Study on chip formation in grinding nickel-based single-crystal superalloy DD5
-
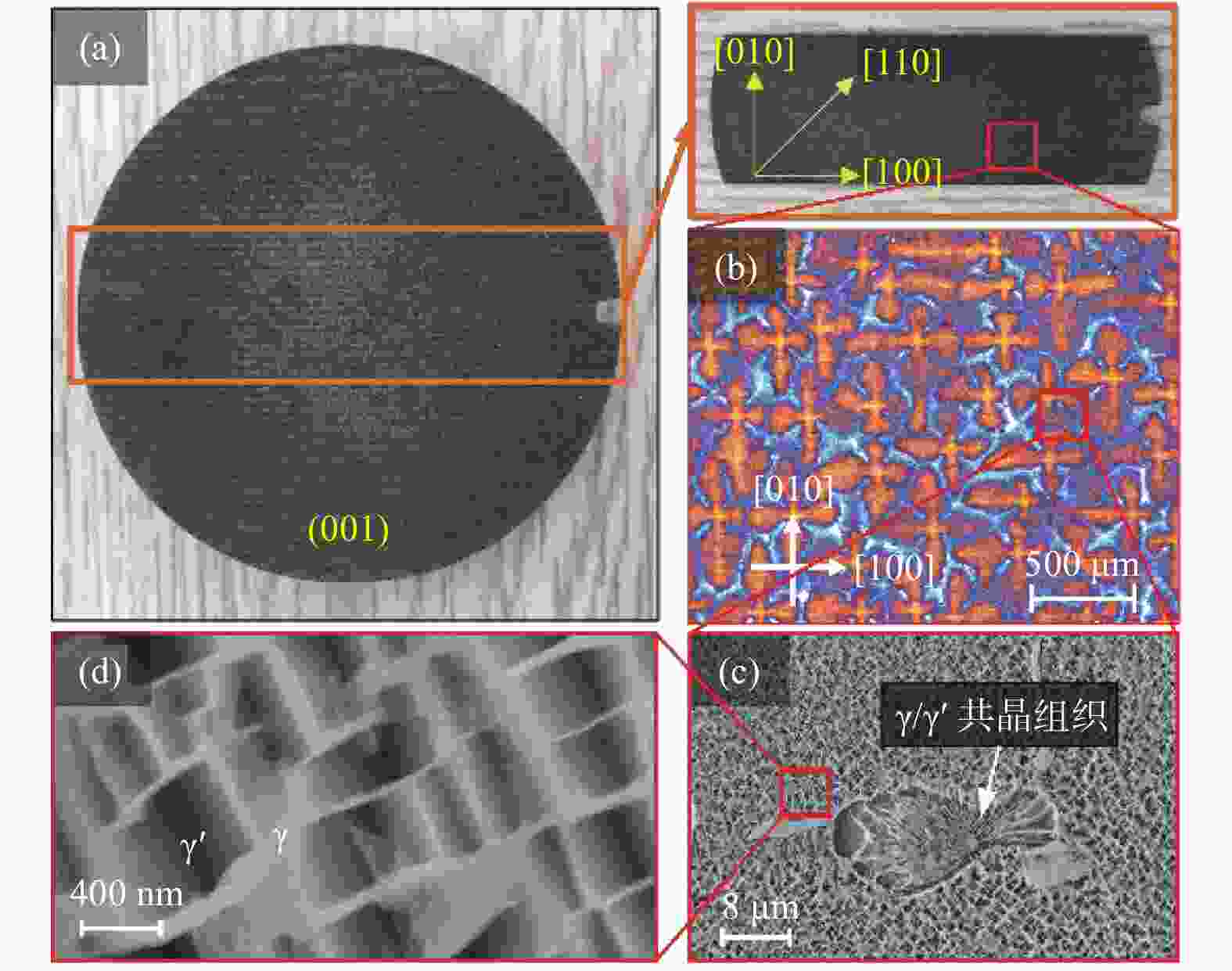
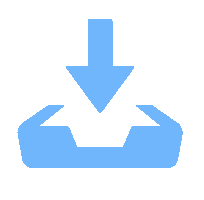
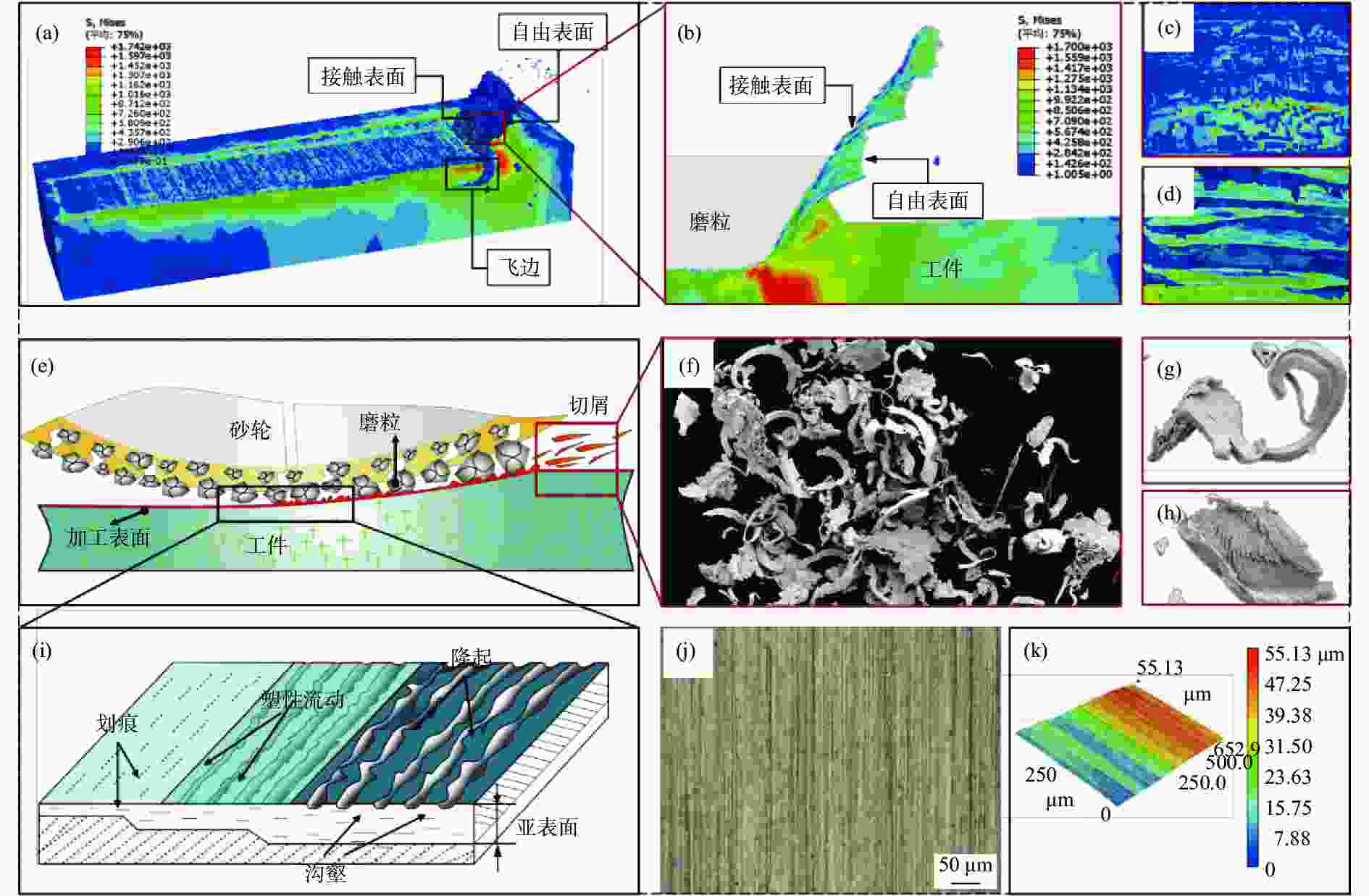
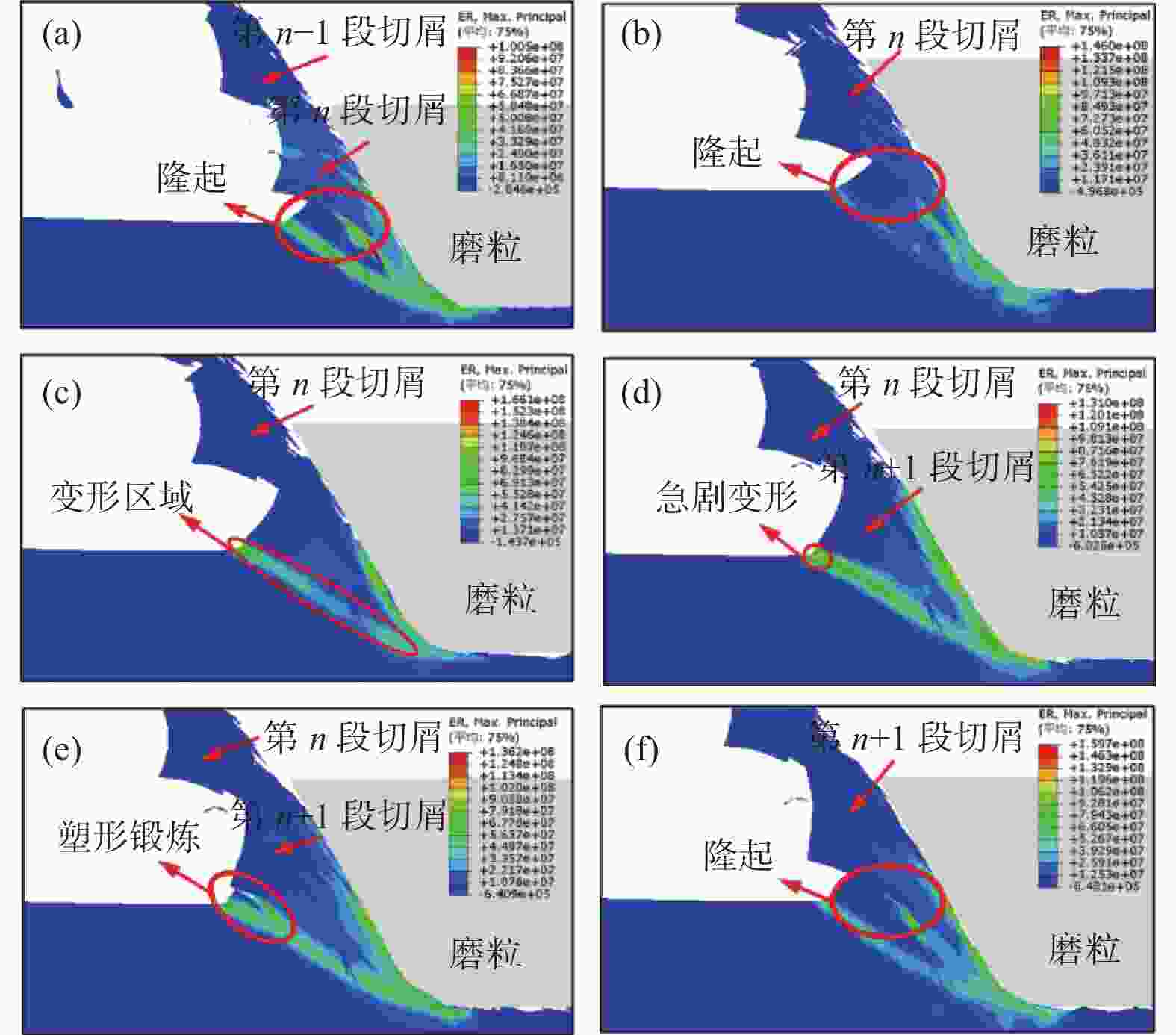
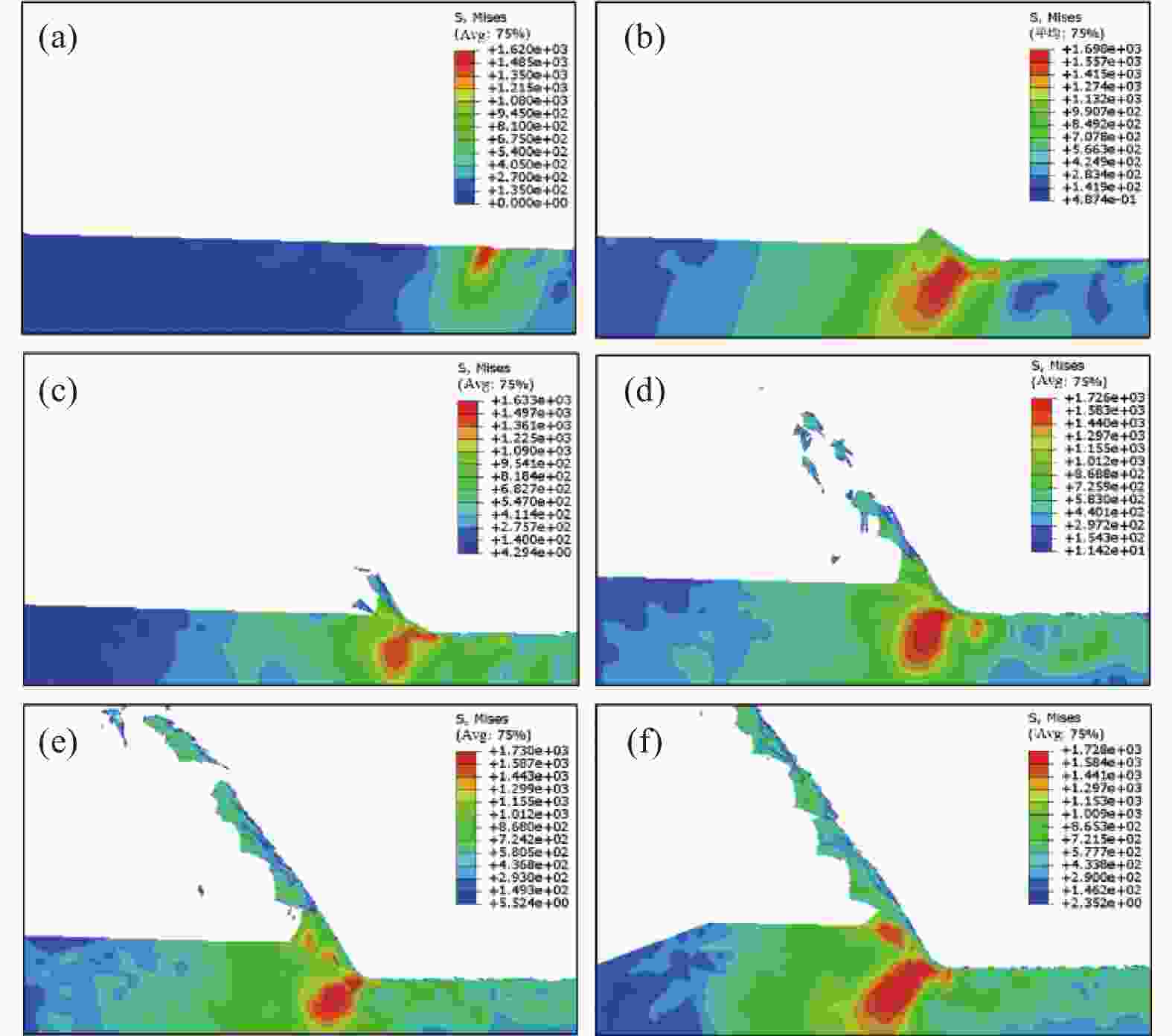
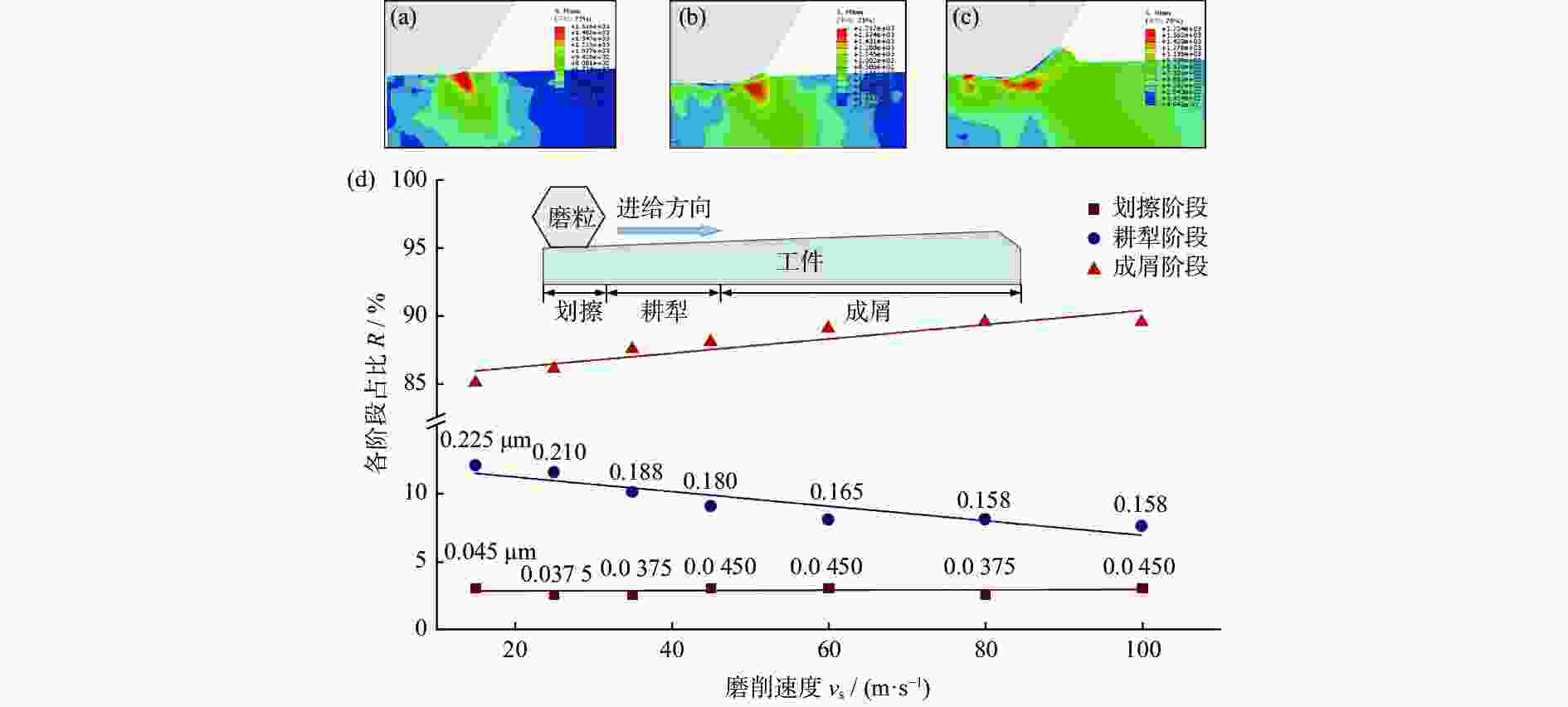
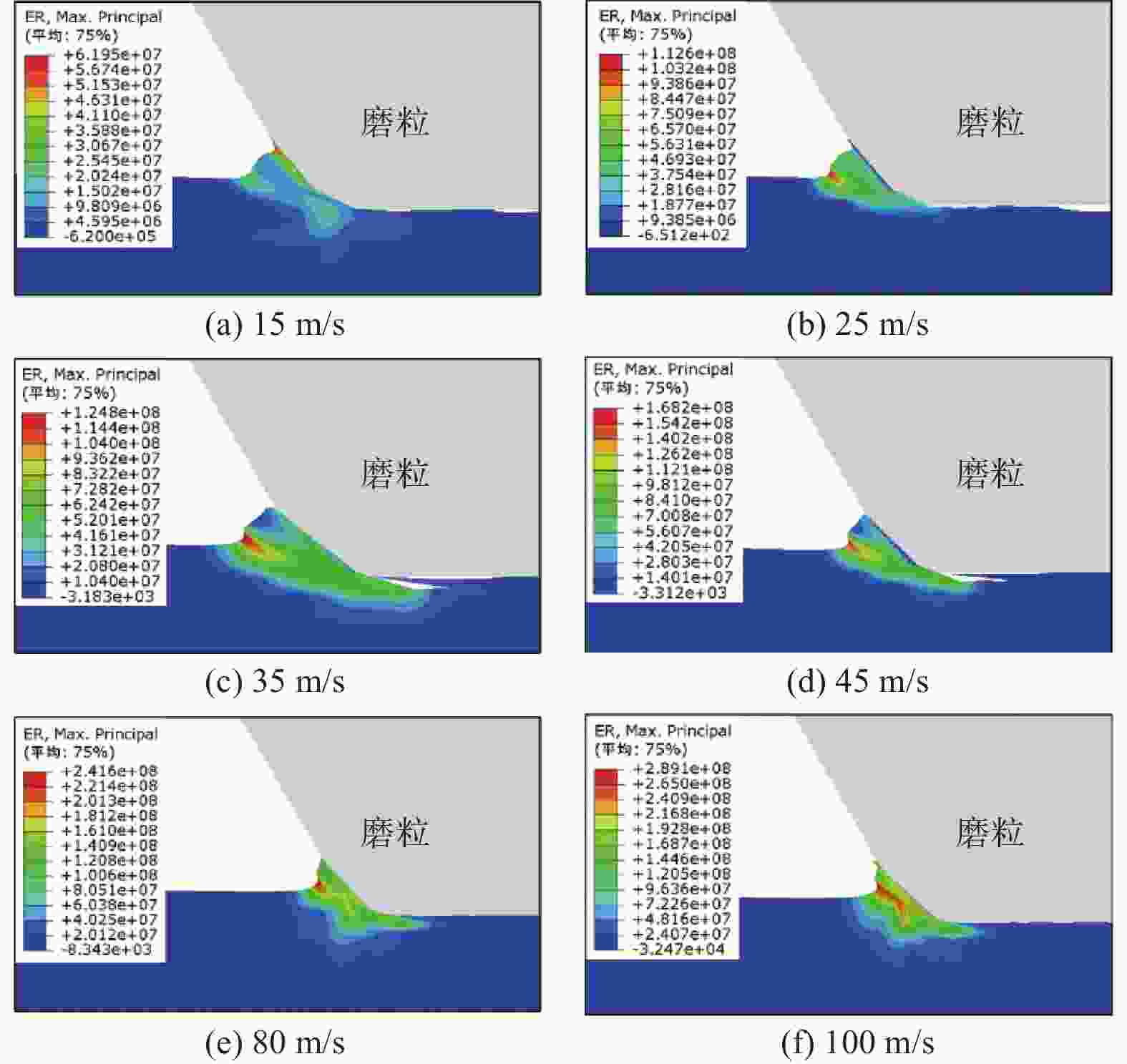
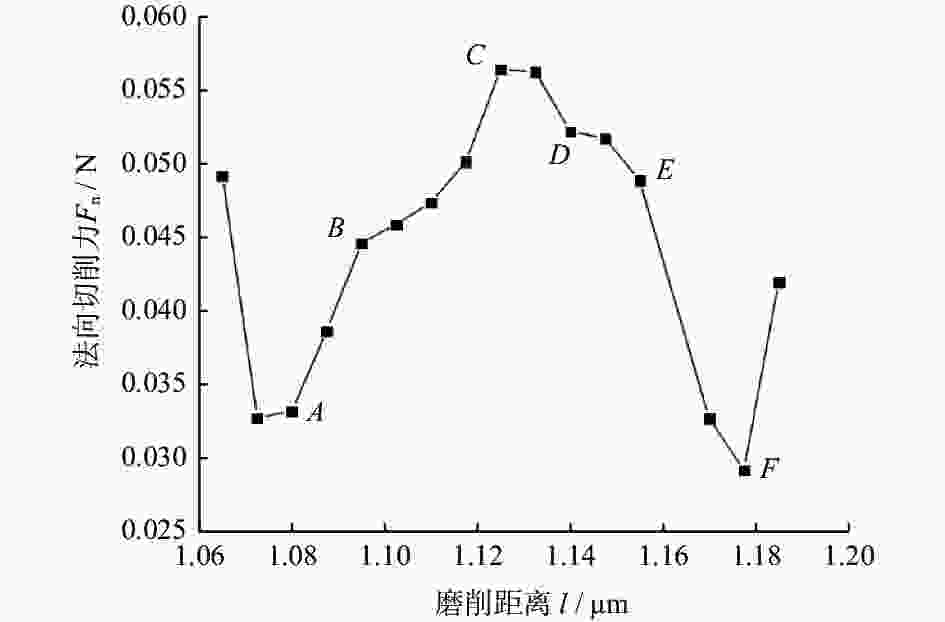
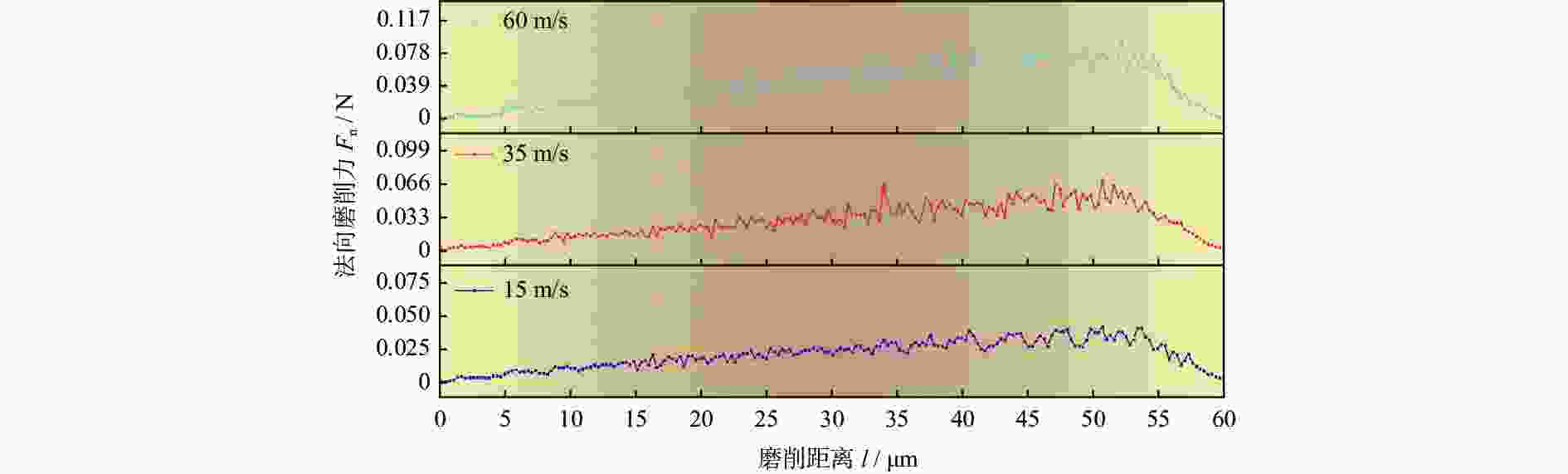
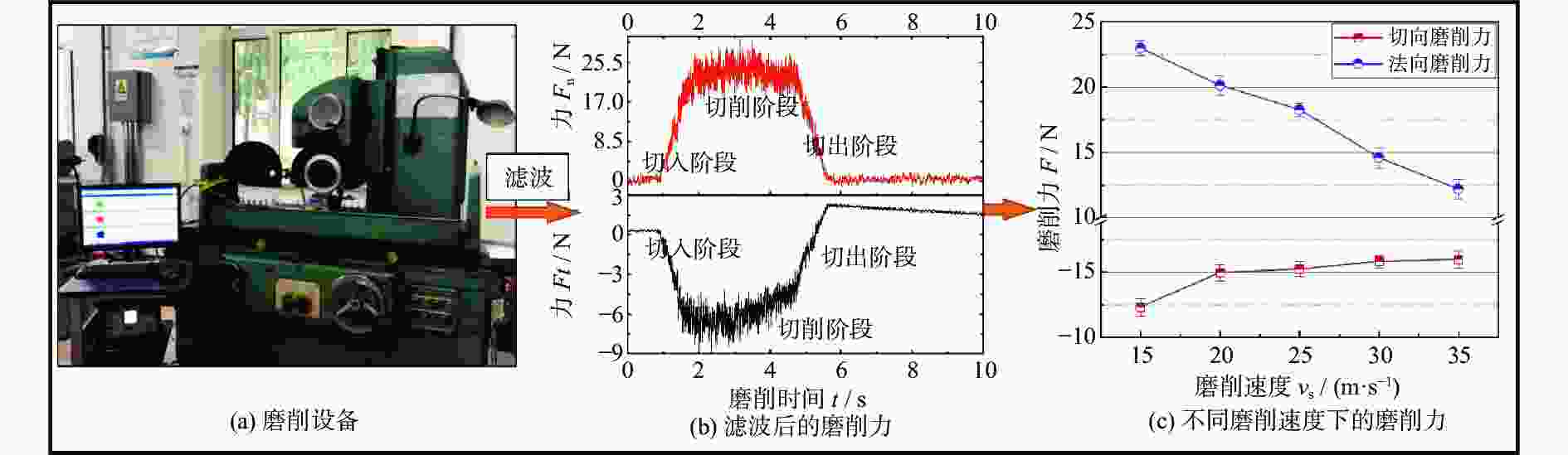
摘要: 为研究镍基单晶高温合金DD5的磨削去除机理,提高其加工效率,针对镍基单晶高温合金具有显著各向异性的特点,建立基于Hill模型的三维有限元磨削模型,研究镍基单晶高温合金DD5的表面加工形貌和切屑形貌,分析切屑形貌演变过程及其磨削力变化,探究磨削速度对切屑形貌和切屑形成频率的影响。研究表明:在磨削参数范围内,加工DD5容易出现锯齿形切屑;磨削力呈稳定增加并伴有一定的周期性波动,其波动情况与锯齿形切屑相对应;随着磨削速度的增大,磨粒能更快进入切削阶段,其临界成屑厚度由0.225 μm最终降为0.158 μm,成屑阶段占比由85.0%提高到89.5%;临界划擦厚度受磨削速度变化影响不大;随着磨削速度的增加,DD5切屑形貌由锯齿分节密集堆叠的单元节状向连续型锯齿状转变,最后发展为条形带状切屑。
-
关键词:
- 磨削 /
- 切屑形貌 /
- 镍基单晶高温合金DD5 /
- 有限元分析
Abstract: According to the significant anisotropy of nickel-based single-crystal superalloy, a three-dimensional single abrasive grinding model based on the Hill model was developed. In this work, the change in the actual grinding thickness (ag) of the abrasive is taken into account in establishing the model. In addition, a combination of theoretical research and experimental research is used. The surface morphology and chip morphology of DD5 were first studied. Then, the evolution of chip morphology and the change in grinding force were investigated. Finally, the influence of grinding speed (vs) on chip morphology and chip segmentation frequency (fc) was studied. The research shows that serrated chips can easily occur when machining DD5 within the range of grinding parameters. The grinding force increased steadily and was accompanied by inevitable periodic fluctuations corresponding to serrated chips. As the grinding speed increased, the abrasive could enter the cutting stage more quickly, and its critical chip thickness (acr) eventually decreased from 0.225 μm to 0.158 μm. The percentage of the cutting phase increased from 85% to 89.5%. However, the critical scratch thickness was not significantly influenced by the change in grinding speed. The grinding speed and thickness substantially influence the morphology and segmentation frequency of DD5 chips. Specifically, as the grinding speed continues to increase, the DD5 chip morphology changes from a densely stacked unit nodal shape with serrated subsections to a continuous type of serrated shape and finally develops into a strip-shaped chip. At different grinding speeds, the chip segmentation frequency of DD5 decreases with increasing grinding depth. -
表 1 DD5主要物理性能
Table 1. Main physical properties of DD5
序号 硬度
H屈服强度
σs弹性模量
E泊松比
ν熔点
Tm收缩比
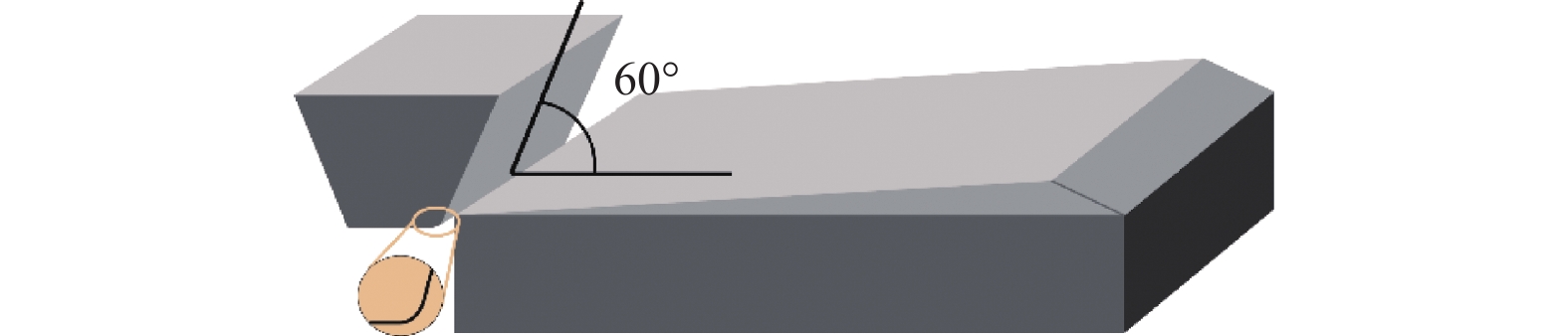
SDD5 550 HV 1109 MPa 134.7 GPa 0.419 1368 °C 13.5% 表 2 单颗磨粒的具体磨削参数
Table 2. Grinding parameters of single abrasive
类型 取值 磨削速度 vs / (m·s−1) 15, 25, 35, 45, 60, 80, 100 最大未变形切削厚度 agmax / µm 1.5 -
[1] POLLOCK T M. Alloy design for aircraft engines [J]. Nature Materials,2016,15(8):809. doi: 10.1038/nmat4709 [2] ZHANG Z, YANG Z, LU S, et al. Strain localization and failure at twin-boundary complexions in nickel-based superalloys [J]. Nature Communication,2020,11:4890. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18641-z [3] SINGH R, SHARMA V. Machining induced surface integrity behavior of nickel-based superalloy: Effect of lubricating environments [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2022,307:117701. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2022.117701 [4] ZHU T, CAI M, GONG Y, et al. Study on chip formation in grinding of nickel-based polycrystalline superalloy GH4169 [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2022,121:1135-1148. doi: 10.1007/s00170-022-09386-8 [5] QU S, YAO P, GONG Y, et al. Environmentally friendly grinding of C/SiCs using carbon nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication technology [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2022,36:132898. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132898 [6] CAI M, GONG Y, SUN Y, et al. Experimental study on grinding surface properties of nickel-based single crystal superalloy DD5 [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2019,101:71-85. doi: 10.1007/s00170-018-2839-3 [7] ZHOU Y, GONG Y, CAI M, et al. Study on surface quality and subsurface recrystallization of nickel-based single-crystal superalloy in micro-grinding [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2017,90:1749-1768. doi: 10.1007/s00170-016-9401-y [8] ZHAO Z, QIAN N, DING W, et al. Profile grinding of DZ125 nickel-based superalloy: Grinding heat, temperature field, and surface quality [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2020,57:10-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.06.022 [9] CAI M, ZHU T, GAO X, et al. Study on machining performance in grinding of Ni-base single crystal superalloy DD5 [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2022,120:7657-7671. doi: 10.1007/s00170-022-09256-3 [10] LIANG Z, WANG X, WU Y, et al. Experimental study on brittle–ductile transition in elliptical ultrasonic assisted grinding (EUAG) of monocrystal sapphire using single diamond abrasive grain [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture,2013,71:41-51. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.797.223 [11] ZHU Y, ZHANG Q, ZHAO Q, et al. The material removal and the nanometric surface characteristics formation mechanism of TiC/Ni cermet in ultra-precision grinding [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials,2021,96:105494. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2021.105494 [12] LI C, ZHANG F, WANG X, et al. Repeated nanoscratch and double nanoscratch tests of Lu2O3 transparent ceramics: Material removal and deformation mechanism, and theoretical model of penetration depth [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society,2018,38(2):705-718. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.09.028 [13] DAI J, DING W, ZHANG L, et al. Understanding the effects of grinding speed and undeformed chip thickness on the chip formation in high-speed grinding [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2015,81:995-1005. doi: 10.1007/s00170-015-7265-1 [14] 巩亚东, 周俊, 周云光, 等. 镍基单晶高温合金微尺度磨削温度仿真 [J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版),2018,39(1):82-86. doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2018.01.017GONG Yadong, ZHOU Jun, ZHOU Yunguang, et al. Micro-grinding temperature simulation for nickel-based single crystal superalloy [J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science),2018,39(1):82-86. doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2018.01.017 [15] ESMAEILI H, ADIBI H, REZAEI S M. Study on surface integrity and material removal mechanism in eco-friendly grinding of Inconel 718 using numerical and experimental investigations [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2021,112:1797-1818. doi: 10.1007/s00170-020-06528-8 [16] MIAO Q, DING W, KUANG W, et al. Grinding force and surface quality in creep feed profile grinding of turbine blade root of nickel-based superalloy with microcrystalline alumina abrasive wheels [J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics,2021,34(2):576-585. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2019.11.006 [17] KUANG W, MIAO Q, DING W, et al. Fretting wear behaviour of machined layer of nickel-based superalloy produced by creep-feed profile grinding [J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics,2022,35(10):401-411. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2021.10.007 [18] 丁文锋, 苗情, 李本凯, 等. 面向航空发动机的镍基合金磨削技术研究进展 [J]. 机械工程学报,2019,55(1):189-215. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.01.189DING Wenfeng, MIAO Qing, LI Benkai, et al. Review on grinding technology of nickel-based superalloys used for aero-engine [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2019,55(1):189-215. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.01.189 [19] 夏江, 丁文锋, 徐九华, 等. 镍基高温合金高速超高速磨削成屑过程的三维仿真研究 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2020,40(6):58-69. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2020.6.0011XIA Jiang, DING Wenfeng, XU Jiuhua, et al. 3D simulation study on the chip formation process in high speed and ultra-high speed grinding of nickel-based superalloy [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2020,40(6):58-69. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2020.6.0011 [20] 丁智平, 刘义伦, 尹泽勇, 等. 镍基单晶高温合金的屈服准则研究 [J]. 机械强度,2004,26(2):175-179. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9669.2004.02.011DING Zhiping, LIU Yilun, YIN Zeyong, et al. Study of yield criterion for single crystal nickel-based superalloys [J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength,2004,26(2):175-179. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9669.2004.02.011 [21] 丁智平, 刘义伦, 尹泽勇, 等. 面心立方晶体单晶材料弹塑性本构模型 [J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2004,35(3):423-428.DING Zhiping, LIU Yilun, YIN Zeyong, et al. Constitutive model for FCC single crystal material [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology),2004,35(3):423-428. [22] 冯露, 张克实, 张光, 等. HILL屈服准则与晶体塑性模型对FCC单晶材料塑性各向异性描述能力的比较 [J]. 计算力学学报,2003,20(5):535-540 + 573. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4708.2003.05.005FENG Lu, ZHANG Keshi, ZHANG Guang, et al. Comparative study of Hill model with crystal plasticity for FCC single crystals [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics,2003,20(5):535-540 + 573. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4708.2003.05.005 [23] 秦健朝, 崔仁杰, 黄朝晖. 小角度晶界对DD5镍基单晶高温合金中、高温条件下力学性能的影响 [J]. 材料工程,2020,48(10):114-122. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2020.000002QIN Jianchao, CUI Renjie, HUANG Chaohui. Effect of low angle grain boundaries on mechanical properties of DD5 single crystal Ni-base superalloy at medium temperature and high temperature [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2020,48(10):114-122. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2020.000002 [24] 田霖, 傅玉灿, 杨路, 等. 基于速度效应的高温合金高速超高速磨削成屑过程及磨削力研究 [J]. 机械工程学报,2013,49(9):169-177. doi: 10.3901/JME.2013.09.169TIAN Lin, FU Yucan, YANG Lu, et al. Investigations of the “speed effect” on critical thickness of chip formation and grinding force in high speed and ultra-high speed grinding of superalloy [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2013,49(9):169-177. doi: 10.3901/JME.2013.09.169 [25] 孙永杰, 朱涛, 蔡明, 等. 镍基单晶高温合金磨削润滑方式对表面完整性的影响 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2022,42(2):201-207. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2021.0114SUN Yongjie, ZHU Tao, CAI Ming, et al. Influence of grinding lubrication methods on surface integrity of nickel-based single crystal superalloy [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2022,42(2):201-207. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2021.0114 [26] 赵恒华, 牟红平, 赵学洋. 介观与宏观角度下的磨削力修正研究 [J]. 辽宁石油化工大学学报,2016,36(5):47-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6952.2016.05.011ZHAO Henghua, MU Hongping, ZHAO Xueyang. Modification of the grinding force in mesoscopic and macroscopic [J]. Journal of Liaoning Shihua University,2016,36(5):47-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6952.2016.05.011 -




 下载:
下载:





 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
