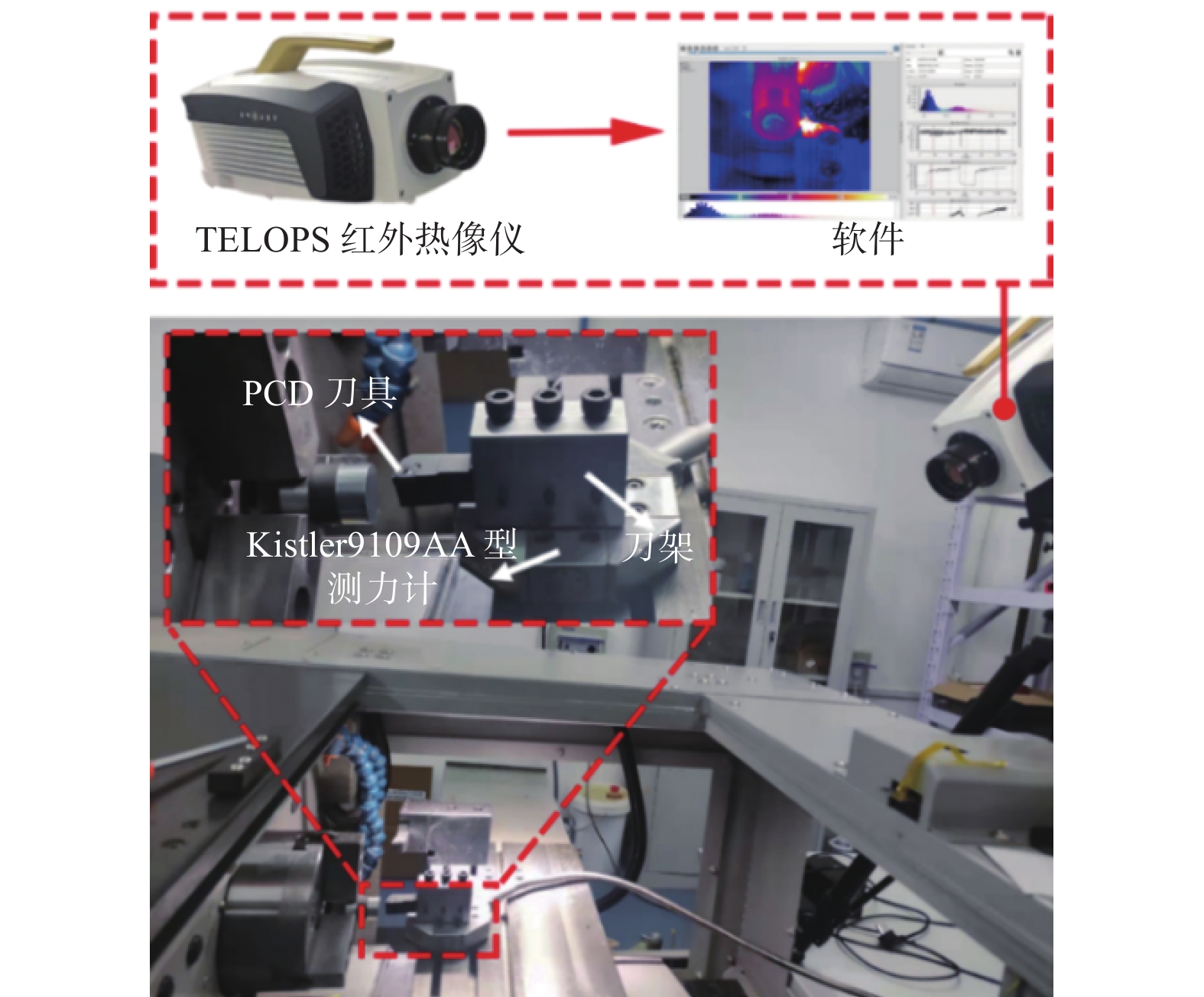
为研究SiCp/6005Al切削时的刀具磨损机制及刀具磨损对切削力、切削温度、工件表面质量的影响,进行不同转速V和不同进给速度f下的切削试验,观察每组试验刀具切削后的磨损形貌,并通过监测动态切削力和切削温度来探究刀具的磨损机制。结果表明:工件转速提高使切削温度明显升高,但对切削力的影响很小;进给速度提高使切削力明显升高,而切削温度的变化范围较小。改变进给速度带来的力载荷变化是影响前刀面磨损的主要因素,改变工件转速带来的切削温度变化是影响后刀面磨损的主要因素。此外,刀具磨损是磨粒磨损、黏结磨损的综合作用结果,且刀具磨损会对切削力、切削温度和加工表面质量产生不利影响。
-
关键词:
- 刀具磨损 /
- PCD刀具 /
- SiCp/6005Al /
- 切削温度 /
- 表面质量
Abstract:To study the tool wear mechanism of turning SiCp/6005Al and the influence of tool wear on cutting force, cutting temperature and workpiece surface quality, cutting experiments at different speeds V and different feed speeds f were carried out. Then the tool wear morphology of each group of experimental tools after cutting was observed and the tool wear mechanism was explored by monitoring the dynamic cutting force and cutting temperature. Finally, the influence of worn tools on cutting force, cutting temperature and surface quality under different process parameters was studied. The results show that the increase of workpiece speed significantly increases the cutting temperature, but it has little effect on the cutting force. However, the increase of feed speed significantly increases the cutting force and the variation range of cutting temperature is small. The change of force load caused by changing feed speed is the main factor affecting the wear of rake face. The change of cutting temperature caused by changing the workpiece speed is the main factor affecting the flank wear. In addition, tool wear is the comprehensive result of abrasive wear and bonding wear. And it will have an adverse impact on cutting force, cutting temperature and machined surface.
-
Key words:
- tool wear /
- PCD tool /
- SiCp/6005Al /
- cutting temperature /
- surface quality
-
表 1 SiCp/6005Al的力学性能
Table 1. Mechanical properties of SiCp/6005Al
材料属性 数值 密度 ρ / (g·cm−3) 2.97 弹性模量 E / GPa 202 抗弯强度 σb / MPa 362 热导率 k / (W·m−1·K−1) 214 扩散系数 α / (mm−2·s) 94.3 比热容 Cp / (J·g−1·K−1) 0.848 热膨胀系数 β / (10−6·℃−1) 6.21 表 2 6005Al合金主要化学成分
Table 2. Main chemical constituents of 6005Al alloy
元素 质量分数 ω / % 铜 0.3 锰 0.5 镁 0.4~0.7 锌 0.2 铝 余量 表 3 试验参数
Table 3. Experimental parameters
切削参数 数值 转速 V / (r·min−1) 500, 800, 1 100, 1 400 进给速度 f / (mm·r−1) 0.04, 0.06, 0.08, 0.10 切削深度 ap / mm 0.03 -
[1] ZHAI C, XU J, LI Y, et al. The study on surface integrity on laser-assisted turning of SiCp/2024Al [J]. International Journal of Optomechatronics,2020,14(1):29-43. doi: 10.1080/15599612.2020.1789251 [2] WEI C, GUO W, PRATOMO E S, et al. High speed, high power density laser-assisted machining of Al-SiC metal matrix composite with significant increase in productivity and surface quality [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2020,285:116784. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.116784 [3] ANDREWES C J E, FENG H Y, LAU W M. Machining of an aluminum/SiC composite using diamond inserts [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2000,102(1/2/3):25-29. [4] 王涛. 高体积分数SiCp/Al复合材料高速铣削基础研究 [D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2015.WANG Tao. Basic research on high speed milling of SiCp/Al composites with high volume fraction [D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2015. [5] FAN Y, HAO Z, ZHENG M, et al. Wear characteristics of cemented carbide tool in dry-machining Ti-6Al-4V [J]. Machining Science and Technology,2016,20(2):249-261. doi: 10.1080/10910344.2016.1165837 [6] PERSSON H, LENRICK F, FRANCA L, et al. Wear mechanisms of PcBN tools when machining AISI 316L [J]. Ceramics International,2021,47(22):31894-31906. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.08.075 [7] SARIKAYA M, GUPTA M K, TOMAZ I, et al. A state-of-the-art review on tool wear and surface integrity characteristics in machining of superalloys [J]. CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology,2021,35:624-658. doi: 10.1016/j.cirpj.2021.08.005 [8] 孔宪俊. 45%SiCp/Al复合材料激光加热辅助车削性能研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017.KONG Xianjun. Research on laser heating assisted turning performance of 45%SiCp/Al composites [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017. [9] 徐丽娜. 加工SiCp/Al复合材料的金刚石刀具的研制及其磨损机理研究 [D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2019.XU Lina. Development and wear mechanism of diamond tool for machining SiCp/Al composites [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2019. [10] 刘汉中. SiCp/2024Al复合材料的精密车削工艺与刀具磨损研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017.LIU Hanzhong. Research on precision turning process and tool wear of SiCp/2024Al composites [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017. [11] GUO J, ZHANG J G, PAN Y N, et al. A critical review on the chemical wear and wear suppression of diamond tools in diamond cutting of ferrous metals [J]. International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing,2020,2(1):1-4. doi: 10.1088/2631-7990/ab5d8f [12] ZHOU Y, GU Y, LIN J, et al. Feasibility study of single-crystal silicon ductile-regime turning via fast tool servo [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2022,16:1478-1493. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.12.095 [13] MUTHUKRISHNAN N, MURUGAN M, RAO K P. Machinability issues in turning of Al-SiC (10p) metal matrix composites [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2008,39(3):211-218. [14] 段春争, 冯占, 孙伟, 等. 不同铝基体SiCp/Al复合材料切削力与刀具的磨损研究 [J]. 工具技术,2018,52(1):40-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2018.01.009DUAN Chunzheng, FENG Zhan, SUN Wei, et al. Research on cutting force and tool wear of SiCp/Al composites with different aluminum matrix [J]. Tool Engineering,2018,52(1):40-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2018.01.009 [15] BUSHLYA V, LENRICK F, GUTNICHENKO O, et al. Performance and wear mechanisms of novel superhard diamond and boron nitride based tools in machining Al-SiCp metal matrix composite [J]. Wear,2017,376:152-164. [16] EL-GALLAB M, SKLAD M. Machining of Al/SiC particulate metal matrix composites part 3: comprehensive tool wear models [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2000,101(1/2/3):10-20. [17] DING X, LIEW W Y H, LIU X D. Evaluation of machining performance of MMC with PCBN and PCD tools [J]. Wear,2005,259(7/8/9/10/11/12):1225-1234. [18] DUAN C, SUN W, FU C, et al. Modeling and simulation of tool-chip interface friction in cutting Al/SiCp composites based on a three-phase friction model [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2018,142:384-396. [19] 段春争, 车明帆, 孙伟, 等. 不同冷却润滑方式对切削SiCp/Al复合材料刀具磨损的影响 [J]. 复合材料学报,2019,36(5):1244-1253.DUAN Chunzheng, CHE Mingfan, SUN Wei, et al. Effect of different cooling and lubrication modes on tool wear of SiCp/Al composites [J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2019,36(5):1244-1253. [20] CHAMBERS A R. The machinability of light alloy MMCs [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,1996,27(2):143-147. doi: 10.1016/1359-835X(95)00001-I [21] MANNA A, BHATTACHARAYYA B. A study on machinability of Al/SiC-MMC [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2003,140(1/2/3):711-716. [22] KONG X, WANG J, WANG M, et al. Mechanisms involved in the tool life improvement of laser assisted machining 45% SiCp/Al composites [J]. Optics & Laser Technology,2021,139:106919. [23] JI J, HUANG Y, LEE K M. Cutting tool temperature field reconstruction using hybrid macro/micro scale modeling for machining of titanium alloy [C]. Canada: IEEE, 2016. [24] ZHAO J, LIU Z, WANG B, et al. Tool coating effects on cutting temperature during metal cutting processes: Comprehensive review and future research directions [J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing,2021,150:107302. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2020.107302 [25] 左俊彦, 林有希, 何明. 基于粘着特性的刀具磨损机理研究 [J]. 表面技术,2019,48(7):364-370.ZUO Junyan, LIN Youxi, HE Ming. Based on adhesive characteristics of tool wear mechanism study [J]. Journal of Surface Technology,2019,48(7):364-370. [26] WANG Q, JIN Z, ZHAO Y, et al. A comparative study on tool life and wear of uncoated and coated cutting tools in turning of tungsten heavy alloys [J]. Wear,2021,482:203929. [27] RASHID R A R, PALANISAMY S, SUN S, et al. Tool wear mechanisms involved in crater formation on uncoated carbide tool when machining Ti6Al4V alloy [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2016,83(9/10/11/12):1457-1465. -




 下载:
下载:




 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
