Prediction model of robot grinding and polishing contact force based on EWOA-LSSVR
-
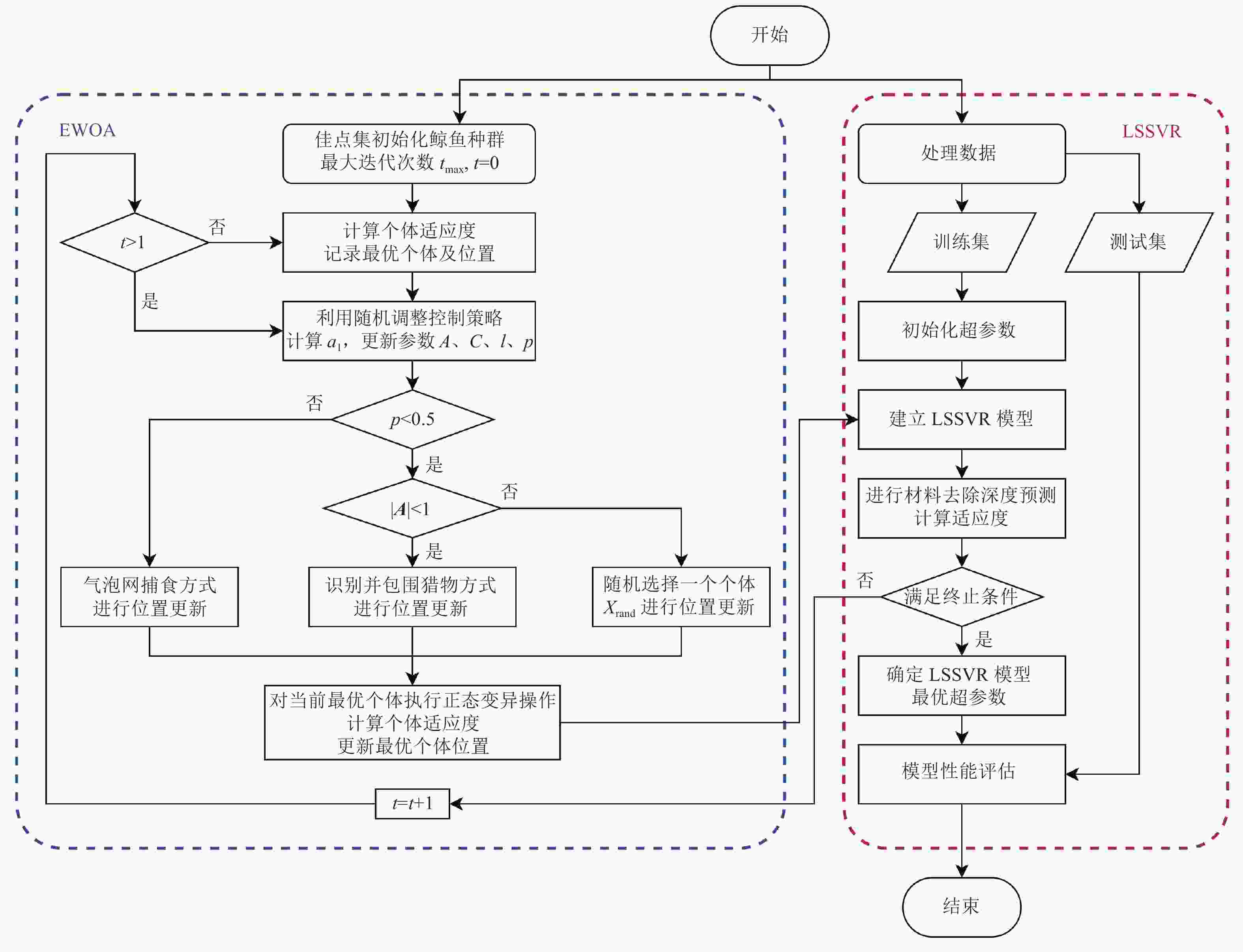
摘要: 为确定航空发动机叶片机器人磨抛过程中材料去除深度与工艺参数之间的关系,获得加工所需的工艺参数,实现叶片表面材料的定点定量去除,建立叶片机器人磨抛加工系统,将各工艺参数考虑在内进行多组正交实验;利用实验数据建立基于最小二乘支持向量回归机(least squares support vector regression,LSSVR)模型,利用增强型鲸鱼优化算法(enhanced whale optimization algorithm,EWOA)提高算法精度、寻优能力和避免陷入局部最优并对LSSVR的超参数进行优化;对比标准鲸鱼优化算法(whale optimization algorithm,WOA)和粒子群优化(particle swarm optimization,PSO)算法预测模型的结果,并利用模型预测的工艺参数进行实验验证。结果表明:EWOA-LSSVR预测模型的决定系数R为96.031%,平均绝对误差RMAE为
0.012128 mm,相较于WOA-LSSVR和PSO-LSSVR模型具有更好的拟合度;且验证实验结果证明EWOA-LSSVR预测模型具有较好的预测准确性,并可为叶片表面材料的定点定量去除提供可靠依据。-
关键词:
- 机器人砂带磨抛 /
- 工艺参数 /
- 机器学习 /
- 最小二乘支持向量回归机 /
- 增强型鲸鱼优化算法
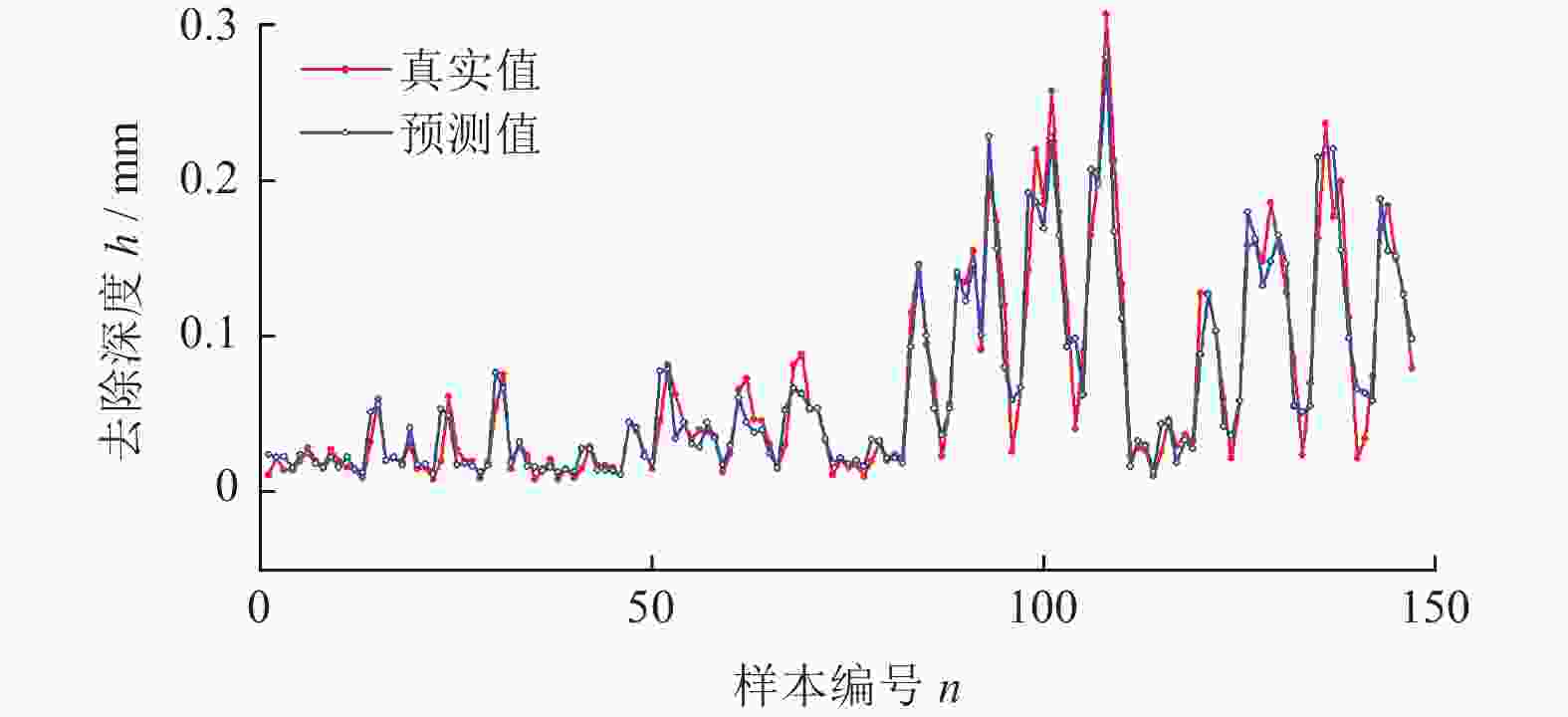
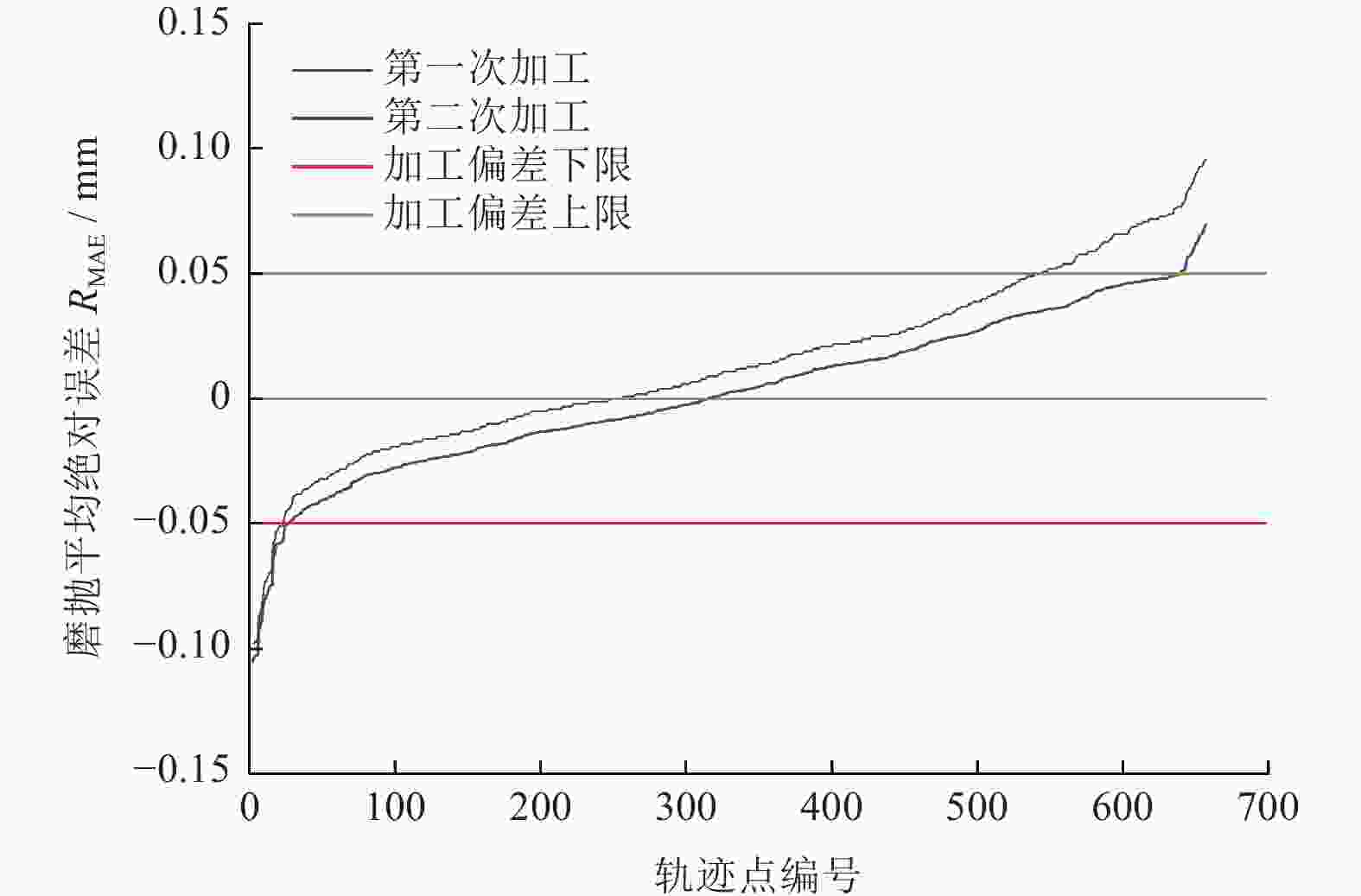
Abstract:Objectives High-pressure turbine blades, as the core components of aviation engines, are subjected to harsh working environments of high temperature, high pressure, and high load for a long time, which places strict requirements on their high-temperature mechanical properties and structural stability. Therefore, the material of turbine blades is often selected as single-crystal high-temperature alloys and the blades are made through precision casting processes. Due to the casting characteristics of the blades, the material distribution of the workpiece is uneven, that is, the deviations of the design sizes from different positions on the blade surfaces vary. Therefore, the fixed-point quantitative removal of the blade surface material plays a very important role in the blade production and manufacturing process. Methods Blade grinding and polishing processing experiments are established by considering various technological parameters. The experimental data are used as the training set for the prediction model, and a prediction model based on the least squares support vector machine (LSSVR) is constructed. In the LSSVR hyperparameter setting stage, the enhanced whale optimization algorithm (EWOA) is used to improve algorithm accuracy, enhance optimization capability, and prevent local optima while optimizing the LSSVR hyperparameters. The prediction models optimized by other algorithms are established for comparison of model prediction capabilities. The prediction results are applied to the reproduction experiments of the material removal amount, and the performance of the prediction model is evaluated by using the processing results. Results From the perspective of model establishment and result prediction, the processing parameter prediction model EWOA-LSSVR based on the enhanced whale optimization algorithm (EWOA)-optimized least squares support vector machine (LSSVR) exhibits high prediction accuracy and good model fitting degree, with a determination coefficient of 96.031% and a mean absolute error RMAE of 0.012 128 mm. The prediction models of LSSVR optimized by the whale optimization algorithm (WOA) and particle swarm optimization (PSO) have determination coefficients of 89.457% and 92.228%, and mean absolute errors (RMAE) of 0.012 358 and 0.012 462 mm, respectively. In contrast, the prediction results of EWOA-LSSVR are more accurate with lower errors. The prediction results of EWOA-LSSVR are used as the process parameters for blade processing. When the dimensional error of the processed area of the blade enters the design tolerance zone of ±0.05 mm, it is considered qualified. The qualified rate of the sampling points in the two processing experiments reaches 93.59%, which plays a certain guiding role in the actual processing of the blade. Conclusions A prediction model for process parameters is established by using the least squares support vector machine suitable for small sample sizes. To improve the algorithm accuracy of model establishment and avoid falling into local optima, the enhanced whale algorithm is adopted to optimize the hyperparameters of the least squares support vector machine, and a prediction model with a determination coefficient of 96.031% and an average absolute error of 0.012 128 mm is established. By comparing with the prediction models optimized by WOA and PSO, the established prediction model has certain advantages in terms of determination coefficient, mean absolute error and mean square error. The reproduction experiment of the removal amount is carried out. After two processing experiments, a processing result with a qualified rate of 93.59% at the sampling points is achieved, proving the feasibility of using this method to achieve fixed-point and quantitative removal of the blade surface material. -
表 1 部分样本数据
Table 1. Partial sample data
样本
编号
n曲率半径
K / m−1砂带线
速度
v / (m·s−1)磨料
代号
m1进给速度
vw /
(mm·s−1)磨抛
接触力
F / N材料去
除深度
h / mm1 −52.032 3 5.86 P180 6 3 0.024 2 47.391 2 5.86 P180 6 3 0.022 3 50.485 4 5.86 P180 6 3 0.025 4 50.472 2 5.86 P180 6 3 0.025 … … … … … … … 1 472 11.545 8 10.89 P320 10 9 0.069 表 2 模型精度对比
Table 2. Comparison of prediction model accuracy
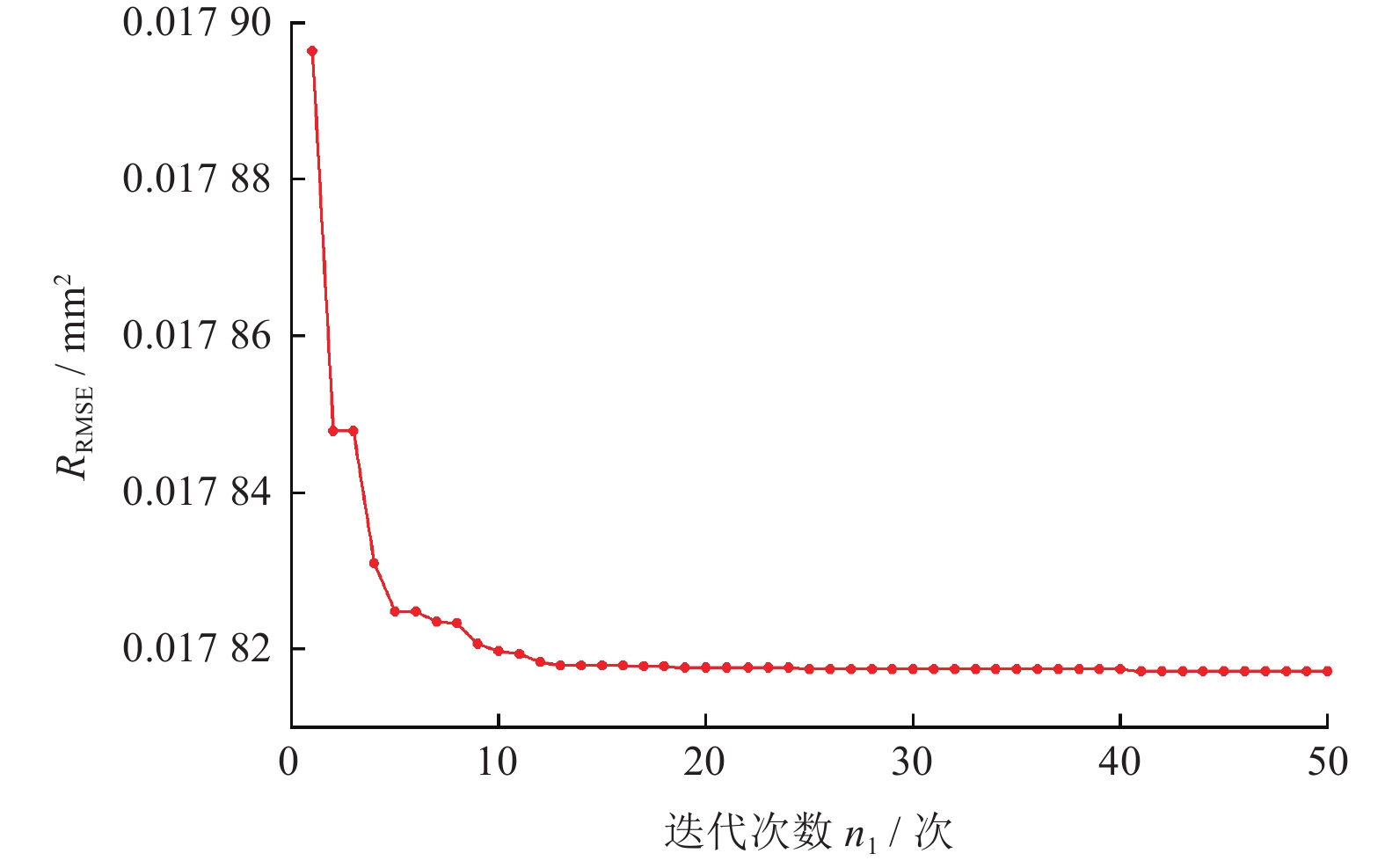
模型类型 评价指标 R RMAE / mm RRMSE / mm2 EWOA-LSSVR 0.960 31 0.012 128 0.017 908 WOA-LSSVR 0.894 57 0.012 358 0.019 127 PSO-LSSVR 0.922 28 0.012 462 0.018 231 -
[1] 郝义意. 涡轮叶片力-热耦合响应分析 [D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2024.HAO Yiyi. Analysis of force-thermal coupling response of high-temperature turbine blades [D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2024. [2] 黄云, 肖贵坚, 邹莱. 航空发动机叶片机器人精密砂带磨削研究现状及发展趋势 [J]. 航空学报, 2019, 40(3): 53-72. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2018.22508HUANG Yun, XIAO Guijian, ZOU Lai. Current situation and development trend of robot precise belt grinding for aero-engine blade [J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2019, 40(3): 53-72. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2018.22508 [3] 王文斌. 航空发动机叶片超声自动检测的三维显示技术研究 [D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2016.WANG Wenbin. Three-dimensional display of automated ultrasonic testing for the aircraft engine blade [D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2016. [4] 王宏丽. 叶片机器人砂带磨削材料去除微观建模及实验研究 [D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2023.WANG Hongli. Microscopic modeling and experimental study of blade robot belt grinding materials [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2023. [5] 魏和平. 整体叶盘叶片内外弧型面砂带磨削技术研究 [D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2014.WEI Heping. Research on abrasive belt grinding of blisk blade inner and outer profile [D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2014. [6] 谢钱龙. 非均匀余量航空叶片机器人磨抛力速调控 [D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2023.XIE Qianlong. Non-uniform margin blade robot grinding and polishing force speed control [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science And Technology, 2023. [7] 崔海军, 张明岐. 航空发动机叶片抛光技术现状及发展趋势 [J]. 航空制造技术, 2015(11): 128-131. doi: 10.16080/j.issn1671-833x.2015.11.128CUI Haijun, ZHANG Mingqi. Current situation and development trend of aircraft engine blade polishing technology [J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2015(11): 128-131. doi: 10.16080/j.issn1671-833x.2015.11.128 [8] 王辉, 赵欢, 罗来臻. 航空发动机叶片自适应磨抛定量去除研究 [J]. 组合机床与自动化加工技术, 2022(5): 28-32. doi: 10.13462/j.cnki.mmtamt.2022.05.007WANG Hui, ZHAO Huan, LUO Laizhen. Research on quantitative removal of adaptive grinding and polishing of aero-engine blades [J]. Modular Machine Tool & Automatic Manufacturing Technique, 2022(5): 28-32. doi: 10.13462/j.cnki.mmtamt.2022.05.007 [9] ZHANG W J, GONG Y D, XU Y C, et al. Modeling of material removal depth in robot abrasive belt grinding based on energy conversion [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2023, 97: 76-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2023.04.055 [10] 张广鹏, 任利娟, 王启文. 基于图像信息的砂带磨削材料去除率预测模型 [J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2019, 40(12): 127-134. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J1905731ZHANG Guangpeng, REN Lijuan, WANG Qiwen. Image-based prediction model for material removal rate of abrasive belt grinding [J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2019, 40(12): 127-134. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J1905731 [11] 杨赫然, 何源, 孙兴伟, 等. 螺杆转子砂带磨削装置开发及材料去除率预测 [J]. 中国机械工程, 2021, 32(17): 2055-2062. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2021.17.006YANG Heran, HEYuan, SUN Xingwei, et al. Development of belt grinding devices for screw rotor and prediction of material removal rates [J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 32(17): 2055-2062. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2021.17.006 [12] 刘速杰, 李论, 赵吉宾, 等. 整体叶轮机器人研磨柔顺控制研究 [J]. 机械设计与制造, 2021(12): 253-256,261. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2021.12.054LIU Sujie, LI Lun, ZHAO Jibin, et al. Research on smooth control of grinding of integral impeller by robot [J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2021(12): 253-256,261. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2021.12.054 [13] SUYKENS J A K, VANDEWALLE J. Recurrent least squares support vector machines [J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I Regular Papers, 2000, 47(7): 1109-1114. doi: 10.1109/81.855471 [14] 王明刚, 曹斌, 黄若愚, 等. 基于PSO优化的LS-SVM氧化铝浓度预测 [J]. 轻金属, 2020(10): 33-40. doi: 10.13662/j.cnki.qjs.2020.10.007WANG Minggang, CAO Bin, HUANG Ruoyu, et al. Prediction of alumina concentration based on LS-SVM with PSO optimization [J]. Light Metals, 2020(10): 33-40. doi: 10.13662/j.cnki.qjs.2020.10.007 [15] 张艳敏, 吴自库. 两点边值问题二尺度小波核LS-SVM解法 [J]. 重庆工商大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 38(5): 91-96.ZHANG Yanmin, WU Ziku. Two-scale wavelet kernel LS-SVM method for the two-point boundary value problem [J]. Journal of Chongqing Technology and Business University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 38(5): 91-96. [16] SHIN J, HWANG C. Varying coefficient modeling via least squares support vector regression [J]. Neurocomputing, 2015, 161: 254-259. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.02.036 [17] YANG X, TAN L, HE L. A robust least squares support vector machine for regression and classification with noise [J]. Neurocomputing, 2014, 140: 41-52. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.03.037 [18] 霍海波, 周帅福, 杨海东, 等. 基于LS-SVM辨识的PEMFC动态建模及仿真 [J]. 电池, 2020, 50(1): 31-34. doi: 10.19535/j.1001-1579.2020.01.008HUO Haibo, ZHOU Shuaifu, YANG Haidong, et al. Dynamic modeling and simulation of PEMFC based on LS-SVM identification [J]. Battery Bimonthly, 2020, 50(1): 31-34. doi: 10.19535/j.1001-1579.2020.01.008 [19] 王权.基于鲸鱼算法优化支持向量机的电机轴承故障诊断 [J]. 电器开关, 2023, 61(6): 83-86, 109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-289X.2023.06.024WANG Quan. Fault diagnosis of motor bearing based on whale algorithm optimized support vector machine [J]. Electric Switchgear, 2023, 61(6): 83-86, 109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-289X.2023.06.024 [20] 吴泽忠, 宋菲. 基于改进螺旋更新位置模型的鲸鱼优化算法 [J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2019, 39(11): 2928-2944. doi: 10.12011/1000-6788-2018-2156-17WU Zezhong, SONG Fei. Whale optimization algorithm based on improved spiral update position model [J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2019, 39(11): 2928-2944. doi: 10.12011/1000-6788-2018-2156-17 [21] 蔡赛男, 宋卫星, 班利明, 等. 基于鲸鱼算法优化LSSVM的滚动轴承故障诊断 [J]. 控制与决策, 2022, 37(1): 230-236. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.1147CAI Sainan, SONG Weixing, BAN Liming, et al. Fault diagnosis method of rolling bearing based on LSSVM optimized by whale optimization algorithm [J]. Control and Decision, 2022, 37(1): 230-236. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.1147 [22] 钟明辉, 龙文. 一种随机调整控制参数的鲸鱼优化算法 [J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(12): 68-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.12.012ZHONG Minghui, LONG Wen. Whale optimization algorithm based on stochastic adjustment control parameter [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(12): 68-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.12.012 [23] 宋壮, 赵玉刚, 刘广新, 等. 基于WOA–LSSVM的磁粒研磨表面粗糙度预测及工艺参数优化 [J]. 表面技术, 2023, 52(1): 242-252,297. doi: 10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2023.01.025SONG Zhuang, ZHAO Yugan, LIU Guangxin, et al. Surface roughness prediction and process parameter optimization of magnetic abrasive finishing based on WOA-LSSVM [J]. Surface Technology, 2023, 52(1): 242-252,297. doi: 10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2023.01.025 [24] 张海博, 潘鹏程, 郑峰. 基于改进鲸鱼算法优化的接地网腐蚀速率预测 [J]. 电子科技, 2025, 38(5): 1-9. doi: 10.16180/j.cnki.issn1007-7820.2025.05.002ZHANG Haibo, PAN Pengcheng, ZHENG Feng. Corrosion rate prediction of grounding grid based on improved whale algorithm optimization [J]. Electronic Science and Technology, 2025, 38(5): 1-9. doi: 10.16180/j.cnki.issn1007-7820.2025.05.002 [25] 徐从东, 张继春, 马鹏飞. 一种平衡全局与局部搜索能力的粒子群优化算法 [J]. 微电子学与计算机, 2016, 33(6): 134-138. doi: 10.19304/j.cnki.issn1000-7180.2016.06.031XU Congdong, ZHANG Jichun, MA Pnegfei. A new particle swarm optimization algorithm with balancing local and global search ability [J]. Microelectronics & Computer, 2016, 33(6): 134-138. doi: 10.19304/j.cnki.issn1000-7180.2016.06.031 [26] 高圣国, 吴忠, 李旭芳, 等. 带两类正态变异的多目标粒子群算法 [J]. 控制与决策, 2015, 30(5): 939-942. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2014.0426GAO Shengguo, WU Zhong, LI Xufang, et al. Multi-objective particle swarm optimization with two normal mutations [J]. Control and Decision, 2015, 30(5): 939-942. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2014.0426 [27] 唐丽晴, 应忠于, 罗云. 基于鲸鱼优化改进算法的基站选址 [J]. 计算机与现代化, 2020(9): 100-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2475.2020.09.018TANG Lijing, YING Zhongyu, LUO Yun. Base station location planning based on improved whale optimization algorithm [J]. Computer and Modernization, 2020(9): 100-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2475.2020.09.018 [28] 王宇硕, 郭锐, 刘荣忠, 等. 基于PSO和SVM的夹层聚能装药结构优化设计 [J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2022, 43(8): 244-249. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2022.08.038WANG Yushuo, GUO Rui, LIU Rongzhong, et al. Optimum design of double layer shaped charge structure based on PSO and SVM [J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2022, 43(8): 244-249. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2022.08.038 -



 下载:
下载:

 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
