Interference analysis and ultra-precision grinding technology of hemispherical resonator curved surface machining
-
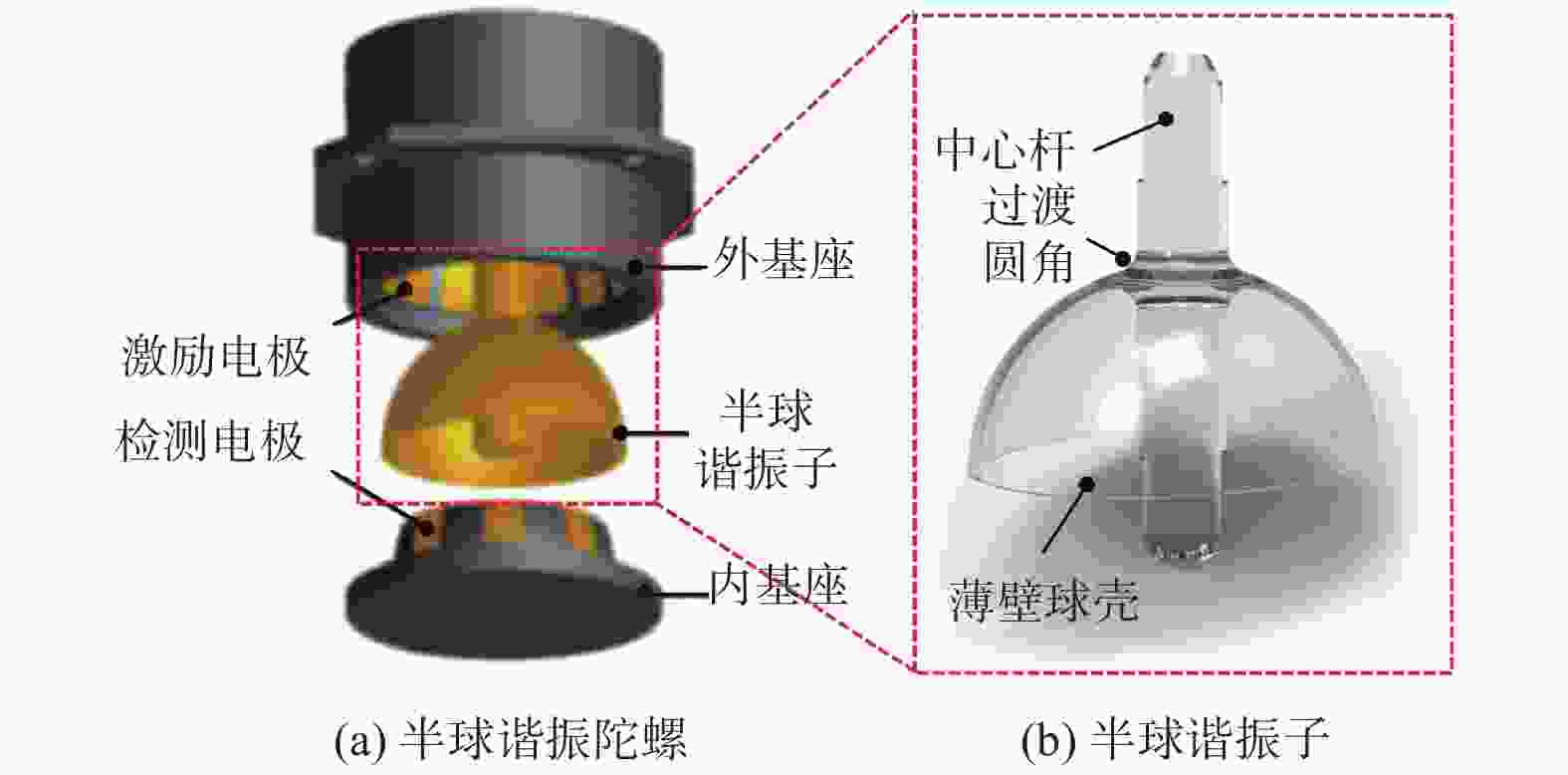
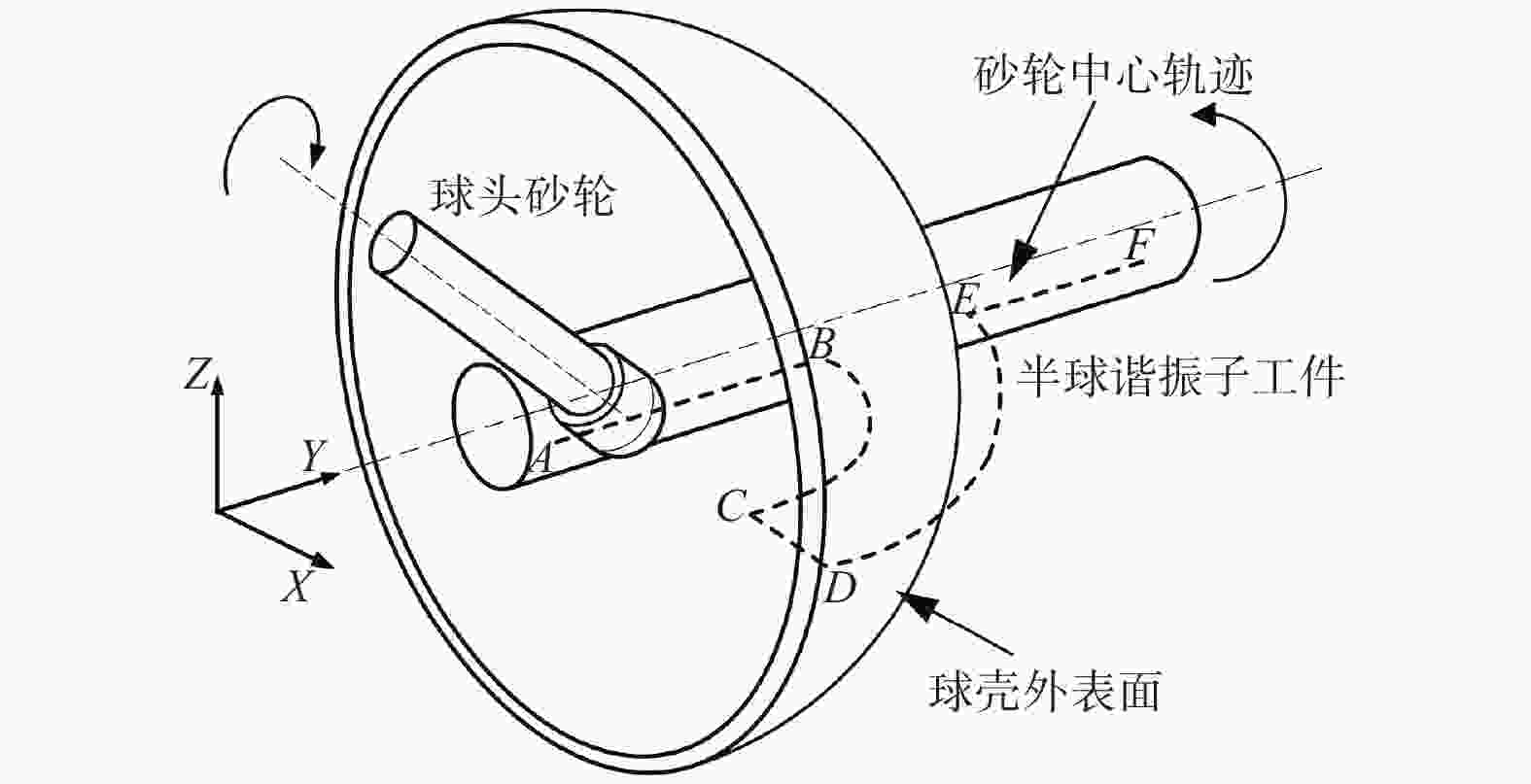
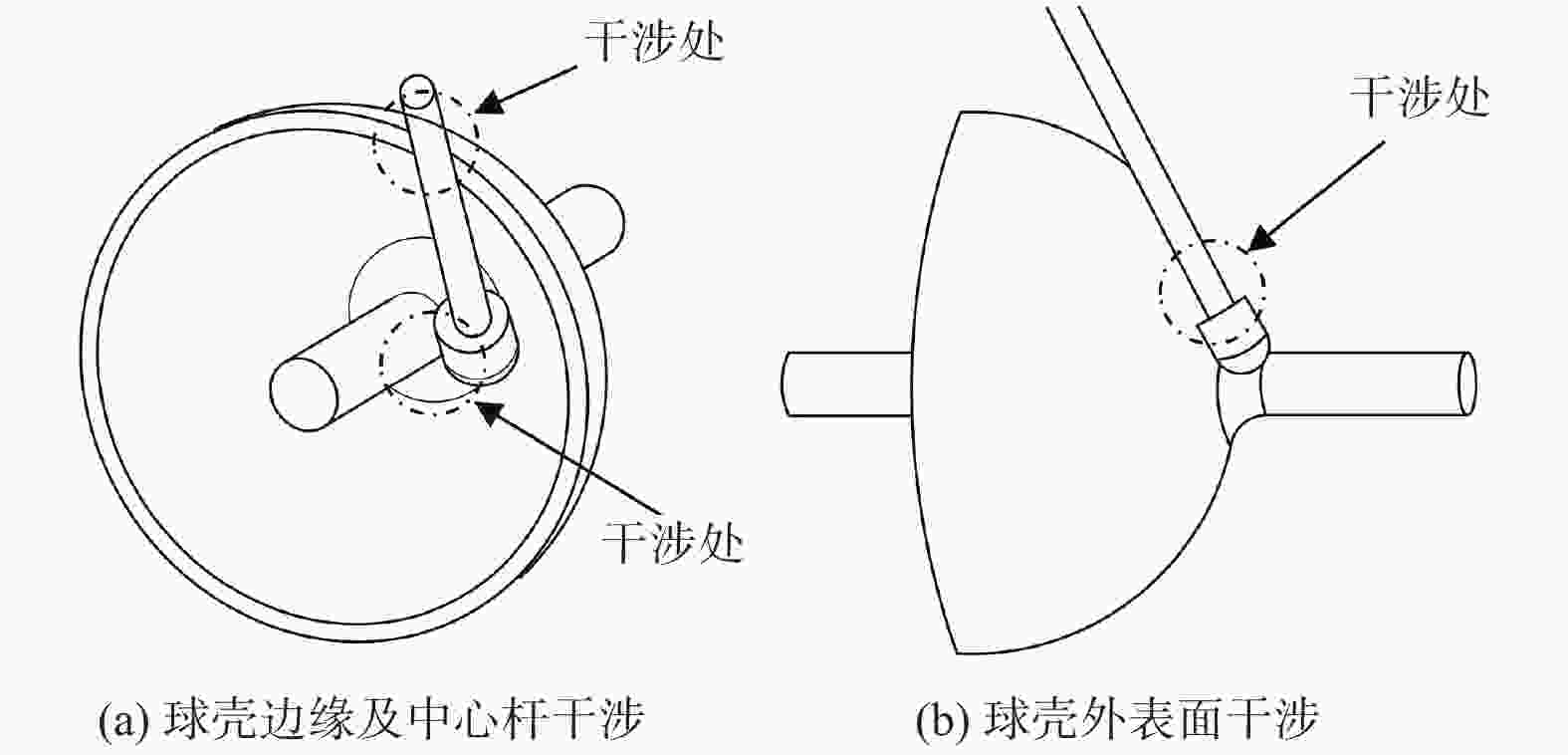
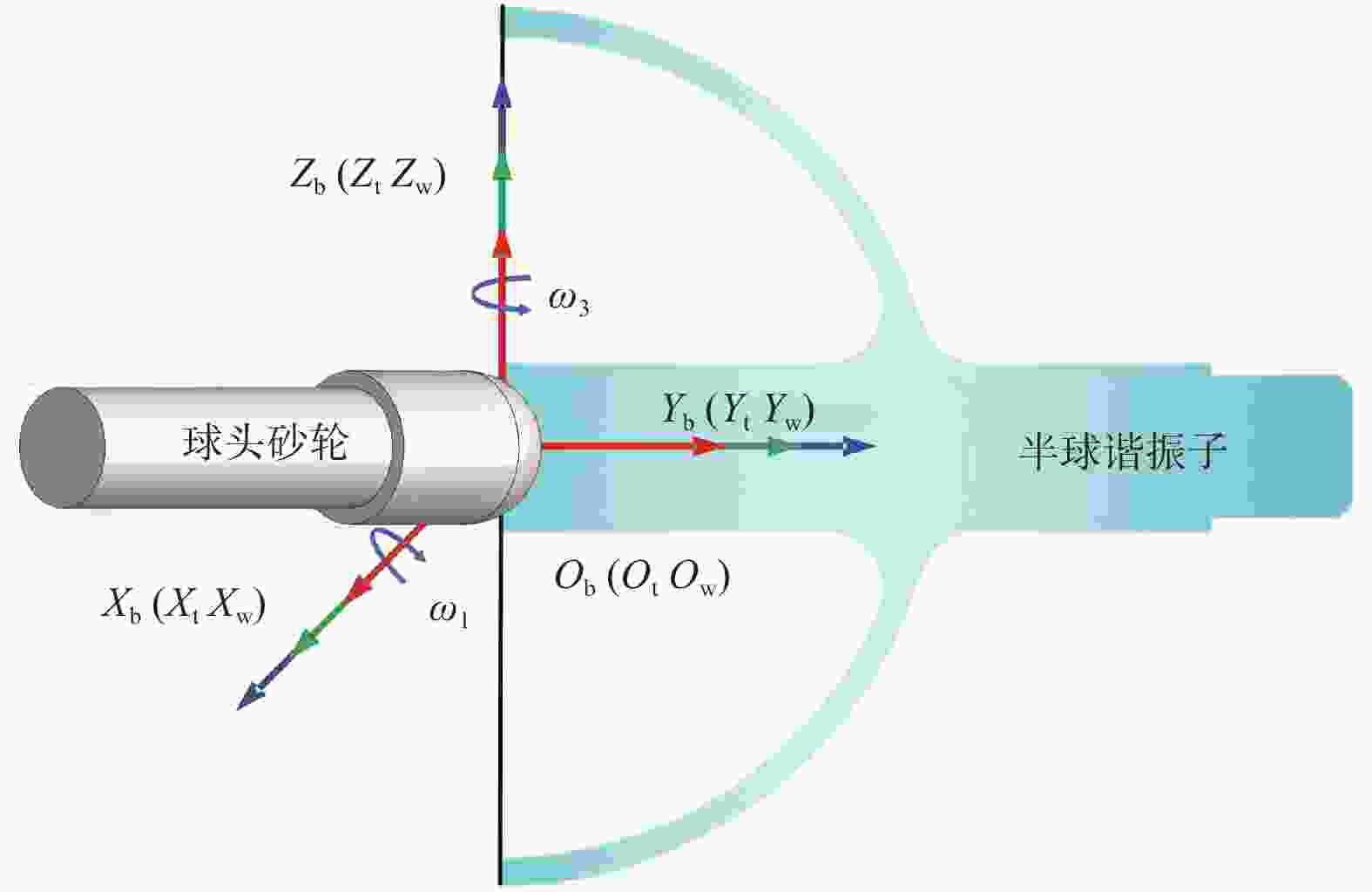
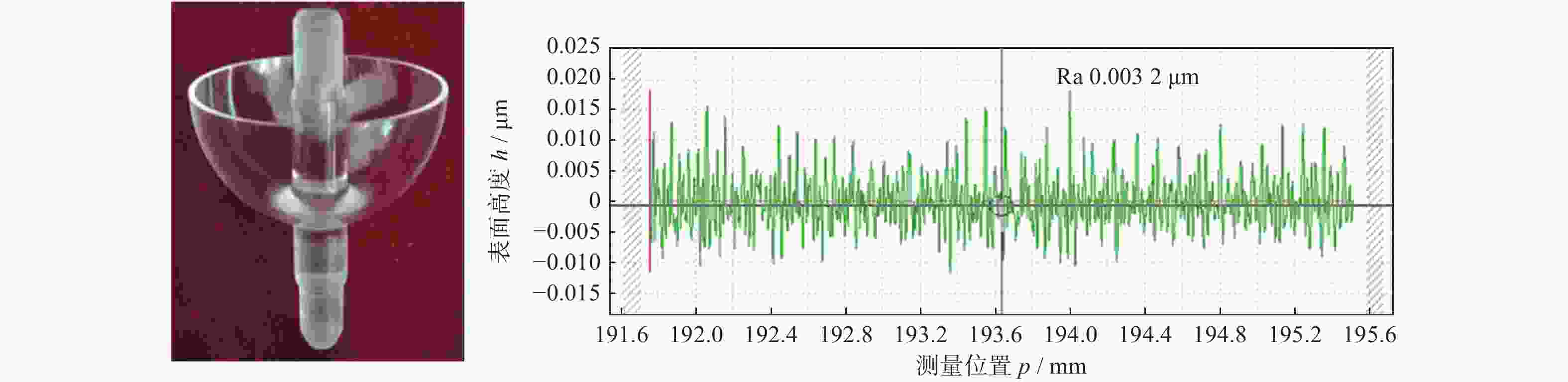
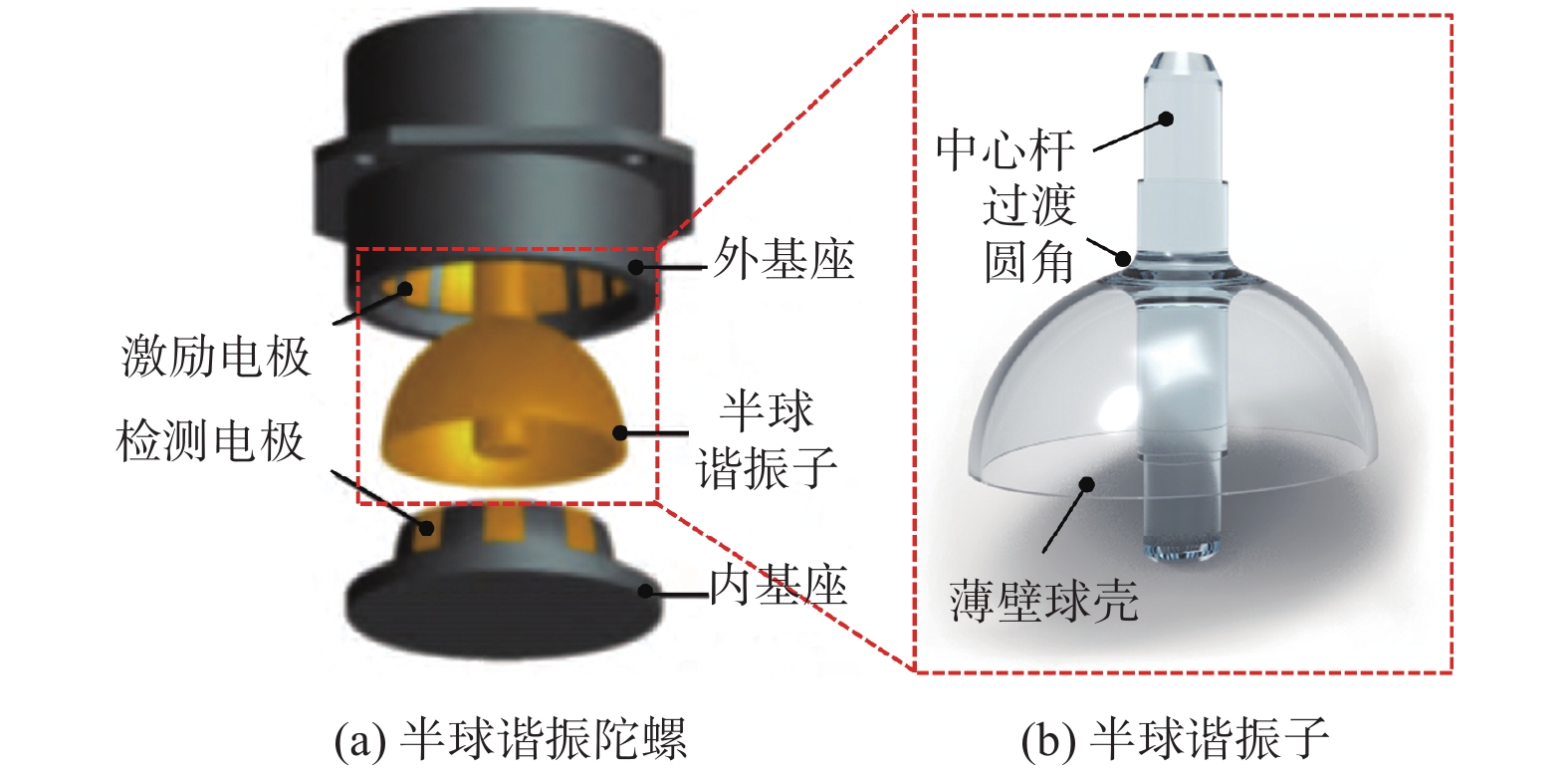
摘要: 半球谐振子作为半球谐振陀螺的核心部件,其加工精度和表面质量直接影响半球谐振陀螺的工作精度和使用寿命。为解决半球谐振子加工难题,提高半球谐振陀螺的性能,从半球谐振子的结构特征出发,对谐振子加工过程中的干涉进行理论分析;再根据球头砂轮磨削区域分布的特点进行磨削轨迹规划,确定谐振子不同磨削阶段球头砂轮的最佳转角;最后在自研的半球谐振子超精密磨削机床上进行加工实验。超精密磨削后的谐振子表面粗糙度(Ra值)由0.6158 μm提升至0.0402 μm,面形精度(PV值)由4.5904 μm提升至0.3390 μm;经磁流变抛光后谐振子表面粗糙度(Ra值)进一步提高至0.0032 μm。研究表明:采用轨迹规划后的磨削工艺可避免砂轮与工件间的干涉,并加工出高质量的半球谐振子零件。Abstract: As the core device of the hemispherical resonator gyroscope (HRG), the processing accuracy and the surface quality of hemispherical resonator directly affect the working accuracy and the service life of HRG. To solve the problem of hemispherical resonator processing and improve the performance of HRG, the interference in the processing of hemispherical resonator is analyzed theoretically according to the structural characteristics of the hemispherical resonator. Then, the grinding trajectory is planned by using the characteristics of the grinding area distribution of the ball-end grinding wheel, and the optimal turning angle of the ball-end grinding wheel during different grinding processing sections of the hemispherical resonator is determined. Finally, grinding experiments of hemispherical resonator are conducted on the developed hemispherical resonator ultra-precision grinding machine tool. The surface roughness (Ra value) of hemispherical resonator is improved from 0.615 8 μm to 0.040 2 μm after ultra-precision grinding processing, while the profile accuracy (PV value) is improved from 4.590 4 μm to 0.339 0 μm. The surface roughness Ra of the hemispherical resonator is further improved to 0.003 2 μm after magnetorheological polishing. The research shows that the grinding process after trajectory planning can avoid the interference between the grinding wheel rod and the workpiece. High-quality hemispherical resonator component is produced by using the above grinding process.
-
表 1 某型号半球谐振子结构参数
Table 1. Structural parameters of certain type of hemispherical resonator
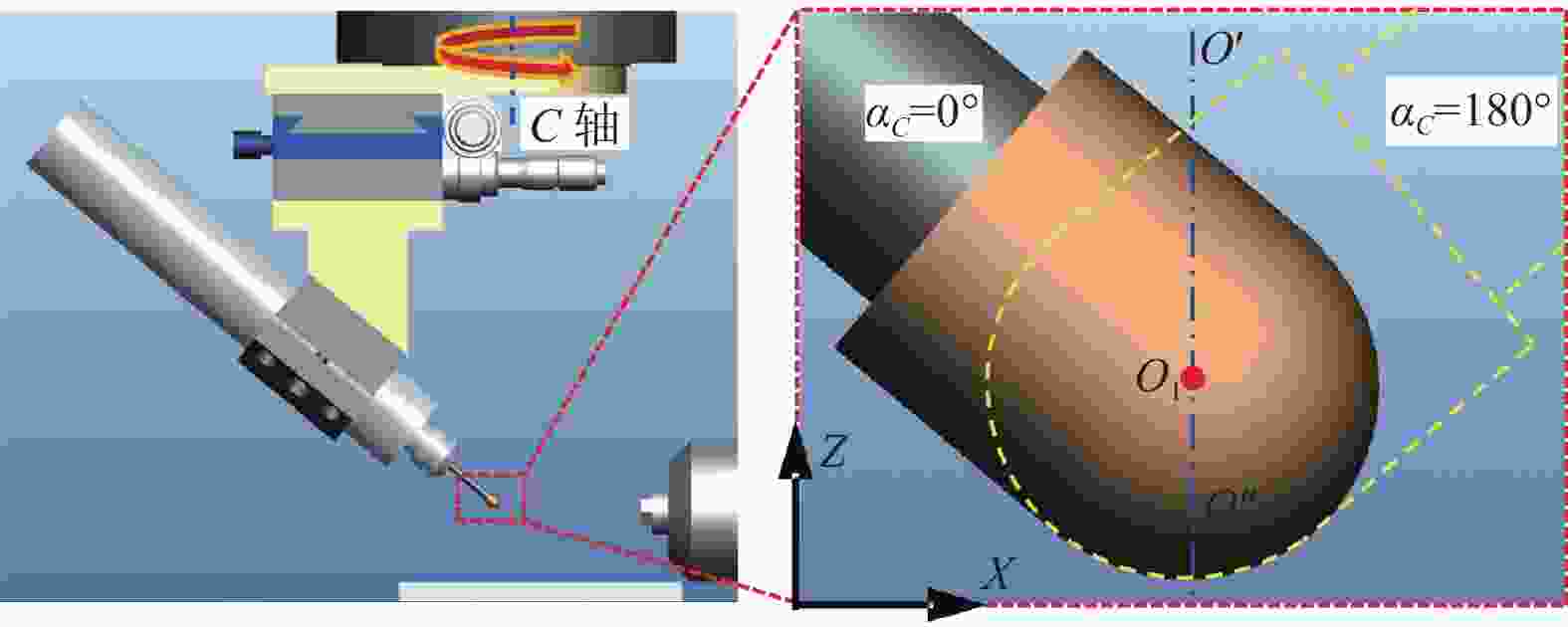
尺寸参数 数值 半球壳外表面半径 rs / mm 15 半球壳壁厚 t / mm 0.8 中心杆直径 d / mm 7 外圆角半径 roa / mm 2 内圆角半径 ria / mm 2 表 2 不同磨削阶段的C轴转角范围
Table 2. C-axis rotation angle range in different grinding sections
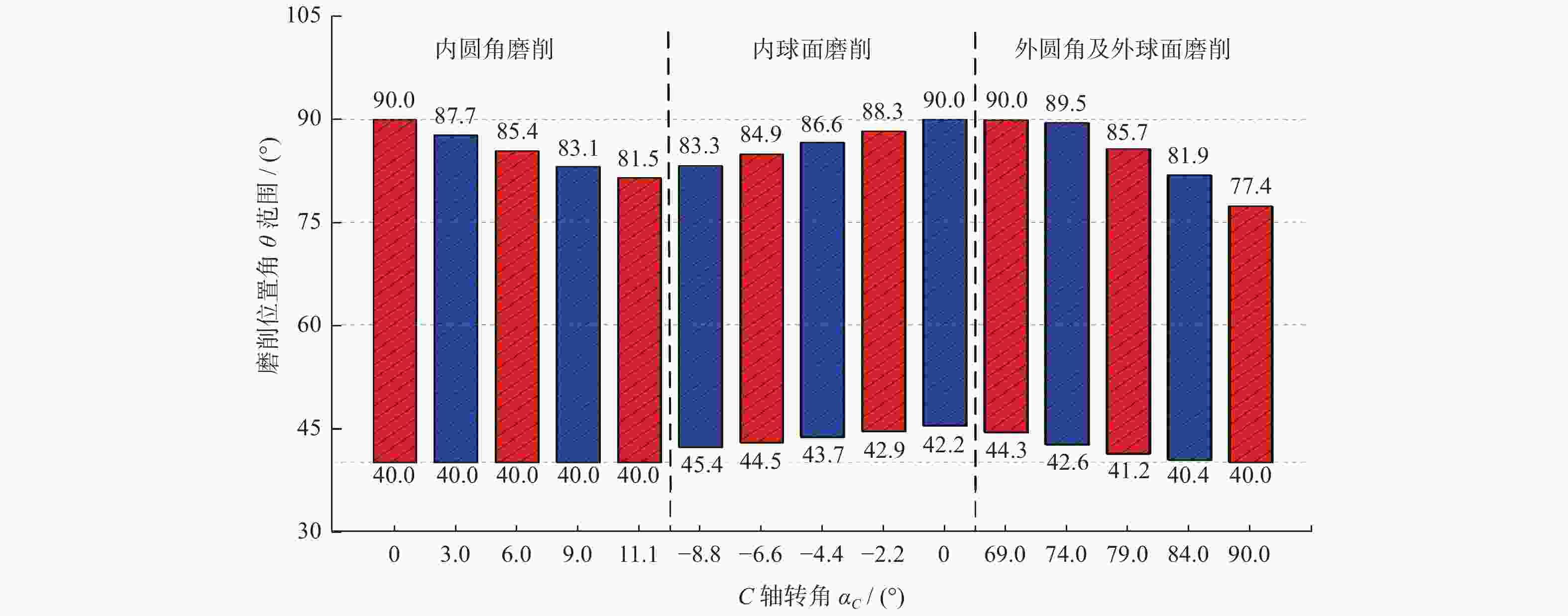
磨削阶段 C轴转角 αC / (°) 内圆杆和内圆角 0.0~11.1 内球面 −8.8~0 外球面、外圆角和外圆杆 66.8~90.0 表 3 不同磨削阶段对应的C轴转角
Table 3. C-axis rotation angles in different grinding sections
磨削阶段 C轴转角 αC / (°) 内圆杆和内圆角 5 内球面 −4 外球面、外圆角和外圆杆 70 表 4 半球谐振子超精密磨削加工参数
Table 4. Ultra-precision grinding processing parameters of hemispherical resonator
磨削参数 数值 进给速度 vf / (μm·s−1) 15 砂轮主轴转速 ωg / (m·s−1) 71 000 工件主轴转速 ωw / (m·s−1) 30 磨削深度 ap / μm 1 砂轮磨粒直径 rp / μm 3 -
[1] ZHANG S J, ZHOU Y P, ZHANG H J, et al. Advances in ultra-precision machining of micro-structured functional surfaces and their typical applications [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture,2019,142:16-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2019.04.009 [2] ZHU L L, LI Z X, FANG F Z, et al. Review on fast tool servo machining of optical freeform surfaces [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2018,95:2071-2092. doi: 10.1007/s00170-017-1271-4 [3] 薛连莉, 翟峻仪, 葛悦涛. 2020年国外惯性技术发展与回顾 [J]. 导航定位与授时,2021,3(3):59-67. doi: 10.19306/j.cnki.2095-8110.2021.03.008XUE Lianli, ZHAI Junyi, GE Yuetao. Development and review of foreign inertial technology in 2020 [J]. Navigation Positioning and Timing,2021,3(3):59-67. doi: 10.19306/j.cnki.2095-8110.2021.03.008 [4] 陈明君, 王廷章, 刘赫男, 等. 高精度小型陀螺仪关键器件加工技术研究进展 [J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报,2020,52(6):218-226.CHEN Mingjun, WANG Tingzhang, LIU Henan, et al. Research process on fabrication techniques for high precision micro gyroscope key component [J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology,2020,52(6):218-226. [5] 彭凯, 方针, 徐思宇, 等. 熔融石英半球谐振子精密磨削工艺研究 [J]. 压电与声光,2021,43(2):294-298.PENG Kai, FANG Zhen, XU Siyu, et al. Research on precision grinding process of fused silica hemispherical resonator [J]. Piezoelectrics and Acoustooptics,2021,43(2):294-298. [6] 徐志强, 刘建梅, 王振, 等. 石英半球谐振子精密加工技术探讨 [J]. 导航与控制,2019,18(2):69-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5558.2019.02.011XU Zhiqiang, LIU Jianmei, WANG Zhen, et al. Discussion on precision machining technology of quartz hemispherical harmonic oscillator [J]. Navigation and Control,2019,18(2):69-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5558.2019.02.011 [7] CHEN M J, LI Z A, YU B, et al. On-machine precision preparation and dressing of ball-headed diamond wheel for the grinding of fused silica [J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2013,26(5):982-987. doi: 10.3901/CJME.2013.05.982 [8] LIU H N, CHEN M J, YU B, et al. Configuration design and accuracy analysis of a novel magnetorheological finishing machine tool for concave surfaces with small radius of curvature [J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology,2016,30(7):3301-3311. doi: 10.1007/s12206-016-0639-y [9] CHEN M J, LIU H N, SU Y R, et al. Design and fabrication of a novel magnetorheological finishing process for small concave surfaces using small ball-end permanent-magnet polishing head [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2016,83:823-834. doi: 10.1007/s00170-015-7573-5 [10] WANG T Z, WU C Y, LIU H N, et al. On-machine electric discharge truing of small ball-end fine diamond grinding wheels [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2019,277:116472. [11] WANG T Z, CHEN M J, LIU H N, et al. Ultra-precision grinding machine design and application in grinding the thin-walled complex component with small ball-end diamond wheel [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2019,101:2097-2110. doi: 10.1007/s00170-018-3102-7 [12] XIANG S T, ALTINTAS Y. Modeling and compensation of volumetric errors for five-axis machine tools [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture,2016,101:65-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2015.11.006 [13] WANG T Z, LIU H N, WU C Y, et al. Three-dimensional modeling and theoretical investigation of grinding marks on the surface in small ball-end diamond wheel grinding [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2020,173:105467. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105467 -




 下载:
下载:







 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
