Exploration of ceramic binder diamond aggregated abrasives
-
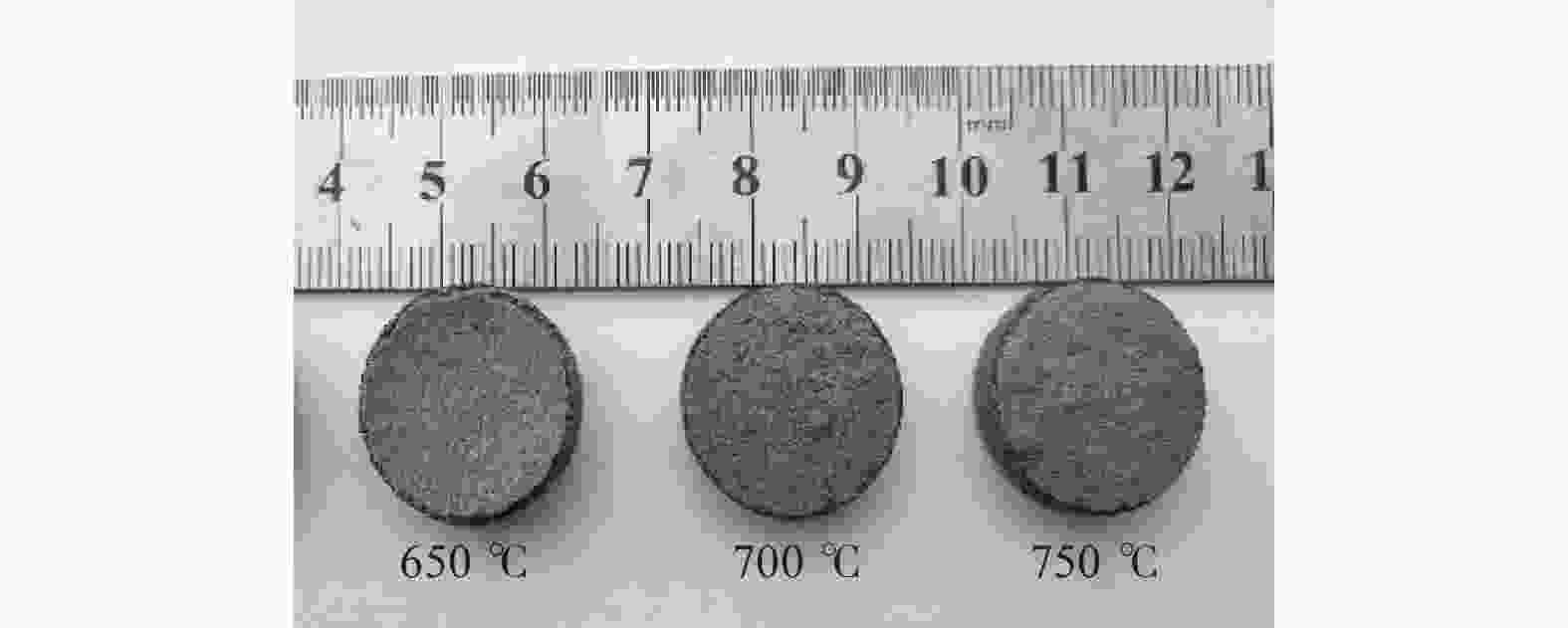
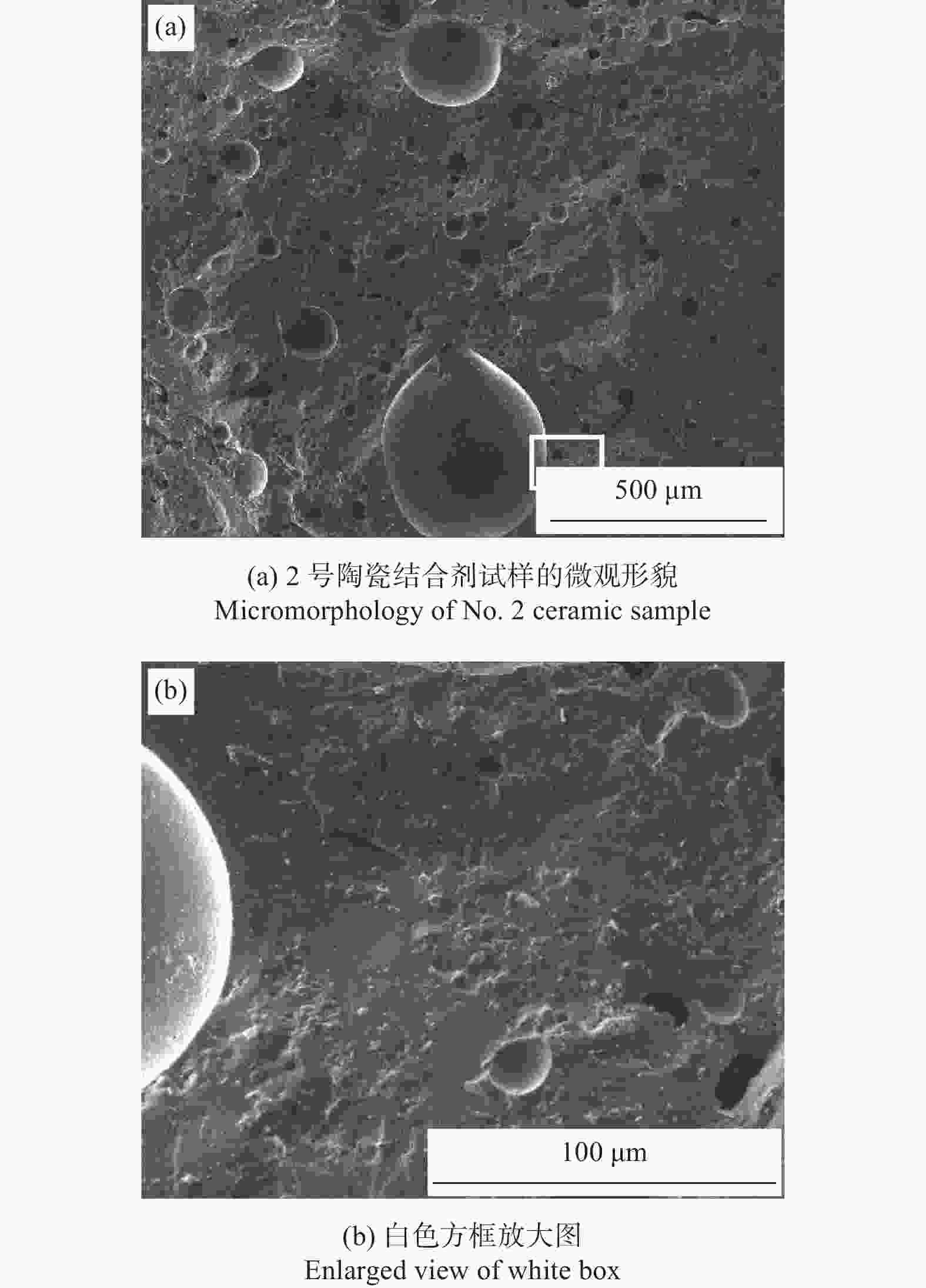
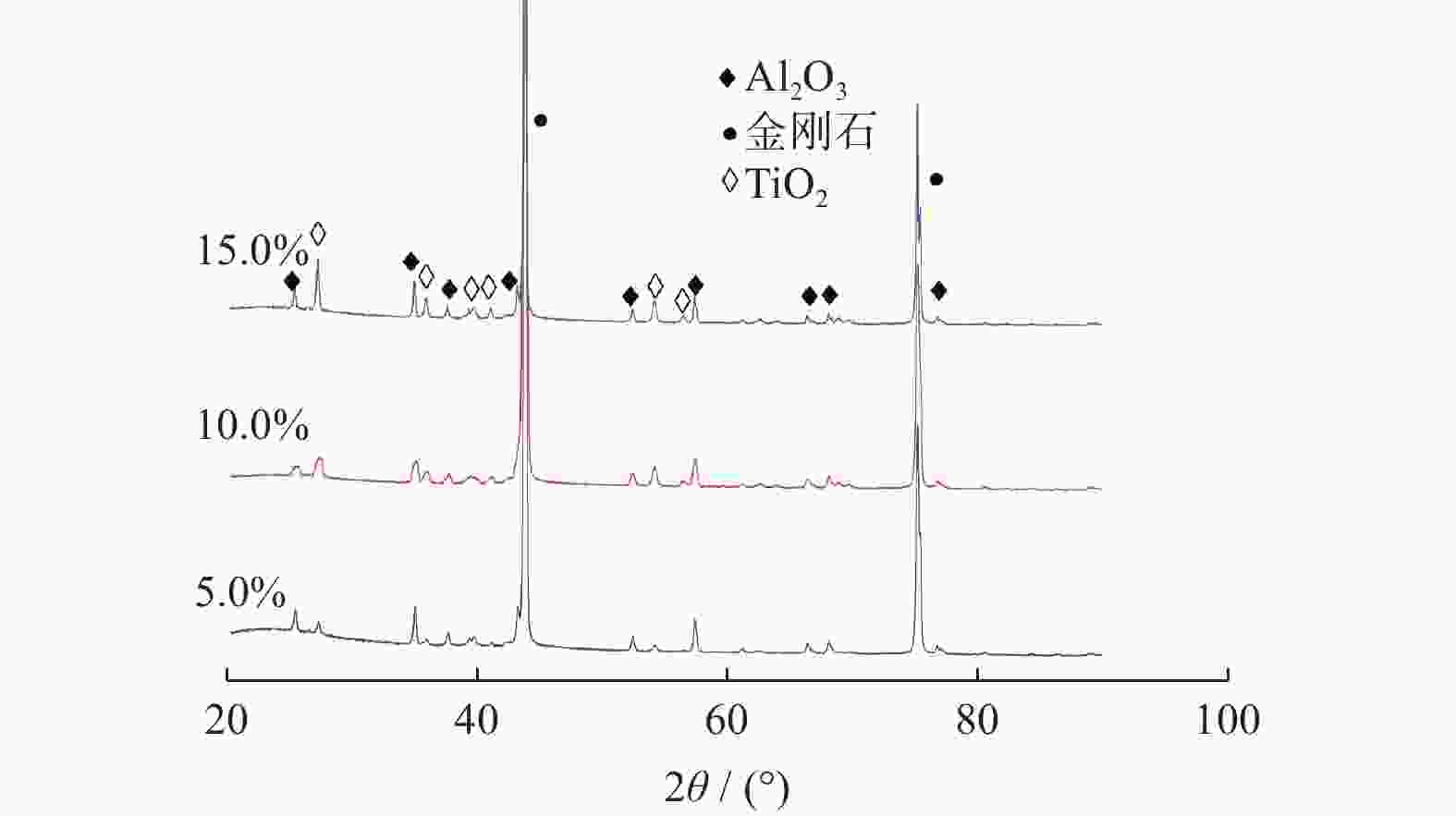
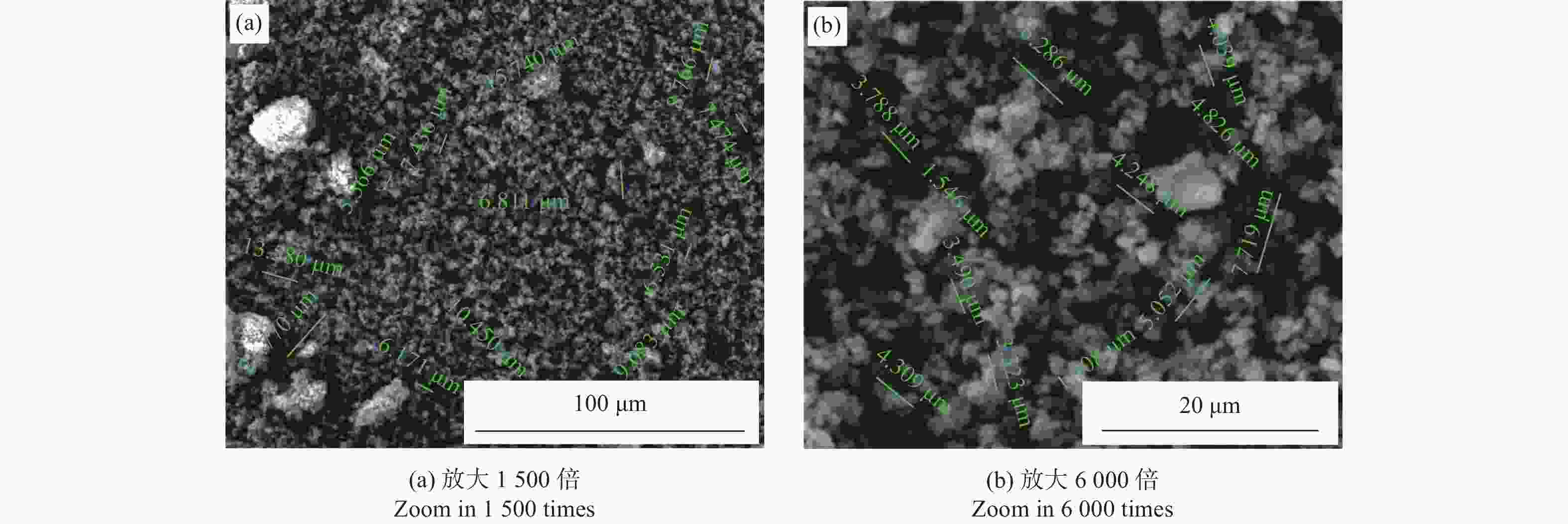
摘要: 细粒度金刚石微粉大量积压是目前金刚石微粉制造行业面临的问题之一,为促进其应用,以铝硼硅结合剂为黏接剂、Si粉和Ti粉为添加剂制造团聚磨料试样,并将制成的团聚磨料加入铝硼硅结合剂中制成陶瓷结合剂试样,对所制试样的抗弯强度、物相构成和微观形貌进行分析。结果表明:添加Si或Ti的铝硼硅黏结剂均能起到团聚金刚石的作用;当团聚磨料中Si或Ti的质量分数为10.0%时,所制得的陶瓷结合剂试样抗弯强度最大,且添加Si的团聚磨料试样抗弯强度为43.74 MPa;当Si或Ti的质量分数超过10.0%时,团聚磨料试样中出现大量Si或者TiO2峰,其抗弯强度急剧下降;添加Si的团聚磨料试样与添加Ti的团聚磨料试样相比,其具有更大的粒度和更均匀的粒度分布,添加Si的铝硼硅黏结剂可将1~2 μm的磨料团聚为5~10 μm的磨料。Abstract: The diamond powder manufacturing industry at present grapples with a large backlog of fine-grained diamond powders. To enhance its applicability, agglomerated abrasive samples were manufactured with aluminum-borosilicate binder as the bonding agent, Si powder and Ti powder as additives. These agglomerated abrasive samples were then added into an aluminum-borosilicate binder to create ceramic bond samples. The bending strength, phase composition, and microscopic morphology of the samples were analyzed. The results show that the Al-B-Si binder, when combined with Si or Ti, can agglomerate diamond. When the mass fraction of Si or Ti in the agglomerated abrasives is 10.0%, the bending strength of the ceramic bond samples prepared is the largest. The bending strength of the agglomerated abrasive sample with Si added is 43.74 MPa. When the mass fraction of Si or Ti exceeds 10.0%, a large number of Si or TiO2 peaks appear in the agglomerated abrasive samples, and its bending strength decreases sharply. Compared with the agglomerated abrasive sample added with Ti, the agglomerated abrasive sample added with Si has a larger particle size and a more uniform particle size distribution. 1~2 μm abrasives can be aggregated into 5~10 μm abrasives with the addition of Al-B-Si binder with Si.
-
表 1 实验设备
Table 1. Experimental equipments
实验仪器及设备 型号 生产厂家 放电等离子烧结炉 SPS-40-10 上海皓越 马弗炉 SX 2-4-10 上海意丰 X射线衍射仪 UITIMA IV 日本理学Rigaku 扫描电子显微镜 Inspect S50 FEI 万能材料试验机 Ae-20I 日本岛津公司 行星式球磨机 XM-4×05 湘潭华丰仪器 表 2 团聚磨料试样配方
Table 2. Formula of agglomerated abrasive samples
试样编号 Al2O3
质量分数
ω1 / %SiO2
质量分数
ω2 / %B2O3
质量分数
ω3 / %无水Na2CO3
质量分数
ω4 / %无水K2CO3
质量分数
ω5 / %Si
质量分数
ω6 / %Ti
质量分数
ω7 / %金刚石
体积分数
φ1 / %1 17.4 26.1 43.5 4.0 4.0 5.0 60 2 16.4 24.6 41.0 4.0 4.0 10.0 60 3 15.4 23.1 38.5 4.0 4.0 15.0 60 4 14.4 21.6 36.0 4.0 4.0 20.0 60 5 17.4 26.1 43.5 4.0 4.0 5.0 60 6 16.4 24.6 41.0 4.0 4.0 10.0 60 7 15.4 23.1 38.5 4.0 4.0 15.0 60 8 14.4 21.6 36.0 4.0 4.0 20.0 60 表 3 陶瓷结合剂试样配方
Table 3. Ceramic bonder sample formula
组成 取值 Al2O3 ω1 / % 18.4 SiO2 ω2 / % 27.6 B2O3 ω3 / % 46.0 无水Na2CO3 ω4 / % 4.0 无水K2CO3 ω5 / % 4.0 团聚磨料体积分数 φ2 / % 40 -
[1] CHOUDHARY D, BELLARE J. Manufacture of gem quality diamonds: A review [J]. Ceramics International,2000,26(1):73-85. doi: 10.1016/S0272-8842(99)00022-X [2] ZHANG Y, RHEE K Y, HUI D, et al. A critical review of nanodiamond based nanocomposites: Synthesis, properties and applications [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2018,143:19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.01.028 [3] 张书达, 张文刚, 王松. 金刚石微粉和抛光液的制造工艺检测技术及应用(上) [J]. 超硬材料工程,2012,24(1):24-28.ZHANG Shuda, ZHANG Wengang, WANG Song. Manufacturing process and testing technology for diamond micron powder and diamond polishing suspension [J]. Superhard Material Engineering,2012,24(1):24-28. [4] 吴元康. 纳米晶多晶体金刚石超细微粉在表面技术中的应用 [J]. 表面技术,2007,36(6):64-65.WU Yuankang. Nano-polycrystal diamond superfine powders and its application in surface techniques [J]. Surface Technology,2007,36(6):64-65. [5] 王艳辉, 李晓虎, 常锐, 等. 金刚石微粉表面镀覆对线锯的关键作用分析 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2013(3):26-30.WANG Yanhui, LI Xiaohu, CHANG Rui, et al. Effect of coated diamond micro powder on diamond wire saw manufacturing technology [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2013(3):26-30. [6] SHAMES A I, MOGILYANSKY D, PANICH A M, et al. XRD, NMR, and EPR study of polycrystalline micro- and nano-diamonds prepared by a shock wave compression method [J]. Physica Status Solidi A,2015,212(11):2400-2409. doi: 10.1002/pssa.201532154 [7] SHIMAOKA T, KOIZUMI S, TANAKA M M. Diamond photovoltaic radiation sensor using pn junction [J]. Applied Physics Letters,2018,113(9):093504.1-093504.4. [8] YANG S, WAN X, WEI K, et al. A new sustainable concept for silicon recovery from diamond wire saw silicon powder waste: Source control and comprehensive conservation [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2022,358:131961.1-131961.13. [9] 周波, 毛剑波. 金刚石线锯质量检验 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2017,37(2):73-77.ZHOU Bo, MAO Jianbo. Quality inspection method for diamond wire saw [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2017,37(2):73-77. [10] WU X, TAN Y, WU H, et al. Structural modification of diamond-wire-cut multicrystalline Si by Cu-catalyzed chemical etching for surface structuring [J]. Thin Solid Films,2022,750:139199-139205. doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2022.139199 [11] PANIGRAHI N, CHAINI R, NAYAK A, et al. Impact of milling time and method on particle size and surface morphology during nano particle synthesis from α-Al2O3 [J]. 2018, 5(9): 20727-20735. [12] SHIN H, LEE S, JUNG H S, et al. Effect of ball size and powder loading on the milling efficiency of a laboratory-scale wet ball mill [J]. Ceramics International,2013,39(8):8963-8968. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.04.093 [13] NUNES D, LIVRAMENTO V, MARDOLCRA U V, et al. Tungsten nanodiamond composite powders produced by ball milling [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials,2012,426(1/2/3):115-119. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2012.03.028 [14] FADDA S, CINCOTTI A, CONCAS A, et al. Modelling breakage and reagglomeration during fine dry grinding in ball milling devices [J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions,2009,17:687-692. [15] CHEN J, SUN T, SU J, et al. A novel agglomerated diamond abrasive with excellent micro-cutting and self-sharpening capabilities in fixed abrasive lapping processes [J]. Wear,2021,464/465:203531-203539. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2020.203531 [16] WANG Z, NIU F, WANG Z, et al. Friction and wear characteristics of agglomerated diamond abrasives and lapping performance of fixed agglomerated diamond pads [J]. Wear,2021,470/471(1):203598-203611. [17] NIU F, WANG K, SUN T, et al. Lapping performance of mixed-size agglomerated diamond abrasives in fixed abrasives pads [J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2021,118:108499-108458. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2021.108499 [18] 朱永伟, 沈琦, 王子琨, 等. 多晶金刚石固结磨料研磨垫精研石英玻璃的性能探索 [J]. 红外与激光工程,2016,45(10):6-10.ZHU Yongwei, SHEN Qi, WANG Zikun, et al. Lapping performance on quartz glass of fixed abrasive pad embedded with multi-grain diamond grits [J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering,2016,45(10):6-10. [19] 陈春晖, 陈哲, 刘一波, 等. 类多晶(堆积)磨料的研究现状与应用 [J]. 超硬材料工程,2020,32(2):6-11.CHEN Chunhui, CHEN Zhe, LIU Yibo, et al. Research status and application of agglomerate abrasives [J]. Superhard Material Engineering,2020,32(2):6-11. [20] 栗正新, 王兆武. 堆积磨料的研究开发与应用 [J]. 中原工学院学报,2016,27(3):4-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6906.2016.03.012LI Zhengxin, WANG Zhaowu. Research and application of stacked abrasives [J]. Journal of Zhongyuan University of Technology,2016,27(3):4-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6906.2016.03.012 [21] SHAO W Z, IVANOV V V, ZHEN L, et al. A study on graphitization of diamond in copper–diamond composite materials [J]. Materials Letters,2004,58(1/2):146-149. [22] FEDOSEEV D V, VNUKOV S P, BUKHOVETS V L, et al. Surface graphitization of diamond at high temperatures [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology,1986,28(2):207-214. doi: 10.1016/0257-8972(86)90059-9 [23] CHENG X, WANG Y, LIANG Y, et al. Avoiding the oxidation of SiC in SiC-borosilicate glass composites by adding zinc [J]. Corrosion Science,2015,90:413-419. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2014.10.039 [24] ZHANG X, WANG Y, ZANG J, et al. Improvement of thermal stability of diamond by adding Ti powder during sintering of diamond/borosilicate glass composites [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society,2011,31(10):1897-1903. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2011.04.009 [25] 关振铎. 无机材料物理性能[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 1992.GUAN Zhenduo. Physical properties of inorganic materials [M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 1992. [26] 田英良, 孙诗兵. 新编玻璃工艺学 [M]. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 2009.TIAN Yingliang, SUN Shibing. New glass technology [M]. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2009. -




 下载:
下载:




 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
